
The River Wharfe is a river in Yorkshire, England originating within the Yorkshire Dales National Park. For much of its middle course it is the county boundary between West Yorkshire and North Yorkshire. Its valley is known as Wharfedale.

Ermine Street is a major Roman road in England that ran from London (Londinium) to Lincoln and York (Eboracum). The Old English name was Earninga Strǣt (1012), named after a tribe called the Earningas, who inhabited a district later known as Armingford Hundred, around Arrington, Cambridgeshire, and Royston, Hertfordshire. "Armingford", and "Arrington" share the same Old English origin. The original Celtic and Roman names for the route remain unknown. It is also known as the Old North Road from London to where it joins the A1 Great North Road near Godmanchester.

Selby District was a local government district of North Yorkshire, England, from 1974 to 2023. Its council was based in the town of Selby. The district had a population of 83,449 at the 2011 Census. The southernmost district of North Yorkshire, it bordered the City of York unitary authority, the Borough of Harrogate in North Yorkshire, the City of Leeds and City of Wakefield districts in West Yorkshire, the City of Doncaster in South Yorkshire, and the ceremonial county of the East Riding of Yorkshire.

Tadcaster is a market town and civil parish in North Yorkshire, England, 12 miles (19 km) north-east of Leeds and 10 miles (16 km) south-west of York. Its historical importance from Roman times onward was largely as the lowest road crossing-point on the River Wharfe until the construction of the A64 Tadcaster by-pass some 660 yards (600 m) to the south, in 1978. There are two rail crossings downstream of the town before the Wharfe joins the River Ouse near Cawood.

The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geographer Ptolemy named the Brigantes as a people in Ireland also, where they could be found around what is now Wexford, Kilkenny and Waterford, while another people named Brigantii is mentioned by Strabo as a sub-tribe of the Vindelici in the region of the Alps.
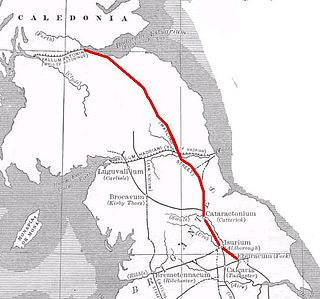
Dere Street or Deere Street is a modern designation of a Roman road which ran north from Eboracum (York), crossing the Stanegate at Corbridge and continuing beyond into what is now Scotland, later at least as far as the Antonine Wall. Portions of its route are still followed by modern roads, including the A1(M), the B6275 road through Piercebridge, where Dere Street crosses the River Tees, and the A68 north of Corbridge in Northumberland.

The Antonine Itinerary is an itinerarium, a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly from a survey carried out under Augustus, it describes the roads of the Roman Empire. Owing to the scarcity of other extant records of this type, it is a valuable historical record.

Durobrivae was a Roman fortified garrison town located at Water Newton in the English county of Cambridgeshire, where Ermine Street crossed the River Nene. More generally, it was in the territory of the Corieltauvi in a region of villas and commercial potteries. The name is a Latinisation of Celtic *Durobrīwās, meaning essentially "fort bridges".

Tadcaster Grammar School founded in 1557, is a coeducational secondary school and sixth form located near Tadcaster, North Yorkshire, England, educating children aged 11–18 years old, and has an on-site sixth form. The school is located in the hamlet of Toulston just outside the brewery town of Tadcaster. The school's catchment includes Tadcaster and its surrounding villages, while traditionally taking pupils from the York area, including villages such as Appleton Roebuck, Copmanthorpe, Bishopthorpe and Bilbrough.
Tadcaster Rural District was a rural district in the West Riding of Yorkshire from 1894 to 1974. It was named after Tadcaster.

Tadcaster Albion Association Football Club is an association football club in Tadcaster, North Yorkshire, England. Formed in 1892, their ground is situated behind the John Smith's brewery in Tadcaster, thus the reason for their nickname "The Brewers". They compete in the Northern Counties East League Premier Division and are managed by Paul Quinn. Quinn was appointed in November 2019, and started his time at Tadcaster with a 2-0 league win at home to Droylsden.

O Barco de Valdeorras is a municipality in Ourense (province) in the Galicia region of north-west Spain. It lies towards the very north-east of Ourense province. Located in the Sil valley, lying in the Serra do Eixo, is the capital of the Valdeorras region. One of its economic foundations, besides mining and slate processing, is wine production, which qualified for the Designation of Origin Valdeorras. Remains of Roman and pre-Roman culture and several stately manor houses are the most important monuments in the town. It is also famous for its wines.
Luguvalium was a Roman town in northern Britain in antiquity. It was located within present-day Carlisle, Cumbria, and may have been the capital of the 4th-century province of Valentia.

Isurium or Isurium of the Brigantes was a Roman fort and town in the province of Britannia at the site of present-day Aldborough in North Yorkshire, England, in the United Kingdom. Its remains—the Aldborough Roman Site—are in the care of English Heritage.

Ancaster was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. It is sited on the Roman road known as the Ermine Street and is situated in the county of Lincolnshire. Its name in Latin is unknown, although it has traditionally been identified with Causennis or Causennæ, a name which occurs as a town on the route of Iter V recorded in the Antonine Itinerary. Rivet and Smith questioned this identification in 1979, and suggested that a more likely identification would be either the Roman settlement at Salters ford, near Grantham in Lincolnshire, or at Sapperton in Lincolnshire.

The Ebor Way is a 70-mile (112 km) long-distance footpath from Helmsley, North Yorkshire to Ilkley, West Yorkshire, via the city of York, England. It takes its name from Eboracum, the Roman name for York.
Cataractonium was a fort and settlement in Roman Britain. The settlement evolved into Catterick, located in North Yorkshire, England.
Caenophrurium was a settlement in the Roman province of Europa, between Byzantium and Heraclea Perinthus. It appears in late Roman and early Byzantine accounts. Caenophrurium translates as the "stronghold of the Caeni", a Thracian tribe.

Derventio, sometimes described as Derventio Brigantium in order to distinguish it from other places called Derventio, was a Roman fort and settlement located beneath the modern town of Malton in North Yorkshire, England. The fort is positioned 18 miles north-east of Eboracum on the River Derwent.
















