
A rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) is a shoulder-fired rocket weapon that launches rockets equipped with an explosive warhead. Most RPGs can be carried by an individual soldier, and are frequently used as anti-tank weapons. These warheads are affixed to a rocket motor which propels the RPG towards the target and they are stabilized in flight with fins. Some types of RPG are reloadable with new rocket-propelled grenades, while others are single-use. RPGs are generally loaded from the front.

The Saudi Arabian Armed Forces (SAAF), also known as the Royal Saudi Armed Forces, is part of the military forces of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. It consists of the Royal Saudi Army, the Royal Saudi Navy, the Royal Saudi Air Force, the Royal Saudi Air Defense, and the Royal Saudi Strategic Missile Force. The King of Saudi Arabia is the commander-in-chief of all the military forces and forms military policy with the Ministry of Defense and the Ministry of Interior. The five Armed Forces are among eight military forces of Saudi Arabia, with the others including the Royal Saudi National Guard, the Royal Saudi Guard Regiment and the Royal Saudi Border Guards.

The Bazooka is a man-portable recoilless anti-tank rocket launcher weapon, widely deployed by the United States Army, especially during World War II. Also referred to as the "stovepipe", the innovative Bazooka was among the first generation of rocket-propelled anti-tank weapons used in infantry combat. Featuring a solid-propellant rocket for propulsion, it allowed for high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) shaped charge warheads to be delivered against armored vehicles, machine gun nests, and fortified bunkers at ranges beyond that of a standard thrown grenade or mine. The universally applied nickname arose from the weapon's M1 variant's vague resemblance to the musical instrument called a bazooka invented and popularized by 1930s American comedian Bob Burns.

High-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) is the effect of a shaped charge explosive that uses the Munroe effect to penetrate heavy armor. The warhead functions by having an explosive charge collapse a metal liner inside the warhead into a high-velocity shaped charge jet; this is capable of penetrating armor steel to a depth of seven or more times the diameter of the charge. The shaped charge jet armor penetration effect is purely kinetic in nature; the round has no explosive or incendiary effect on the armor.

Missile d'Infanterie Léger Antichar or MILAN is a Franco-West German anti-tank guided missile system. Design of the MILAN began in 1962; it was ready for trials in 1971, and accepted for service in 1972. It is a wire-guided semi-automatic command to line of sight (SACLOS) missile, which means the sight of the launch unit must be aimed at a target to guide the missile. The MILAN can be equipped with a MIRA or MILIS thermal sight to give it night-firing ability.

The Carl Gustaf 8.4 cm recoilless rifle is a Swedish-developed 84 mm (3.3 in) caliber shoulder-fired recoilless rifle, initially developed by the Royal Swedish Army Materiel Administration during the second half of the 1940s as a crew-served man-portable infantry support gun for close-range multi-role anti-armour, anti-personnel, battlefield illumination, smoke screening and marking fire, which has seen great export success around the globe and continues to be a popular multi-purpose support weapon in use by many nations. The Carl Gustaf 84 mm recoilless rifle is a lightweight, low-cost weapon that uses a wide range of ammunition, which makes it extremely flexible and suitable for a wide variety of roles.

The M79 Osa is a Yugoslav-made portable 90 mm anti-tank weapon made of fibre-reinforced plastics. It resembles the French portable anti-tank launcher 89 mm LRAC F1. It consists of the launcher, a CN-6 sighting piece, rocket and carrying case for the rocket. The M79 shoots unguided projectiles in direct sight and is effective against armoured fighting vehicles and fortifications.

The RPG-7 is a portable, reusable, unguided, shoulder-launched, anti-tank, rocket launcher. The RPG-7 and its predecessor, the RPG-2, were designed by the Soviet Union, and are now manufactured by the Russian company Bazalt. The weapon has the GRAU index 6G3.

The M72 LAW is a portable one-shot 66 mm (2.6 in) unguided anti-tank weapon.

The MATADOR is a 90-millimetre (3.5 in) man-portable, disposable anti-armour and anti-brickwall weapon system developed by Germany, Israel and Singapore. It is an updated version of the German Armbrust design, and operates on the same principles. The development of this weapon began in 2000 and the MATADOR will eventually replace the German Armbrust Light Anti-tank Weapon, which has been in service since the 1980s.

The RPG-26 Aglen is a disposable anti-tank rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) launcher developed by the Soviet Union. It fires a one-stage rocket with jack-knife fins, which unfold after launch. The rocket carries a 72.5-millimetre (2.85 in) diameter high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) single shaped charge warhead able to penetrate 440 millimetres (17 in) of armour, 1 metre of reinforced concrete or 1.5 metres of brickwork. It has a maximum effective range of around 250 metres (820 ft). The similar sized rocket features a slightly heavier and more powerful HEAT warhead and more powerful rocket engine. The limited extension of the RPG-22 launch tube was found of little use. Thus, the RPG-26 has a rigid non-telescoping launch tube.
The RPG-27 is a Soviet single shot disposable rocket-propelled grenade (RPG) shoulder-fired missile and rocket launcher. It entered service with the Soviet Army in 1989.

The Spanish Army is the terrestrial army of the Spanish Armed Forces responsible for land-based military operations. It is one of the oldest active armies – dating back to the late 15th century.

OTR-21 Tochka is a Soviet tactical ballistic missile. Its GRAU designation is 9K79. Its NATO reporting name is the SS-21 Scarab. One missile is transported per 9P129 vehicle and raised prior to launch. It uses an inertial guidance system.

Alcotán-100 is a recoilless, one-man portable, single-use anti-tank rocket launcher system used by infantry, manufactured by Instalaza. The firing control unit predicts the future aiming point based on calculation before the rocket fire. It is being used as an infantry-type weapon and fireable from confined spaces. Instalaza claiming it to be, "the highest performance in unguided shoulder launched systems". It is in service with the Spanish Armed Forces and exported to other countries.

The RPG-32 Barkas is a reusable Russian shoulder-launched, unguided anti-tank rocket system. It was designed and developed by state-owned Unitary enterprise (FGUP) "Bazalt" weapon manufacturing company. It is also assembled in Jordan from Russian-made kits from Bazalt under the name "RPG Nashab".
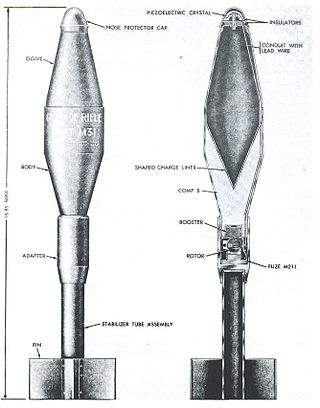
The M31 HEAT is a fin-stabilized anti-tank rifle grenade designed in the late 1950s to replace the Belgian ENERGA rifle grenade which was adopted by the US Army and US Marines as an emergency stop-gap measure during the Korean War. Like the ENERGA, it has a nose-initiated, based-detonated HEAT warhead, but unlike the ENERGA, the mechanical impact fuse system is replaced with a less complex and more reliable piezo-electric fuse system which also allows higher angles of impact, up to 65 degrees.

Instalaza SA is a Spanish firm that designs, develops and manufactures equipment and other military material for infantry. The company, founded in 1943, is headquartered in Zaragoza, Aragon, where its production plant is also located.

The AT4 is a Swedish 84 mm (3.31 in) unguided, man-portable, disposable, shoulder-fired recoilless anti-tank weapon manufactured by Saab Bofors Dynamics. The AT4 is not a rocket launcher strictly speaking, because the explosive warhead is not propelled by a rocket motor. Rather, it is a smooth-bore recoilless gun. Saab has had considerable sales success with the AT4, making it one of the most common light anti-tank weapons in the world. The M136 AT4 is a variant used by the United States Army.



















