| CACUL1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CACUL1 , C10orf46, CAC1, CDK2 associated cullin domain 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1926082 HomoloGene: 17821 GeneCards: CACUL1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CDK2 associated cullin domain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACUL1 gene. [5]
| CACUL1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | CACUL1 , C10orf46, CAC1, CDK2 associated cullin domain 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 1926082 HomoloGene: 17821 GeneCards: CACUL1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CDK2 associated cullin domain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACUL1 gene. [5]

p21Cip1, also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 or CDK-interacting protein 1, is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) that is capable of inhibiting all cyclin/CDK complexes, though is primarily associated with inhibition of CDK2. p21 represents a major target of p53 activity and thus is associated with linking DNA damage to cell cycle arrest. This protein is encoded by the CDKN1A gene located on chromosome 6 (6p21.2) in humans.
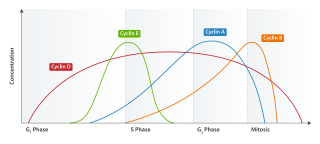
Cyclin E is a member of the cyclin family.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, also known as cell division protein kinase 2, or Cdk2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK2 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family of Ser/Thr protein kinases. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2, also known as Cdk1 in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle, where cells make proteins necessary for mitosis and replicate their DNA. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E or A. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase. Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation. Multiple alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initiation sites of this gene have been reported. The role of this protein in G1-S transition has been recently questioned as cells lacking Cdk2 are reported to have no problem during this transition.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 also known as cell division protein kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK4 gene. CDK4 is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase family.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 9 or CDK9 is a cyclin-dependent kinase associated with P-TEFb.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 also known as CDK1 or cell division cycle protein 2 homolog is a highly conserved protein that functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase, and is a key player in cell cycle regulation. It has been highly studied in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae, and the fission yeast S. pombe, where it is encoded by genes cdc28 and cdc2, respectively. With its cyclin partners, Cdk1 forms complexes that phosphorylate a variety of target substrates ; phosphorylation of these proteins leads to cell cycle progression.
Transcription factor E2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the E2F1 gene.

M-phase inducer phosphatase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDC25B gene.

G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNE1 gene.

Cyclin-A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNA2 gene. It is one of the two types of cyclin A: cyclin A1 is expressed during meiosis and embryogenesis while cyclin A2 is expressed in the mitotic division of somatic cells.

Cell division cycle 7-related protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDC7 gene. The Cdc7 kinase is involved in regulation of the cell cycle at the point of chromosomal DNA replication. The gene CDC7 appears to be conserved throughout eukaryotic evolution; this means that most eukaryotic cells have the Cdc7 kinase protein.

Cyclin-dependent kinases regulatory subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CKS1B gene.

Cullin-4B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CUL4B gene which is located on the X chromosome. CUL4B has high sequence similarity with CUL4A, with which it shares certain E3 ubiquitin ligase functions. CUL4B is largely expressed in the nucleus and regulates several key functions including: cell cycle progression, chromatin remodeling and neurological and placental development in mice. In humans, CUL4B has been implicated in X-linked intellectual disability and is frequently mutated in pancreatic adenocarcinomas and a small percentage of various lung cancers. Viruses such as HIV can also co-opt CUL4B-based complexes to promote viral pathogenesis. CUL4B complexes containing Cereblon are also targeted by the teratogenic drug thalidomide.

RING-box protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNF7 gene.

Cell division protein kinase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK3 gene.

Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDKN3 gene.

CDK5 and ABL1 enzyme substrate 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CABLES1 gene.

WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 3 is a matricellular protein that in humans is encoded by the WISP3 gene.

Cyclin-dependent kinase 2-associated protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK2AP1 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 23, also known as low molecular mass dual specificity phosphatase 3 (LDP-3), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP23 gene.