Lesotho is a mountainous, landlocked country located in Southern Africa. It is an enclave, surrounded by South Africa. The total length of the country's borders is 909 kilometres (565 mi). Lesotho covers an area of around 30,355 square kilometres (11,720 sq mi), of which a negligible percentage is covered with water.

Politics of Lesotho takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic constitutional monarchy, whereby the Prime Minister of Lesotho is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the two chambers of Parliament, the Senate and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature.

The Free State, formerly known as the Orange Free State, is a province of South Africa. Its capital is Bloemfontein, which is also South Africa's judicial capital. Its historical origins lie in the Boer republic called the Orange Free State and later the Orange Free State Province.

Berea is a district of Lesotho. In the west, Berea borders on the Free State Province of South Africa. Domestically, it borders on the following districts: Leribe District in the north, Thaba-Tseka District in southeast and Maseru District in the south. Teyateyaneng is the capital of the district. It is also home to the Kome Cave Dwellings. It is also the only district in Lesotho which is not named after its capital.

Thaba-Tseka is a district of Lesotho. Thaba-Tseka is also the name of the district's capital or camptown, which is the only town in the district. In the east, Thaba-Tseka borders on the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Domestically, it borders on Mokhotlong District in northeast, Leribe District in north, Berea District in northwest, Maseru District in west, Mohale's Hoek District in southwest and Qacha's Nek District in the southern direction. The district is one of the major tourist attractions in Lesotho because of the second largest arch dam in Africa Katse Dam.

Mokhotlong district is a district of Lesotho. It includes the highest terrain in the Maloti Mountains and the source of the Senqu River, Lesotho's primary watershed. Mokhotlong is the capital or camptown, and only town in the district. Mokhotlong borders on the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa, with its north point bordering the Free State Province. Domestically, it borders on Butha-Buthe District in northwest, Leribe District in west, and Thaba-Tseka District in the south.

Leribè is a district of Lesotho. It has an area of 2,828 km2 and a population in 2016 of approximately 337,500. Hlotse is the capital or camptown of the district. The district has one additional town, namely Maputsoe. In the west, Leribe borders on the Free State Province of South Africa. Domestically, it borders Butha-Buthe District in the north, Mokhotlong District in the east, Thaba-Tseka District in southeast and Berea District in southwest.

Mafeteng is a district of Lesotho. It has an area of 2,119 km2 and a population in 2016 of 178,222. Mafeteng is the capital or camptown, and only town in the district. In the west, Mafeteng borders on the Free State Province of South Africa. Domestically, it borders on the following districts Maseru District in the northeast and Mohale's Hoek District in the southeast.

Maseru is a district of Lesotho. Maseru is also the name of the district's capital, and is the only city in the district and also the capital of the country. It is the largest urban area in the country, and therefore the only city. The city of Maseru is located on Lesotho's western border with the Free State Province of South Africa, the frontier being the Caledon River. Maseru borders on Berea District in north, Thaba-Tseka District in the east, Mohale's Hoek District in south, and Mafeteng District in southwest.

Mohale's Hoek is a district of Lesotho. Mohale's Hoek is the capital city or camptown, and only town in the district. In the southwest, Mohale's Hoek borders on South Africa, while domestically, it borders on Mafeteng District in northwest, Maseru District in north, Thaba-Tseka District in northeast, Qacha's Nek District in east, and Quthing District in southeast.

Mokhotlong is a constituency, city and seat of Mokhotlong District in the mountainous northeastern part of Lesotho. It is the first major city with an airport along the road from South Africa across the Sani Pass, near the Maloti Mountains. The name of the city is named in Sesotho, the language of the people of Lesotho, meaning "Place of the Bald Ibis." Thabana Ntlenyana, the highest point in southern Africa, is found in Mokhotlong.

Qacha's Nek is a district of Lesotho. Qacha's Nek is the capital or camptown, and only town in the district. In the south, Qacha's Nek borders on the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa, and it has a short border with KwaZulu-Natal Province in the far east. Domestically, it borders on Quthing District in southwest, Mohale's Hoek District in west and Thaba-Tseka District in the northern direction.

Quthing is a district of Lesotho. Moyeni, is the camp town or capital of the district. There are two of the most important sets of dinosaur footprints in the region. There is a large panel of Bushman paintings at Qomoqomong. Quthing district is home to the Masitise Cave House, a satellite location of the Morija Museum & Archives. In the southwest, south and east, Quthing borders on the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Domestically, it borders Mohale's Hoek District in the north and Qacha's Nek District in the northeast.

The Lesotho Premier League, also known as Vodacom Premier League for sponsorship reasons, is the top football division in Lesotho and was created in 1970. Econet Telecom Lesotho was the league sponsor, from 2017/2018 to 2019/2020 season. Vodacom Lesotho are again the current league sponsor and were also the sponsor of the now cancelled Vodacom Soccer Spectacular knockout competition, which was the Lesotho's annual national cup tournament.

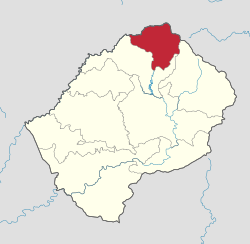
Administratively, Lesotho is divided into ten districts, each headed by a district administrator. Each district has a capital known as a camptown.
Kao, Lesotho is a community council located in the Butha-Buthe District of Lesotho. Its population in 2006 was 5,304.
Likila is a community council located in the Butha-Buthe District of Lesotho. Its population in 2006 was 19,340.
Lipelaneng is a community council located in the Butha-Buthe and Leribe Districts of Lesotho. Its population in 2006 was 30,320.
Liqhobong is a community council located in the Butha-Buthe District of Lesotho. Its population in 2006 was 5,524.
Sekhobe is a community council located in the Butha-Buthe District of Lesotho. Its population in 2006 was 3,874.