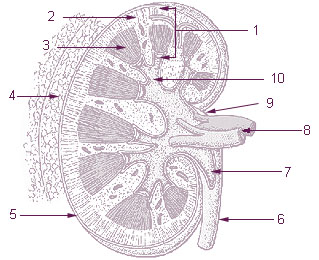
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the Loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter.

Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 is a deubiquitinating enzyme.

Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a membrane protein and anion channel in vertebrates that is encoded by the CFTR gene.

EGR-1 also known as ZNF268 or NGFI-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EGR1 gene.

Bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP-15) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMP15 gene. It is involved in folliculogenesis, the process in which primordial follicles develop into pre-ovulatory follicles.

Paired-like homeobox 2b (PHOX2B), also known as neuroblastoma Phox (NBPhox), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHOX2B gene located on chromosome 4.

Growth Associated Protein 43 (GAP43) is a protein encoded by the GAP43 gene in humans.

CTGF, also known as CCN2 or connective tissue growth factor, is a matricellular protein of the CCN family of extracellular matrix-associated heparin-binding proteins. CTGF has important roles in many biological processes, including cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, angiogenesis, skeletal development, and tissue wound repair, and is critically involved in fibrotic disease and several forms of cancers.

CLOCK is a gene encoding a basic helix-loop-helix-PAS transcription factor that is known to affect both the persistence and period of circadian rhythms.

Cathepsin B belongs to a family of lysosomal cysteine proteases known as the cysteine cathepsins and plays an important role in intracellular proteolysis. In humans, cathepsin B is encoded by the CTSB gene. Cathepsin B is upregulated in certain cancers, in pre-malignant lesions, and in various other pathological conditions.

Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] also known as superoxide dismutase 1 or hSod1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOD1 gene, located on chromosome 21. SOD1 is one of three human superoxide dismutases. It is implicated in apoptosis, familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson's disease.

CD163 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD163 gene. CD163 is the high affinity scavenger receptor for the hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex and in the absence of haptoglobin - with lower affinity - for hemoglobin alone. It also is a marker of cells from the monocyte/macrophage lineage. CD163 functions as innate immune sensor for gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The receptor was discovered in 1987.

Excitatory amino acid transporter 3 (EAAT3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC1A1 gene.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 5, also known as cysteine string protein or CSP is a protein, that in humans encoded by the DNAJC5 gene. It was first described in 1990.

Slit homolog 3 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLIT3 gene.

Anoctamin-1 (ANO1) also known as Transmembrane member 16A (TMEM16A) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ANO1 gene. Anoctamin-1 is a voltage-gated calcium-activated anion channel, which acts as a chloride channel and a bicarbonate channel. additionally Anoctamin-1 is apical iodide channel. It is expressed in smooth muscle, epithelial cells, vomeronasal neurons, olfactory sustentacular cells, and is highly expressed in interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) throughout the gastrointestinal tract.

T-box, brain, 1 is a transcription factor protein important in vertebrate embryo development. It is encoded by the TBR1 gene. This gene is also known by several other names: T-Brain 1, TBR-1, TES-56, and MGC141978. TBR1 is a member of the TBR1 subfamily of T-box family transcription factors, which share a common DNA-binding domain. Other members of the TBR1 subfamily include EOMES and TBX21. TBR1 is involved in the differentiation and migration of neurons and is required for normal brain development. TBR1 interacts with various genes and proteins in order to regulate cortical development, specifically within layer VI of the developing six-layered human cortex. Studies show that TBR1 may play a role in major neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD).

Gap junction delta-2 protein (GJD2) also known as connexin-36 (Cx36) or gap junction alpha-9 protein (GJA9) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJD2 gene.

Polyphosphoinositide phosphatase also known as phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase or SAC domain-containing protein 3 (Sac3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FIG4 gene. Fig4 is an abbreviation for Factor-Induced Gene.

ATP/GTP binding protein 1 is gene that encodes the protein known as cytosolic carboxypeptidase 1 (CCP1), originally named NNA1. Mice with a naturally occurring mutation of the Agtpbp1 gene are known as pcd mice.























