Related Research Articles

A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the simulation represents the evolution of the model over time. Often, computers are used to execute the simulation.

In chemical engineering and related fields, a unit operation is a basic step in a process. Unit operations involve a physical change or chemical transformation such as separation, crystallization, evaporation, filtration, polymerization, isomerization, and other reactions. For example, in milk processing, the following unit operations are involved: homogenization, pasteurization, and packaging. These unit operations are connected to create the overall process. A process may require many unit operations to obtain the desired product from the starting materials, or feedstocks.

The Common Image Generator Interface (CIGI), is an on-the-wire data protocol that allows communication between an Image Generator and its host simulation. The interface is designed to promote a standard way for a host device to communicate with an image generator (IG) within the industry.
In chemical engineering, process design is the choice and sequencing of units for desired physical and/or chemical transformation of materials. Process design is central to chemical engineering, and it can be considered to be the summit of that field, bringing together all of the field's components.
ProMax is a chemical process simulator for process troubleshooting and design, developed and sold by Bryan Research and Engineering, Inc. Initially released in late 2005, ProMax is a continuance of two previous process simulators, PROSIM and TSWEET. ProMax is considered the industry standard for designing amine gas treating and glycol dehydration units.
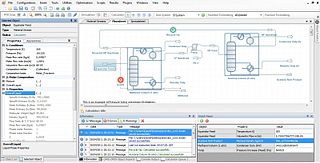
Process simulation is used for the design, development, analysis, and optimization of technical processes such as: chemical plants, chemical processes, environmental systems, power stations, complex manufacturing operations, biological processes, and similar technical functions.
Live, Virtual, & Constructive (LVC) Simulation is a broadly used taxonomy for classifying Models and Simulation (M&S). However, categorizing a simulation as a live, virtual, or constructive environment is problematic since there is no clear division between these categories. The degree of human participation in a simulation is infinitely variable, as is the degree of equipment realism. The categorization of simulations also lacks a category for simulated people working real equipment.
Chemical WorkBench is a proprietary simulation software tool aimed at the reactor scale kinetic modeling of homogeneous gas-phase and heterogeneous processes and kinetic mechanism development. It can be effectively used for the modeling, optimization, and design of a wide range of industrially and environmentally important chemistry-loaded processes. Chemical WorkBench is a modeling environment based on advanced scientific approaches, complementary databases, and accurate solution methods. Chemical WorkBench is developed and distributed by Kintech Lab.
EMSO simulator is an equation-oriented process simulator with a graphical interface for modeling complex dynamic or steady-state processes. It is CAPE-OPEN compliant. EMSO stands for Environment for Modeling, Simulation, and Optimization. The ALSOC Project - a Portuguese acronym for Free Environment for Simulation, Optimization and Control of Processes -, which is based at the UFRGS, develops, maintains and distributes this object-oriented software. Pre-built models are available in the EMSO Modeling Library (EML). New models can be written in the EMSO modeling language or a user can embed models coded in C, C++ or Fortran into the simulation environment.

DWSIM is an open-source CAPE-OPEN compliant chemical process simulator for Windows, Linux and macOS. DWSIM is built on top of the Microsoft .NET and Mono Platforms and features a Graphical User Interface (GUI), advanced thermodynamics calculations, reactions support and petroleum characterization / hypothetical component generation tools.
JModelica.org is a commercial software platform based on the Modelica modeling language for modeling, simulating, optimizing and analyzing complex dynamic systems. The platform is maintained and developed by Modelon AB in collaboration with academic and industrial institutions, notably Lund University and the Lund Center for Control of Complex Systems (LCCC). The platform has been used in industrial projects with applications in robotics, vehicle systems, energy systems, CO2 separation and polyethylene production.
MAK Technologies, formerly doing business as VT MAK, Inc. is a software company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts that provides commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) modeling and simulation software. The company develops and sells software for distributed simulations that system integrators, governments, and research institutions use to build and populate 3D simulated environments. Users include medical, aerospace, defense, and transportation industries. In addition to offering COTS software, MAK provides the following services: simulation content creation, software customization, interoperability, research and development, and training.
Aspen Plus, Aspen HYSYS, ChemCad and MATLAB, PRO are the commonly used process simulators for modeling, simulation and optimization of a distillation process in the chemical industries. Distillation is the technique of preferential separation of the more volatile components from the less volatile ones in a feed followed by condensation. The vapor produced is richer in the more volatile components. The distribution of the component in the two phase is governed by the vapour-liquid equilibrium relationship. In practice, distillation may be carried out by either two principal methods. The first method is based on the production of vapor boiling the liquid mixture to be separated and condensing the vapors without allowing any liquid to return to the still. There is no reflux. The second method is based on the return of part of the condensate to still under such conditions that this returning liquid is brought into intimate contact with the vapors on their way to condenser.
The CAPE-OPEN Interface Standard consists of a series of specifications to expand the range of application of process simulation technologies. The CAPE-OPEN specifications define a set of software interfaces that allow plug and play inter-operability between a given Process Modelling Environment and a third-party Process Modelling Component.
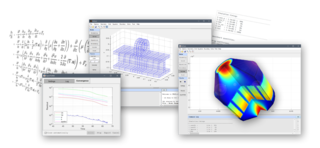
FEATool Multiphysics is a physics, finite element analysis (FEA), and PDE simulation toolbox. FEATool Multiphysics features the ability to model fully coupled heat transfer, fluid dynamics, chemical engineering, structural mechanics, fluid-structure interaction (FSI), electromagnetics, as well as user-defined and custom PDE problems in 1D, 2D (axisymmetry), or 3D, all within a graphical user interface (GUI) or optionally as script files. FEATool has been employed and used in academic research, teaching, and industrial engineering simulation contexts.
References
- ↑ W.D. Seider; J.D. Seader; D.R. Lewin (1999). Process Design Principles. Wiley. ISBN 0-471-24312-4.
- ↑ J.M. Douglas (1988). Conceptual Design of Chemical Processes. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-017762-7.
- ↑ W.L. McCabe; J.C. Smith; P. Harriot (1993). Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering (5th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-044844-2.
- ↑ Perry, Robert H.; Green, Don W. (1997). Perry's Chemical Engineers' Handbook (7th ed.). McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-049841-5. p. 13-53