Related Research Articles
Teneurins are a family of phylogenetically conserved single-pass transmembrane glycoproteins expressed during pattern formation and morphogenesis. The name refers to "ten-a" and "neurons", the primary site of teneurin expression. Ten-m refers to tenascin-like protein major.

Emodepside is an anthelmintic drug that is effective against a number of gastrointestinal nematodes, is licensed for use in cats and belongs to the class of drugs known as the octadepsipeptides, a relatively new class of anthelmintic, which are suspected to achieve their anti-parasitic effect by a novel mechanism of action due to their ability to kill nematodes resistant to other anthelmintics.

The miR-124 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that has been identified in flies, nematode worms, mouse and human. The mature ~21 nucleotide microRNAs are processed from hairpin precursor sequences by the Dicer enzyme, and in this case originates from the 3' arm. miR-124 has been found to be the most abundant microRNA expressed in neuronal cells. Experiments to alter expression of miR-124 in neural cells did not appear to affect differentiation. However these results are controversial since other reports have described a role for miR-124 during neuronal differentiation.
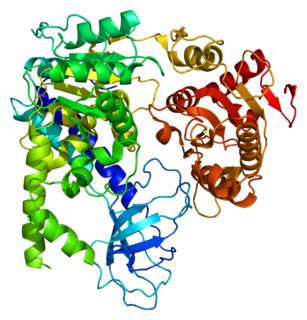
Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF1 gene.
POU is a family of proteins that have well-conserved homeodomains.

Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CACNB1 gene.

Semaphorin-3F is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEMA3F gene.

Uncoordinated-119 (Unc-119) is a protein that has been identified in C. elegans, humans, mice, zebrafish, rabbits, pig, calf, monkey, and protozoa. They have been classified in the GMP phophodiesterase, delta superfamily. Unc-119 proteins are categorized into their own family but are shown to be ancestrally related to PrBP and rhoGDI. It has been given many different names: Retinal Protein 4, HRG4, POC7 Centriolar Protein Homolog A, IMD13, POC7A, and RG4.

Neuron navigator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NAV2 gene.

Potassium channel subfamily K member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNK4 gene. KCNK4 protein channels are also called TRAAK channels.

Fasciculation and elongation protein zeta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FEZ1 gene.

CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDK5RAP1 gene.

Unc-93 homolog B1 , also known as UNC93B1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the UNC93B1 gene.

Transgelin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAGLN3 gene.

Neuron navigator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NAV1 gene.
In molecular biology, the FEZ-like protein family is a family of eukaryotic proteins thought to be involved in axonal outgrowth and fasciculation. The N-terminal regions of these sequences are less conserved than the C-terminal regions, and are highly acidic. The Caenorhabditis elegans homologue, UNC-76, may play structural and signalling roles in the control of axonal extension and adhesion and these roles have also been postulated for other FEZ family proteins. Certain homologues have been definitively found to interact with the N-terminal variable region (V1) of PKC-zeta, and this interaction causes cytoplasmic translocation of the FEZ family protein in mammalian neuronal cells. The C-terminal region probably participates in the association with the regulatory domain of PKC-zeta. The members of this family are predicted to form coiled-coil structures which may interact with members of the RhoA family of signalling proteins, but are not thought to contain other characteristic protein motifs. Certain members of this family are expressed almost exclusively in the brain, whereas others are expressed in other tissues, and are thought to perform similar but unknown functions in these tissues.
UNC is a set of proteins first identified through a set of screening tests in Caenorhabditis elegans, looking for roundworms with movement problems. Worms with which were un-coordinated were analysed in order to identify the genetic defect. Such proteins include UNC-5, a receptor for UNC-6 which is one of the netrins. Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. UNC-5 uses repulsion (genetics) to direct axons while the other netrin receptor UNC-40 attracts axons to the source of netrin production.
UNC-5 is a receptor for netrins including UNC-6. Netrins are a class of proteins involved in axon guidance. UNC-5 uses repulsion to direct axons while the other netrin receptor UNC-40 attracts axons to the source of netrin production.

Unc-93 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UNC93A gene.

Calponin 1 is a basic smooth muscle protein that in humans is encoded by the CNN1 gene.
References
- ↑ Goetinck S, Waterston RH (October 1994). "The Caenorhabditis elegans muscle-affecting gene unc-87 encodes a novel thin filament-associated protein". J. Cell Biol. 127 (1): 79–93. doi:10.1083/jcb.127.1.79. PMC 2120179 . PMID 7929573.
- ↑ Ren WZ, Ng GY, Wang RX, Wu PH, O'Dowd BF, Osmond DH, George SR, Liew CC (March 1994). "The identification of NP25: a novel protein that is differentially expressed by neuronal subpopulations". Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 22 (1–4): 173–85. doi:10.1016/0169-328X(94)90045-0. PMID 8015377.
- ↑ Irvine M, Huima T, Prince AM, Lustigman S (May 1994). "Identification and characterization of an Onchocerca volvulus cDNA clone encoding a highly immunogenic calponin-like protein". Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 65 (1): 135–46. doi:10.1016/0166-6851(94)90122-8. PMID 7935620.