
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells.

Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and secondary spermatocytes. Primary and secondary spermatocytes are formed through the process of spermatocytogenesis.

Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the RHOA gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is primarily associated with cytoskeleton regulation, mostly actin stress fibers formation and actomyosin contractility. It acts upon several effectors. Among them, ROCK1 and DIAPH1 are the best described. RhoA, and the other Rho GTPases, are part of a larger family of related proteins known as the Ras superfamily, a family of proteins involved in the regulation and timing of cell division. RhoA is one of the oldest Rho GTPases, with homologues present in the genomes since 1.5 billion years. As a consequence, RhoA is somehow involved in many cellular processes which emerged throughout evolution. RhoA specifically is regarded as a prominent regulatory factor in other functions such as the regulation of cytoskeletal dynamics, transcription, cell cycle progression and cell transformation.
Tektins are cytoskeletal proteins found in cilia and flagella as structural components of outer doublet microtubules. They are also present in centrioles and basal bodies. They are polymeric in nature, and form filaments.

Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGDIB gene. Aliases of this gene include RhoGDI2, GDID4, Rho GDI 2, and others.

Rab GDP dissociation inhibitor beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDI2 gene.

Citron Rho-interacting kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CIT gene.

Sperm-associated antigen 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPAG1 gene.

Sperm-associated antigen 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPAG8 gene.

Sperm flagellar protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPEF2 gene.

Intraflagellar transport protein 20 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFT20 gene. The gene is composed of 6 exons and is located on human chromosome 17p11.1. This gene is expressed in human brain, lung, kidney and pancreas, and lower expression were also detected in human placenta, liver, thymus, prostate and testis.
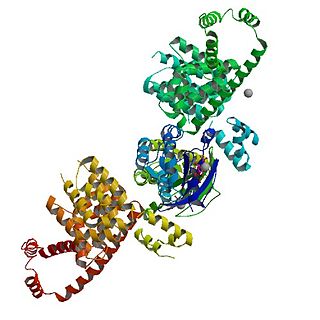
mDia1 is a member of the protein family called the formins and is a Rho effector. It is the mouse version of the diaphanous homolog 1 of Drosophila. mDia1 localizes to cells' mitotic spindle and midbody, plays a role in stress fiber and filopodia formation, phagocytosis, activation of serum response factor, formation of adherens junctions, and it can act as a transcription factor. mDia1 accelerates actin nucleation and elongation by interacting with barbed ends of actin filaments. The gene encoding mDia1 is located on Chromosome 18 of Mus musculus and named Diap1.

Coiled-coil domain containing 109B (CCDC109B) is a potential calcium uniporter protein found in the membrane of human cells and is encoded by the CCDC109B gene. While CCDC109B is a transmembrane protein it is unclear if it is located within the cell membrane or mitochondrial membrane.

TATA-box binding protein associated factor 7-like also known as CT40 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAF7l gene. It is a close homologue to the TAF7 gene, although its function may be different. Currently, little is known about this gene. It was originally demonstrated to be a testis-specific gene based on RT-PCR experiments on tissue extracts, however, it has now been found in white and brown adipose tissue, as well as in certain types of cancer.

Cilia- and flagella-associated protein 299 (CFAP299), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFAP299 gene. CFAP299 is predicted to play a role in spermatogenesis and cell apoptosis.

Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 198 (CCDC198) is a gene that encodes for a protein of the same name.
Spermatogenesis-associated protein 16 is a mammalian protein encoded by the SPATA16 gene. SPATA16, also known as NYD-SP12, is a developmental protein that aids in differentiation of germ cells for spermatogenesis and participates in acrosome formation for appropriate sperm-egg fusion. SPATA16 is located on chromosome 3 at position 26.31 and is a member of the tetratricopeptide repeat-like superfamily, which facilitate interactions and assemblies between proteins and protein complexes.

Coiled-coil domain containing 121 (CCDC121) is a protein encoded by the CCDC121 gene in humans. CCDC121 is located on the minus strand of chromosome 2 and encodes three protein isoforms. All isoforms of CCDC121 contain a domain of unknown function referred to as DUF4515 or pfam14988.

Coiled-Coil Domain Containing 190, also known as C1orf110, the Chromosome 1 Open Reading Frame 110, MGC48998 and CCDC190, is found to be a protein coding gene widely expressed in vertebrates. RNA-seq gene expression profile shows that this gene selectively expressed in different organs of human body like lung brain and heart. The expression product of c1orf110 is often called Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 190 with a size of 302 aa. It may get the name because a coiled-coil domain is found from position 14 to 72. At least 6 spliced variants of its mRNA and 3 isoforms of this protein can be identified, which is caused by alternative splicing in human.

CCDC188 or coiled-coil domain containing protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC188 gene.





















