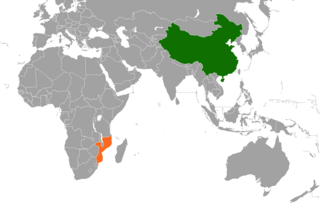
China–Mozambique relations date back to the 1960s, when China began to support the struggle of Mozambique's Marxist-oriented FRELIMO party against Portuguese colonialism. Diplomatic relations were formally established on 25 June 1975, soon after Mozambique gained independence from Portugal. In November 2006, Mozambique became the thirteenth African country to be added to China's official list of tourism destinations.
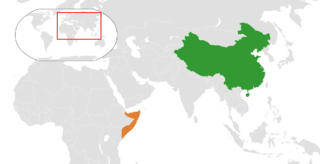
China–Somalia relations are the bilateral relations between China and Somalia. Somalia maintains an embassy in Beijing. China has an embassy in Mogadishu. It is led by Ambassador Wei Hongtian.
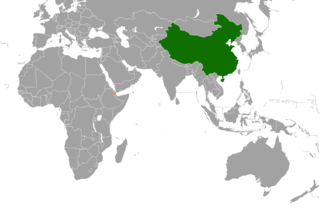
People's Republic of China–Djibouti relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China and Djibouti. China and Djibouti established relations on January 8, 1979. China has financed a number of public works projects in Djibouti, including a stadium, the offices of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the People's Palace. In September 2010, Type 920 Hospital Ship, also known as the "Peace Ark", visited Djibouti.

China–Denmark relations are foreign relations between China and Denmark. Denmark recognized the People's Republic of China on January 9, 1950, and the two countries established diplomatic relations on May 11, 1950. On February 15, 1956, the two countries upgraded diplomatic relations from ministerial to ambassadorial level and exchanged ambassadors. China has an embassy in Copenhagen. Denmark has an embassy in Beijing and 4 general consulates in Chongqing, Guangzhou, Hong Kong and Shanghai.

Central African Republic–People's Republic of China relations refer to the bilateral relations of the Central African Republic and the People's Republic of China. Diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the Central African Republic were established on September 29, 1964, when the CAR's government severed diplomatic relations with the Republic of China (Taiwan). China's ambassador to the Central African Republic is Ma Fulin as of 2017.

People's Republic of China–Liberia relations refer to the bilateral relations of the People's Republic of China and Liberia. Official relations began in 1977, but were broken on multiple occasions, only to be reformed later on. As of 2009, significant amounts of both investment and foreign aid came from China to Liberia.

Antigua and Barbuda–China relations refer to bilateral relations between China and Antigua and Barbuda. China has an embassy in St. John's. Diplomatic relations were established on January 1, 1983, less than two years after the Caribbean nation's independence, under Deng Xiaoping and Prime Minister Vere Bird, respectively. Diplomatic relations between the two countries have been smooth since then, as China supported Antigua and Barbuda's bid to join the United Nations.

Botswana - People's Republic of China relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the Botswana and the People's Republic of China. Relations were first established on 6 January 1975. In 2010, upon the 35th anniversary of relations being formalized, the relationship between the two states was considered "strong" and "rapidly growing" by then Chinese ambassador to Botswana, Liu Huanxing. Botswana follows the One China Policy which means Botswana does not have relations with the Republic of China (Taiwan). Following the 2008 Sichuan earthquake in China, the Botswana government donated one million pula.

Cape Verde–People's Republic of China relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China and Cape Verde. The two states established bilateral relations in April 1976, shortly after Cape Verde gained independence from the Portuguese Empire. Cape Verde is an adherent to PR China's One China Policy. China maintained relations with Cape Verde throughout from 1970s to mid-1990s mainly to prevent the Republic of China (Taiwan) from gaining Cape Verde's international recognition through checkbook diplomacy. However, in the mid-1990s, a number of Chinese capitalists began investing in the island nation and relations grew during the 2000s as a result.

People's Republic of China–Ethiopia relations were established in 1970. Ethiopia has an embassy in Beijing and the People's Republic of China has an embassy in Addis Ababa. Relations are longstanding, with Chinese direct investment (FDI) in Ethiopia reaching US$4 billion and bilateral trade growing to $5.4 billion by 2016-2018.
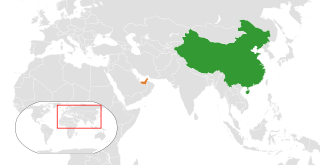
China – United Arab Emirates relations refer to the diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the United Arab Emirates. Diplomatic ties were first established in 1984. The UAE maintains an embassy in Beijing and a consulate-general in Hong Kong while China has an embassy in Abu Dhabi and consulate-general in Dubai. The UAE and China have been strong international allies, with significant cooperation across economic, political and cultural aspects.

China–Comoros relations refers to the current and historical relationship between China and the Comoros. China has an embassy in Moroni and the Comoros has an embassy in Beijing. Relations were established by Comorian President Ali Soilih on 13 November 1975 and have been described as "friendly and cooperative".

People's Republic of China – Guinea-Bissau relations refers to the current and historical relationship between the People's Republic of China and Guinea-Bissau. Relations were established in March 1974, several months before Guinea-Bissau's September 1974 independence. From 1990 to 1998, Guinea-Bissau maintained diplomatic relations with the Republic of China (Taiwan) rather than with the People's Republic. Relations were reestablished in 1998 and maintained since.

China-Ghanaian relations refer to the current and historical relationship between the Republic of Ghana and the People's Republic of China (PRC).

China–Togo relations refer to the foreign relations between the People's Republic of China and Togo. They established diplomatic relations on September 19, 1972.

China–South Sudan relations refers to the bilateral relations between the People's Republic of China and the Republic of South Sudan. China recognized South Sudan's independence on July 9, 2011.

China–Sierra Leone relations refer to the foreign relations between China and Sierra Leone. The People's Republic of China and the Republic of Sierra Leone established diplomatic relations on July 29, 1971. China has an embassy in Freetown, while Sierra Leone has an embassy in Beijing.

China–Niger relations refer to the foreign relations between China and Niger. China has an embassy in Niamey and Niger has an embassy in Beijing.

China–Mauritania relations refer to the bilateral relations between China and Mauritania. China and Mauritania established diplomatic relations on July 19, 1965. China has an embassy in Nouakchott. Mauritania has an embassy in Beijing.

China–Republic of the Congo relations refer to the bilateral relations between China and Republic of the Congo. On September 10, 1960, China established diplomatic relations with the Republic of the Congo and switch recognition to the People's Republic of China on February 22, 1964, as the sole legitimate government of China.






















