The Ebola River, also commonly known by its indigenous name Legbala, is the headstream of the Mongala River, a tributary of the Congo River, in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is roughly 250 kilometers (160 mi) in length.
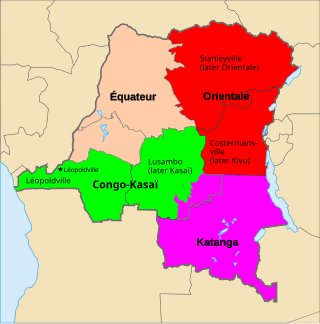
Équateur was a province in the northwest of the Belgian Congo and the successor Republic of the Congo, now known as Democratic Republic of the Congo. It had its origins in the Équateur District of the Congo Free State, the private property of King Leopold II of Belgium. It was upgraded to the status of a province in 1917. Between 1933 and 1947 it was named Coquilhatville. In 1962 it was divided into three smaller provinces, but there were recombined in 1966. Équateur was one of the eleven provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo until 2015, when it was split into the new, smaller Équateur province, as well as the Tshuapa, Mongala, Nord-Ubangi and Sud-Ubangi provinces.

Beni is a city in north eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, lying immediately west of the Virunga National Park and the Rwenzori Mountains, on the edge of the Ituri Forest.

Mbandaka is a city on the Congo River in the Democratic Republic of Congo located near the confluence of the Congo and Ruki rivers. It is the capital of Équateur Province.

Bumba is a town and river port in Mongala Province, in the northern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo, lying on the River Congo. As of 2009 it had an estimated population of 107,626. The town has neither electricity nor running water.

Yambuku is a small village in Mongala Province in northern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was the center of the first documented outbreak of Ebola virus disease, in 1976, with the World Health Organization identifying a man from Yambuku as the index case. It is 1,098 kilometres (682 mi) northeast of the capital city of Kinshasa.

Lisala is the capital of the Mongala Province in northwestern Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Bongandanga is a small town in Mongala Province in the northwestern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In 2009, it had an estimated population of 4625. It is the administrative center of the Bongandanga Territory.
Lisala Airport is an airport serving the Congo River city of Lisala, the capital of the Mongala District in the Mongala Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The runway is on the northwestern side of the city.

Bas-Uélé is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Bas-Uélé, Haut-Uélé, Ituri, and Tshopo provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Orientale Province. Bas-Uélé was formed from the Bas-Uele District whose town of Buta was elevated to capital city of the new province.
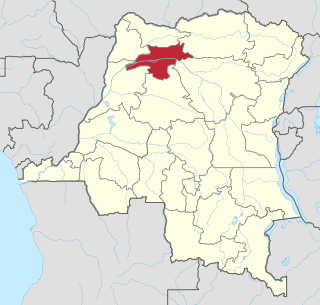
Mongala is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Mongala, Équateur, Nord-Ubangi, Sud-Ubangi, and Tshuapa provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Équateur province. Mongala was formed from the Mongala District whose town of Lisala was elevated to capital city of the new province.
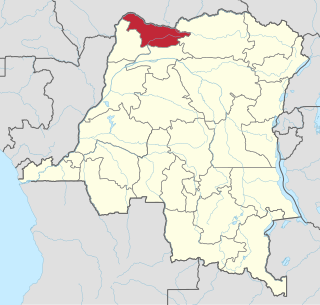
Nord-Ubangi is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Nord-Ubangi, Équateur, Mongala, Sud-Ubangi, and Tshuapa provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Équateur province.

The Mongala River in the northern Democratic Republic of the Congo is a right tributary of the Congo River.

In 2014, an outbreak of Ebola virus disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) occurred. Genome sequencing has shown that this outbreak was not related to the 2014–15 West Africa Ebola virus epidemic, but was of the same EBOV species. It began in August 2014 and was declared over in November of that year, after 42 days without any new cases. This is the 7th outbreak there, three of which occurred during the period of Zaire.

Tshuapa District, was a district of the Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in 1933 in the Coquilhatville Province. At its greatest extent it roughly corresponded to the present provinces of Équateur and Tshuapa.

The 2018 Équateur province Ebola outbreak occurred in the north-west of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) from May to July 2018. It was contained entirely within Équateur province, and was the first time that vaccination with the rVSV-ZEBOV Ebola vaccine had been attempted in the early stages of an Ebola outbreak, with a total of 3,481 people vaccinated. It was the ninth recorded Ebola outbreak in the DRC.

In August–November 1976, an outbreak of Ebola virus disease occurred in Zaire. The first recorded case was from Yambuku, a small village in Mongala District, 1,098 kilometres (682 mi) northeast of the capital city of Kinshasa.
Congo-Ubangi District, was a district of the Belgian Congo created in 1933 in the Coquilhatville Province. It had been dissolved by 1954.

Ernest Baert was a Belgian soldier, explorer and colonial administrator who was active in the Congo Free State.