
Actin, cytoplasmic 2, or gamma-actin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTG1 gene. Gamma-actin is widely expressed in cellular cytoskeletons of many tissues; in adult striated muscle cells, gamma-actin is localized to Z-discs and costamere structures, which are responsible for force transduction and transmission in muscle cells. Mutations in ACTG1 have been associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss and Baraitser-Winter syndrome, as well as susceptibility of adolescent patients to vincristine toxicity.

Adenylyl cyclase type 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY6 gene.

Drebrin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DBN1 gene.

Visinin-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VSNL1 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY5 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY1 gene.

Dynamin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dynamin family which possess mechanochemical properties involved in actin-membrane processes, predominantly in membrane budding. DNM3 is upregulated in Sézary's syndrome.

Protein SEC13 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEC13 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 2 is an enzyme typically expressed in the brain of humans, that is encoded by the ADCY2 gene. It belongs to the adenylyl cyclase class-3 or guanylyl cyclase family because it contains two guanylate cyclase domains. ADCY2 is one of ten different mammalian isoforms of adenylyl cyclases. ADCY2 can be found on chromosome 5 and the "MIR2113-POU3F2" region of chromosome 6, with a length of 1091 amino-acids. An essential cofactor for ADCY2 is magnesium; two ions bind per subunit.

Adenylyl cyclase type 7 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY7 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY9 gene.

Resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase-8A (Ric-8A), also known as Synembryn-A, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RIC8A gene.

RNA 3'-terminal phosphate cyclase-like protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RCL1 gene.

Coronin-1C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CORO1C gene.

Actin-related protein 2/3 complex subunit 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARPC1A gene.

Adenylyl cyclase type 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADCY4 gene.

Serpin B8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SERPINB8 gene.

Adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAP2 gene.
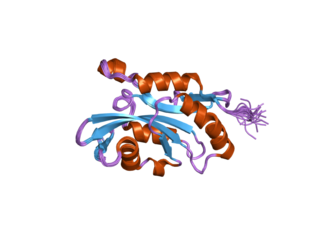
Cofilin 2 (muscle) also known as CFL2 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CFL2 gene.

In molecular biology, the cyclase-associated protein family (CAP) is a family of highly conserved actin-binding proteins present in a wide range of organisms including yeast, flies, plants, and mammals. CAPs are multifunctional proteins that contain several structural domains. CAP is involved in species-specific signalling pathways. In Drosophila, CAP functions in Hedgehog-mediated eye development and in establishing oocyte polarity. In Dictyostelium discoideum, CAP is involved in microfilament reorganisation near the plasma membrane in a PIP2-regulated manner and is required to perpetuate the cAMP relay signal to organise fruitbody formation. In plants, CAP is involved in plant signalling pathways required for co-ordinated organ expansion. In yeast, CAP is involved in adenylate cyclase activation, as well as in vesicle trafficking and endocytosis. In both yeast and mammals, CAPs appear to be involved in recycling G-actin monomers from ADF/cofilins for subsequent rounds of filament assembly. In mammals, there are two different CAPs that share 64% amino acid identity.
























