
The CSS Colonel Lamb was a twin Confederate blockade runner of the CSS Hope who participated in the American Civil War.

The CSS Colonel Lamb was a twin Confederate blockade runner of the CSS Hope who participated in the American Civil War.
The CSS Colonel Lamb had a length of 281, a beam of 36, and a draft of 10, and was one of the most famous and successful blockade runners in the Confederate States Navy. She was built in 1864 by Jones, Quiggin & Company, a sister ship to the CSS Hope (which preceded it that year) but with a much longer house and without the usual turtle foredeck that the Hope had. She is identified with the handsome Captain Tom Lockwood and was christened by his wife. Shipbuilder Wiliiam Quiggin registered CSS Colonel Lamb in her name and then quietly transferred her to Confederate agent J. B. Lafitte, CSN in Nassau, where she was outfitted. She survived the war intact and was sold through Fraser, Trenholm & Co. to the Brazilian government; After loading a shipment of explosives for Brazil into Liverpool, she exploded at anchor in the river Mersey the night before setting sail. [1]

USS Housatonic was a screw sloop-of-war of the United States Navy, taking its name from the Housatonic River of New England.

CSS Alabama was a screw sloop-of-war built in 1862 for the Confederate States Navy. The vessel was built in Birkenhead on the River Mersey opposite Liverpool, England, by John Laird Sons and Company. Launched as Enrica, she was fitted out as a cruiser and commissioned as CSS Alabama on August 24, 1862. Under Captain Raphael Semmes, Alabama served as a successful commerce raider, attacking, capturing, and burning Union merchant and naval ships in the North Atlantic, as well as intercepting American grain ships bound for Europe. The Alabama continued through the West Indies and further into the East Indies, destroying over seven ships before returning to Europe. On June 11, 1864, the Alabama arrived at Cherbourg, France, where she was overhauled. Shortly after, a Union sloop-of-war, USS Kearsarge, arrived; and on June 19, the Battle of Cherbourg commenced outside the port of Cherbourg, France, whereby the Kearsarge sank the Alabama in approximately one hour after the Alabama's opening shot.

CSS Florida was a sloop-of-war in the service of the Confederate States Navy. She served as a commerce raider during the American Civil War before being sunk in 1864.
CSS Raleigh was a steam-powered Civil War casemate ironclad. She was fitted with a spar torpedo instead of an iron ram and was built in 1863–1864 by the Confederate States Navy at Wilmington, North Carolina. While she was being built her commander was Lieutenant John Wilkinson (CSN). She was put into commission on April 30, 1864 under the command of Lieutenant J. Pembroke Jones, CSN.

CSS Robert E. Lee was a fast paddle-steamer, originally built as a Glasgow-Belfast packet boat named Giraffe, which was bought as a blockade runner for the Confederate States during the American Civil War, then subsequently served in the United States Navy as USS Fort Donelson and in the Chilean Navy as Concepción.
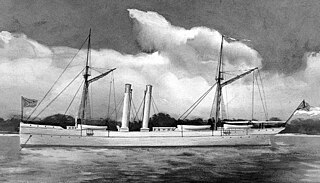
CSS Chickamauga, originally the blockade runner Edith, was purchased by the Confederate States Navy at Wilmington, North Carolina, in September 1864. In September, when she was nearly ready for sea, the Confederate Army sought unsuccessfully to retain her at that place for use as a troop and supply transport. On October 28, 1864, she put to sea under Lieutenant John Wilkinson (CSN) for a cruise north to the entrance of Long Island Sound, thence to St. George, Bermuda, for repairs and coal. She took several prizes before returning to Wilmington on November 19.

The third USS Water Witch was a wooden-hulled, sidewheel gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She is best known as the ship fired on by Paraguay in 1855. In 1864 she was captured by the Confederate States Navy, and subsequently was taken into that Navy as CSS Water Witch.
The first USS Mohican was a steam sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for the Mohican tribe and was the first ship of her class.

CSS Sumter, converted from the 1859-built merchant steamer Habana, was the first steam cruiser of the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. She operated as a commerce raider in the Caribbean and in the Atlantic Ocean against Union merchant shipping between July and December 1861, taking eighteen prizes, but was trapped in Gibraltar by Union Navy warships. Decommissioned, she was sold in 1862 to the British office of a Confederate merchant and renamed Gibraltar, successfully running the Union blockade in 1863 and surviving the war.

The first USS Seminole was a steam sloop-of-war in the United States Navy during the American Civil War.
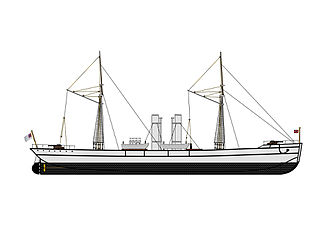
The CSS Tallahassee was a twin-screw steamer and cruiser in the Confederate States Navy, purchased in 1864, and used for commerce raiding off the Atlantic coast. She later operated under the names CSS Olustee and CSS Chameleon.

CSS Rob Roy was a Confederate blockade runner commanded by Captain William Watson, that ran to and from Bermuda, the Bahamas and Cuba from 1862 to 1864, during the American Civil War.

The USS Iosco was a 1173-ton Sassacus class "double-ender" steam gunboat built at Bath, Maine. The ship fought during the Civil War, and was an important combatant during the battles at Fort Fisher. The ship was named Iosco after a Native American word meaning "water of light", the namesake for Iosco County, Michigan.

USS Vanderbilt was a heavy (3,360-ton) passenger steamship obtained by the Union Navy during the second year of the American Civil War and utilized as a cruiser.

USS Howquah was a screw steamer purchased by the Union Navy in Boston from G. W. Upton on 17 June 1863, for action against Confederate commerce raider CSS Tacony which was then preying upon Northern merchantmen during what Professor Richard S. West has called "the most brilliant daredevil cruise of the war."

USS Calhoun was a captured Confederate steamer and blockade runner acquired by the Union Navy from the prize court during the American Civil War.
USS Tristram Shandy was a 444-ton steamer and blockade runner captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS Mobile was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as part of blockade forces to prevent Confederate forces from trading with other countries.

During the American Civil War, blockade runners were used to get supplies through the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America that extended some 3,500 miles (5,600 km) along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coastlines and the lower Mississippi River. The Confederacy had little industrial capability and could not produce the quantity of arms and other supplies needed to fight against the Union. To meet this need, British investors financed numerous blockade runners that were constructed in the British Isles and were used to import the guns, ordnance and other supplies, in exchange for cotton that the British textile industry needed greatly. To penetrate the blockade, these relatively lightweight shallow draft ships, mostly built in British shipyards and specially designed for speed, but not suited for transporting large quantities of cotton, had to cruise undetected, usually at night, through the Union blockade. The typical blockade runners were privately owned vessels often operating with a letter of marque issued by the Confederate government. If spotted, the blockade runners would attempt to outmaneuver or simply outrun any Union Navy warships on blockade patrol, often successfully.
![]() This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships .The entry can be found here.
This article incorporates text from the public domain Dictionary of American Naval Fighting Ships .The entry can be found here.