Beta Sextantis, Latinized from β Sextantis, is a variable star in the equatorial constellation of Sextans. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.07, it is faintly visible to the naked eye on a dark night. According to the Bortle scale, it can be viewed from brighter lit suburban skies. The distance to this star, based upon an annual parallax shift of 8.96 mas, is around 364 light years.

Iota Arae, Latinized from ι Arae, is the Bayer designation for a star in the southern constellation of Ara. It is 920 light-years from Earth, give or take a 20 light-year margin of error, and has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.2. Based upon the Bortle Dark-Sky Scale, this means the star is visible to the naked eye from suburban skies.

21 Aquilae is a solitary variable star in the equatorial constellation of Aquila. It has the variable star designation V1288 Aql; 21 Aquilae is its Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of about 5.1. The star is located at a distance of around 680 light-years from Earth, give or take a 20 light-year margin of error. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of –5 km/s.

10 Canis Majoris is a single variable star in the southern constellation of Canis Major, located roughly 1,980 light years away from the Sun. It has the variable star designation FT Canis Majoris; 10 Canis Majoris is the Flamsteed designation. This body is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 5.23. It is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +34 km/s.
Mu Crucis, Latinized from μ Crucis, is the seventh-brightest star in the constellation Crux commonly known as the Southern Cross. μ Crucis is a wide double star of spectral class B stars, magnitude 4.0 and 5.2 respectively. They lie about 370 light-years away, and both stars are likely physically attached. The brighter component is known as μ1 Crucis or μ Crucis A, while the fainter is μ2 Crucis or μ Crucis B.
HD 102776, also known by its Bayer designation j Centauri, is a suspected astrometric binary star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It has a blue-white hue and is faintly visible to the naked eye with a typical apparent visual magnitude of 4.30. The distance to this star is approximately 600 light years based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of ~29 km/s. It is a member of the Lower Centaurus Crux subgroup of the Sco OB2 association. HD 102776 has a relatively large peculiar velocity of 31.1 km/s and is a candidate runaway star that was ejected from its association, most likely by a supernova explosion.
3 Centauri is a triple star system in the southern constellation of Centaurus, located approximately 300 light years from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.32. As of 2017, the two visible components had an angular separation of 7.851″ along a position angle of 106°. The system has the Bayer designation k Centauri; 3 Centauri is the Flamsteed designation. It is a suspected eclipsing binary with a variable star designation V983 Centauri.
VZ Arietis is single, white-hued star in the northern zodiac constellation of Aries. Varying between magnitudes 5.82 and 5.89, the star can be seen with the naked eye in dark, unpolluted areas. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.8 mas, it is located 560 light years from the Sun. It is moving further away with a heliocentric radial velocity of +14 km/s. The star was formerly known as 16 Trianguli, but as the star is no longer in the constellation Triangulum, this designation has fallen out of use.
HD 102350 is a single star in the constellation Centaurus. It has a yellow hue and is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.11. The distance to this star is approximately 390 light years based on parallax, but it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −3 km/s. It has an absolute magnitude of −1.51.

64 Eridani is a single, yellow-white hued star in the constellation Eridanus having variable star designation S Eridani. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.77. The annual parallax shift is measured at 12.01 mas, which equates to a distance of about 272 light years. In addition to its proper motion, it is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of around −9 km/s.

KT Lupi is a visual binary star system in the constellation Lupus. It is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.55. As of 1983, the pair had an angular separation of 2.19″±0.03″. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 7.6 mas as seen from Earth's orbit, it is located 430 light-years from the Sun. The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +6.5 km/s. It is a member of the Lower Centaurus–Crux sub-group of the Scorpius–Centaurus association.

31 Orionis is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Orion, located near the bright star Mintaka. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.71. The distance to this system is approximately 490 light years away based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a mean radial velocity of +6 km/s.

ET Virginis is a single, red-hued star in the equatorial constellation of Virgo. It can be viewed with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.91. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.9 mas, it is located 560 light years away. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +18.6 km/s, having come within 177 ly of the Sun around 6.3 million years ago.
7 Cephei is a single star located approximately 820 light years away, in the northern circumpolar constellation of Cepheus. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.42.

Upsilon Coronae Borealis, Latinized from υ Coronae Borealis, is a solitary star in the northern constellation of Corona Borealis. It is a white-hued star that is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.78. The distance to this object is approximately 630 light-years based on parallax.
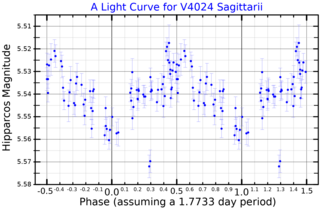
V4024 Sagittarii is a single variable star in the southern constellation of Sagittarius. It has a blue-white hue and is dimly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates from about 5.3 to 5.6. The star is located at a distance of approximately 1,700 light years based on stellar parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −20 km/s. The position of this star near the ecliptic means it is subject to lunar occultations.
HR 4729 is a multiple star system located about 95 parsecs (310 ly) from the Sun in the constellation of Crux and part of the asterism known as the Southern Cross. It is a close companion of α Crucis and sometimes called α Crucis C.

HD 111395 is a single, variable star in the northern constellation of Coma Berenices. It has the variable star designation LW Com, short for LW Comae Berenices; HD 111395 is the Henry Draper Catalogue designation. The star has a yellow hue and is just bright enough to be barely visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 6.29. Based upon parallax measurements, it is located at a distance of 55.8 light years from the Sun. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −8.9 km/s. It is a member of the Eta Chamaeleontis stellar kinematic group.

Xi Octantis, Latinized from ξ Octantis, is a solitary variable star in the southern circumpolar constellation Octans. It has an apparent magnitude of about 5.3, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye; however, this varies slightly. Located 514 light years away, the object is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 22 km/s.

HD 174387 is a solitary star in the southern constellation Telescopium. With an apparent magnitude of 5.49, it is faintly visible to the naked eye if viewed under dark skies. Parallax measurements put the object at a distance of 810 light years and it is currently approaching the Solar System with a heliocentric radial velocity of −28.1 km/s.












