The gens Tullia was a family at ancient Rome, with both patrician and plebeian branches. The first of this gens to obtain the consulship was Manius Tullius Longus in 500 BC, but the most illustrious of the family was Marcus Tullius Cicero, the statesman, orator, and scholar of the first century BC. The earliest of the Tullii who appear in history were patrician, but all of the Tullii mentioned in later times were plebeian, and some of them were descended from freedmen. The English form Tully, often found in older works, especially in reference to Cicero, is now considered antiquated.

The gens Furia, originally written Fusia, and sometimes found as Fouria on coins, was one of the most ancient and noble patrician houses at Rome. Its members held the highest offices of the state throughout the period of the Roman Republic. The first of the Furii to attain the consulship was Sextus Furius in 488 BC.
The gens Baebia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Gnaeus Baebius Tamphilus, in 182 BC. During the later Republic, the Baebii were frequently connected with the patrician family of the Aemilii.

The gens Licinia was a celebrated plebeian family at ancient Rome, which appears from the earliest days of the Republic until imperial times, and which eventually obtained the imperial dignity. The first of the gens to obtain the consulship was Gaius Licinius Calvus Stolo, who, as tribune of the plebs from 376 to 367 BC, prevented the election of any of the annual magistrates, until the patricians acquiesced to the passage of the lex Licinia Sextia, or Licinian Rogations. This law, named for Licinius and his colleague, Lucius Sextius, opened the consulship for the first time to the plebeians. Licinius himself was subsequently elected consul in 364 and 361 BC, and from this time, the Licinii became one of the most illustrious gentes in the Republic.

The gens Junia was one of the most celebrated families of ancient Rome. The gens may originally have been patrician, and was already prominent in the last days of the Roman monarchy. Lucius Junius Brutus was the nephew of Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, the seventh and last King of Rome, and on the expulsion of Tarquin in 509 BC, he became one of the first consuls of the Roman Republic.

The gens Minucia was an ancient Roman family, which flourished from the earliest days of the Republic until imperial times. The gens was apparently of patrician origin, but was better known by its plebeian branches. The first of the Minucii to hold the consulship was Marcus Minucius Augurinus, elected consul in 497 BC.
The gens Pinaria was one of the most ancient patrician families at Rome. According to tradition, the gens originated long before the founding of the city. The Pinarii are mentioned under the kings, and members of this gens attained the highest offices of the Roman state soon after the establishment of the Republic, beginning with Publius Pinarius Mamercinus Rufus, consul in 489 BC.
The gens Decia was a plebeian family of high antiquity, which became illustrious in Roman history by the example of its members sacrificing themselves for the preservation of their country. The first of the family known to history was Marcus Decius, chosen as a representative of the plebeians during the secession of 495 BC.

The gens Postumia was a noble patrician family at ancient Rome. Throughout the history of the Republic, the Postumii frequently occupied the chief magistracies of the Roman state, beginning with Publius Postumius Tubertus, consul in 505 BC, the fifth year of the Republic. Although like much of the old Roman aristocracy, the Postumii faded for a time into obscurity under the Empire, individuals bearing the name of Postumius again filled a number of important offices from the second century AD to the end of the Western Empire.
The gens Carvilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome, which first distinguished itself during the Samnite Wars. The first member of this gens to achieve the consulship was Spurius Carvilius Maximus, in 293 BC.

The gens Antistia, sometimes written Antestia on coins, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. The first of the gens to achieve prominence was Sextus Antistius, tribune of the plebs in 422 BC.
The gens Servilia was a patrician family at ancient Rome. The gens was celebrated during the early ages of the Republic, and the names of few gentes appear more frequently at this period in the consular Fasti. It continued to produce men of influence in the state down to the latest times of the Republic, and even in the imperial period. The first member of the gens who obtained the consulship was Publius Servilius Priscus Structus in 495 BC, and the last of the name who appears in the consular Fasti is Quintus Servilius Silanus, in AD 189, thus occupying a prominent position in the Roman state for nearly seven hundred years.

The gens Pomponia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Its members appear throughout the history of the Roman Republic, and into imperial times. The first of the gens to achieve prominence was Marcus Pomponius, tribune of the plebs in 449 BC; the first who obtained the consulship was Manius Pomponius Matho in 233 BC.
The gens Verginia or Virginia was a prominent family at ancient Rome, which from an early period was divided into patrician and plebeian branches. The gens was of great antiquity. It frequently filled the highest honors of the state during the early years of the Republic. The first of the family who obtained the consulship was Opiter Verginius Tricostus in 502 BC, the seventh year of the Republic. The plebeian members of the family were also numbered amongst the early tribunes of the people.
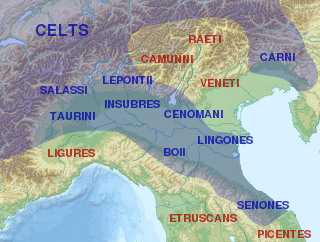
Over the course of nearly four centuries, the Roman Republic fought a series of wars against various Celtic tribes, whom they collectively described as Galli, or Gauls. Among the principal Gallic peoples described as antagonists by Greek and Roman writers were the Senones, Insubres, Boii, and Gaesatae.
The gens Rutilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens appear in history beginning in the second century BC. The first to obtain the consulship was Publius Rutilius Rufus in 105 BC.
The gens Genucia was a prominent family of the Roman Republic. It was probably of patrician origin, but most of the Genucii appearing in history were plebeian. The first of the Genucii to hold the consulship was Titus Genucius Augurinus in 451 BC.
The gens Maenia, occasionally written Mainia, was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned soon after the establishment of the Republic, and occur in history down to the second century BC. Several of them held the position of tribune of the plebs, from which they strenuously advocated on behalf of their order. The most illustrious of the family was Gaius Maenius, consul in 338 BC, and dictator in both 320 and 314. In some manuscripts, the nomen Maenius appears to have been erroneously substituted for Menenius or Manlius; there are also instances of confusion with Manilius, Maelius, and Maevius.
The gens Oppia was an ancient Roman family, known from the first century of the Republic down to imperial times. The gens may originally have been patrician, as they supplied priestesses to the College of Vestals at a very early date, but all of the Oppii known to history were plebeians. None of them obtained the consulship until imperial times.
Quintus Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus was a consular tribune of the Roman Republic in 402 and 398 BC.








