
Synaptosomal-Associated Protein, 25kDa (SNAP-25) is a Target Soluble NSF (N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor) Attachment Protein Receptor (t-SNARE) protein encoded by the SNAP25 gene found on chromosome 20p12.2 in humans. SNAP-25 is a component of the trans-SNARE complex, which accounts for membrane fusion specificity and directly executes fusion by forming a tight complex that brings the synaptic vesicle and plasma membranes together.

Complexin (also known as synaphin) refers to a one of a small set of eukaryotic cytoplasmic neuronal proteins which binds to the SNARE protein complex (SNAREpin) with a high affinity. These are called synaphin 1 and 2. In the presence of Ca2+, the transport vesicle protein synaptotagmin displaces complexin, allowing the SNARE protein complex to bind the transport vesicle to the presynaptic membrane.

Syntaxin-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STX1A gene.
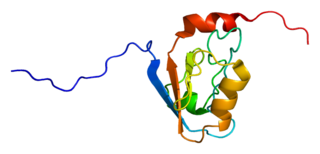
Disks large homolog 3 (DLG3) also known as neuroendocrine-DLG or synapse-associated protein 102 (SAP-102) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLG3 gene. DLG3 is a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) superfamily of proteins.

Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 (VAMP2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAMP2 gene.

Glutamate receptor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIA1 gene.
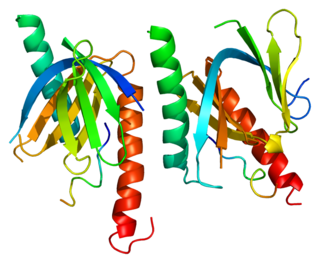
Amyloid beta A4 precursor protein-binding family A member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APBA1 gene.

N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor Attachment Protein Alpha, also known as SNAP-α, is a SNAP protein that is involved in the intra-cellular trafficking and fusing of vesicles to target membranes in cells.

Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RIMS1 gene.

Vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VAMP8 gene.

Rabphilin-3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPH3A gene. It contains two C2 domains and binds calcium ions at low micromolar concentration. Rabphilin was shown to regulate neurotransmitter release in hippocampal neurons after neurons had an increased synaptic activity and their release rate was depressed.

Syntaxin-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STXBP2 gene.

Neurabin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPP1R9B gene.

Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RIMS2 gene.

Complexin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CPLX1 gene.

Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNQ5 gene.

Glutamate receptor, ionotropic kainate 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRIK5 gene.

Syntaxin-binding protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STXBP5 gene. It is also known as tomosyn, after 友, "friend" in Japanese, for its role as a binding protein.

Ryanodine receptor 3 is one of a class of ryanodine receptors and a protein that in humans is encoded by the RYR3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is both a calcium channel and a receptor for the plant alkaloid ryanodine. RYR3 and RYR1 control the resting calcium ion concentration in skeletal muscle.

Syntaxin 3, also known as STX3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the STX3 gene.





















