
Mantidae is one of the largest families in the order of praying mantises, based on the type species Mantis religiosa; however, most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family in the order, and many references still use the term "mantid" to refer to any mantis. Technically, however, "mantid" refers only to members of the family Mantidae, and not the 14 remaining families of mantises. Some of the most recent classifications have promoted a number of the mantid subfamilies to the rank of family, e.g. Iridopterygidae, Sibyllidae, Tarachodidae, Thespidae, and Toxoderidae, while other classifications have reduced the number of subfamilies without elevating to higher rank.

Metallyticus is a genus of praying mantis. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Metallyticidae. They are mostly found in South-East Asia. The species of the genus are dark, somewhat flattened and cockroach-like, and often with a cuticle that is reflective and metallic in appearance.
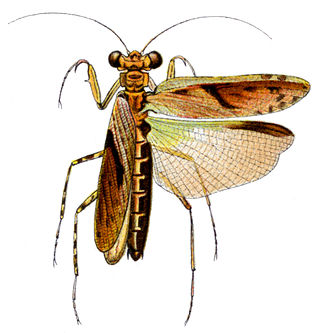
Amorphoscelidae is a family of mantises in the order Mantodea.

Eremiaphilidae is a small Old World family of praying mantids, based on the type genus Eremiaphila. As part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy, this family now contains the subfamily Tarachodinae, which includes tribes and genera previously placed in the now obsolete Tarachodidae.

Flower mantises are praying mantises that use a special form of camouflage referred to as aggressive mimicry, which they not only use to attract prey, but avoid predators as well. These insects have specific colorations and behaviors that mimic flowers in their surrounding habitats.
Boxer mantis is a common name given to various species of praying mantis. The name comes from the way these mantises move their oversized grasping forelimbs as they communicate with each other.

Acanthops is a genus of mantises in the family Acanthopidae, containing 20 species that can be found in Central and South America.

Acromantis is a genus of Asian praying mantids in the subfamily Acromantinae of the family Hymenopodidae.

Amorphoscelis is a genus of praying mantis in the family Amorphoscelidae; records of occurrence are from Africa and tropical Asia.
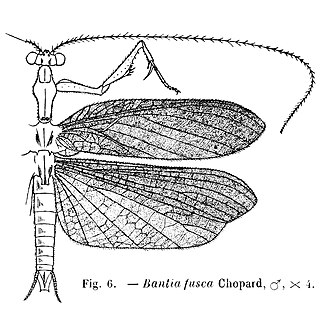
Thespidae is a family of insects in the order Mantodea. Following a major revision of this order in 2019, the old-world subfamilies Haaniinae and Hoplocoryphinae, previously placed here, have been upgraded to family level. Many genera are Neotropical, but the Thespinae are represented in Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America.

Rivetina is a genus of praying mantises in the family Rivetinidae.
Fulcinini is an Australian praying mantis tribe in the subfamily Fulciniinae.
Calofulcinia is a genus of praying mantises in the family Nanomantidae.

Acromantini is a tribe of mantis in the family Hymenopodidae, which contains 9 genera and 35 species:
Caliris is a genus of mantises in the family Haaniidae. Species in this genus are found in Asia.

Miomantidae is a family of praying mantises in the order Mantodea.

Theopropus is an Asian genus of praying mantids in the family Hymenopodidae: subfamily Hymenopodinae and tribe Hymenopodini.
Heliomantis is an Asian genus of praying mantids in the family Hymenopodidae, subfamily Hymenopodinae. The genus is monotypic.

The Nanomantidae are a new (2019) family of praying mantises, based on the type genus Nanomantis. As part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy, genera and tribes have been moved here, substantially replacing the old family Iridopterygidae.












