
The Yass River, a perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Southern Tablelands and South Western Slopes districts of New South Wales, Australia.

Goodradigbee River, a perennial stream that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Snowy Mountains district of New South Wales, Australia.

Darbalara is a rural community on the east bank of the junction of the Murrumbidgee River and Tumut River in the Riverina. It is situated by road, about 25 kilometres north east of Gundagai and 25 kilometres south of Coolac.

Beresford County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains Cooma and Bredbo. Part of the Murrumbidgee River forms the boundary in the north-west, and a separate part of the river forms part of the western boundary.
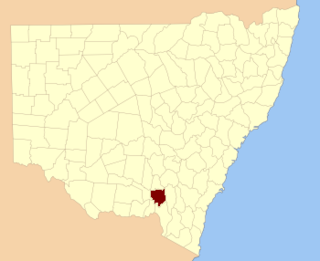
Wynyard County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the city of Wagga Wagga. The Murrumbidgee River lies on the northern edge of the county, and the Tumut River on the eastern edge.

Buccleuch County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the locality of Adjungbilly. The Murrumbidgee River is at the northern boundary, with the Goodradigbee River on the eastern boundary, and the Tumut River on the western boundary. It includes the northern part of the Kosciuszko National Park.
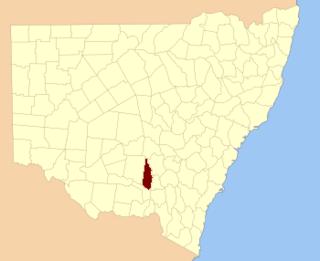
Bourke County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the town of Ardlethan. The Murrumbidgee River is the southern boundary.
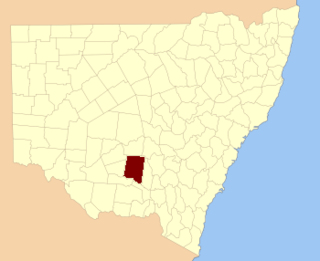
Cooper County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the town of Barellan. The Murrumbidgee River is the southern boundary.

Clarendon County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the towns of Gundagai, Junee and Bethungra. The Murrumbidgee River is the boundary to the south.
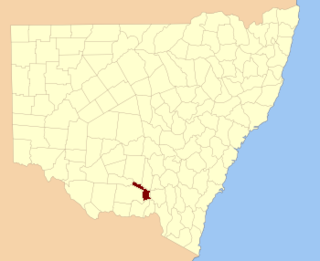
Mitchell County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the town of Collingullie. The Murrumbidgee River is the northern boundary.

Waradgery County is one of the 141 Cadastral divisions of New South Wales. It contains the town of Hay. It includes the area between the Lachlan River and the Murrumbidgee River where they meet. The Lachlan River is the northern boundary of the county, and the Murrumbidgee for a small section is the southern boundary, but the county also includes some of the land to the south of the Murrumbidgee near Hay.
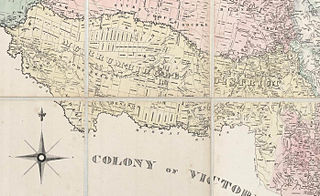
The Murrumbidgee District was a district used in New South Wales in the nineteenth century to refer to the land between the Murrumbidgee River and Murray River, that is now mostly known as the Riverina region. Some maps show the district included the parts of what is now the Australian Capital Territory that was to the west of the Murrumbidgee River. The district was originally one of the districts used to refer to the area outside the limits of location, but later continued to be used as the name after counties were proclaimed within this area. It went out of use after 1884, when new districts were proclaimed.
Bredbo River, a perennial stream that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Monaro region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Adelong Creek, a perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the South West Slopes, and Riverina regions of New South Wales, Australia.

The Jugiong Creek, a mostly–perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the South West Slopes region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Burkes Creek, a mostly–perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Riverina region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Burra Creek, a mostly–perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the South West Slopes region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Cooma Creek, a mostly–perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Monaro region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Cooma Back Creek, a mostly–perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Monaro region of New South Wales, Australia.

The Happy Jacks Creek, a perennial river that is part of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Snowy Mountains region of New South Wales, Australia.

















