
USS Housatonic was a screw sloop-of-war of the United States Navy, gaining its namesake from the Housatonic River of New England.

H. L. Hunley, often referred to as Hunley, CSS H. L. Hunley, or as CSS Hunley, was a submarine of the Confederate States of America that played a small part in the American Civil War. Hunley demonstrated the advantages and the dangers of undersea warfare. She was the first combat submarine to sink a warship (USS Housatonic), although Hunley was not completely submerged and, following her successful attack, was lost along with her crew before she could return to base. The Confederacy lost 21 crewmen in three sinkings of Hunley during her short career. She was named for her inventor, Horace Lawson Hunley, shortly after she was taken into government service under the control of the Confederate States Army at Charleston, South Carolina.

The Confederate States Navy (CSN) was the naval branch of the Confederate States Armed Forces, established by an act of the Confederate States Congress on February 21, 1861. It was responsible for Confederate naval operations during the American Civil War against the United States's Union Navy.

CSS Manassas, formerly the steam icebreaker Enoch Train, was built in 1855 by James O. Curtis as a twin-screw towboat at Medford, Massachusetts. A New Orleans commission merchant, Captain John A. Stevenson, acquired her for use as a privateer after she was captured by another privateer CSS Ivy. Her fitting out as Manassas was completed at Algiers, Louisiana; her conversion to a ram of a radically modern design made her the first ironclad ship built for the Confederacy.
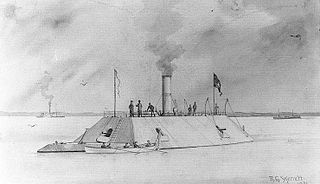
CSS Palmetto State was an ironclad ram built in January 1862 by Cameron and Co., Charleston, South Carolina, under the supervision of Flag Officer D. N. Ingraham, CSN. She was readied for service in the American Civil War by September 1862 when Lieutenant Commander John Rutledge, CSN, was placed in command. Her casemate armor was 4 inches (102 mm) thick, backed by 22 inches (559 mm) of wood, while 2 inches (51 mm) of iron armor was used everywhere else. Her pilothouse was not placed forward but was positioned abaft of the smokestack.

CSS Chicora was a Confederate ironclad ram that fought in the American Civil War. It was built under contract at Charleston, South Carolina in 1862. James M. Eason built it to John L. Porter's plans, using up most of a $300,000 State appropriation for construction of marine batteries; Eason received a bonus for "skill and promptitude." Its iron shield was 4 inches (102 mm) thick, backed by 22 inches (559 mm) of oak and pine, with 2-inch (51 mm) armor at its ends. Keeled in March, it was commissioned in November, Commander John Randolph Tucker, CSN assuming command.

USS New Ironsides was a wooden-hulled broadside ironclad built for the United States Navy during the American Civil War. The ship spent most of her career blockading the Confederate ports of Charleston, South Carolina, and Wilmington, North Carolina, in 1863–65. New Ironsides bombarded the fortifications defending Charleston in 1863 during the First and Second Battles of Charleston Harbor. At the end of 1864 and the beginning of 1865 she bombarded the defenses of Wilmington in the First and Second Battles of Fort Fisher.
CSS Raleigh was a steam-powered Civil War casemate ironclad. She was fitted with a spar torpedo instead of an iron ram and was built in 1863–1864 by the Confederate States Navy at Wilmington, North Carolina. While she was being built her commander was Lieutenant John Wilkinson (CSN). She was put into commission on April 30, 1864 under the command of Lieutenant J. Pembroke Jones, CSN.

The second USS Memphis was a 7-gun screw steamer, built by William Denny and Brothers, Dumbarton, Scotland in 1861, which briefly served as a Confederate blockade runner before being captured and taken into the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was destroyed by fire in 1883.

William Thornton Glassell was an officer in the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War. He laid out the city of Orange, California.

The First Battle of Charleston Harbor was an engagement near Charleston, South Carolina that took place April 7, 1863, during the American Civil War. The striking force was a fleet of nine ironclad warships of the Union Navy, including seven monitors that were improved versions of the original USS Monitor. A Union Army contingent associated with the attack took no active part in the battle. The ships, under command of Rear Admiral Samuel Francis Du Pont, attacked the Confederate defenses near the entrance to Charleston Harbor. Navy Department officials in Washington hoped for a stunning success that would validate a new form of warfare, with armored warships mounting heavy guns reducing traditional forts.

USS Winona was a Unadilla-class gunboat built for service with the Union Navy during the American Civil War. Winona was heavily armed, with large guns for duels at sea, and 24-pounder howitzers for shore bombardment. Winona saw significant action in the Gulf of Mexico and in the waterways of the Mississippi River and was fortunate to return home safely after the war for decommissioning.

USS General Putnam (1857) – also known as the USS William G. Putnam – was acquired by the Union Navy during the first year of the American Civil War and outfitted as a gunboat and assigned to the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America. She also served as a tugboat and as a ship's tender when so required.
USS Britannia (1862) was a steamer captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat and patrol vessel in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways.

USS Kinsman, sometimes called USS Colonel Kinsman, was a sidewheel steamer captured by the Union Army during the American Civil War. She was used by the Army and then by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. On 23 February 1863, she hit a snag and sank.
USS Alpha (1864) was a side wheel paddle steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War.
USS T. A. Ward (1861) was a 284-ton schooner was purchased by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War.

The Sinking of USS Housatonic on 17 February 1864 during the American Civil War was an important turning point in naval warfare. The Confederate States Navy submarine, H.L. Hunley made her first and only attack on a Union Navy warship when she staged a clandestine night attack on USS Housatonic in Charleston harbor. H.L. Hunley approached just under the surface, avoiding detection until the last moments, then embedded and remotely detonated a spar torpedo that rapidly sank the 1,240 long tons (1,260 t) sloop-of-war with the loss of five Union sailors. H.L. Hunley became renowned as the first submarine to successfully sink an enemy vessel in combat, and was the direct progenitor of what would eventually become international submarine warfare, although the victory was Pyrrhic and short-lived, since the submarine did not survive the attack and was lost with all eight Confederate crewmen.

The attack on USS New Ironsides in October 1863 was one of the first successful torpedo boat engagements in history. Confederate forces in Charleston, South Carolina deployed the newly built semi-submersible CSS David to attach a spar torpedo to the hull of USS New Ironsides. Though the attack is regarded as a rebel victory, the Union ship was saved from serious damage.

The Squib class consisted of four completed torpedo boats built for the Confederate States Navy. Four vessels of the class – CSS Hornet, CSS Wasp, CSS Squib, and CSS Scorpion – were constructed in Richmond, Virginia, in 1864. All were armed with a single spar torpedo and were powered by steam engines. Squib damaged the gunboat USS Minnesota in an attack on April 9, 1864, and was later sent to Wilmington, North Carolina, where she was scuttled in February 1865. The other three vessels of the class were all part of the James River Squadron and participated in the Battle of Trent's Reach. Scorpion ran aground during the battle, and was forced downriver and out of control after the tender CSS Drewry exploded on January 24, 1865. She was later captured by Union forces and may have been burned. Hornet was sunk in a collision with another vessel on January 27, and Wasp was scuttled on the night of April 2/3, as the Confederates were abandoning Richmond.




















