Babur was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also given the posthumous name of Firdaws Makani.

Nasir al-Din Muhammad, commonly known by his regnal name Humayun, was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from 1530 to 1540 and again from 1555 to his death in 1556. At the time of his death, the Mughal Empire spanned almost one million square kilometers.

The Hazaras are an ethnic group and a principal component of Afghanistan’s population. They are one of the largest ethnic groups in Afghanistan, primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan. Hazaras also form significant minority communities in Pakistan, mainly in Quetta, and in Iran, primarily in Mashhad. They speak the Dari and Hazaragi dialects of Persian. Dari, also known as Dari Persian, is one of the two official languages of Afghanistan.

The First Battle of Panipat, on 21 April 1526 was fought between the invading forces of Babur against Ibrahim Lodi, the Sultan of Delhi, in North India. Babur's forces, employing gunpowder firearms and cannons, defeated Ibrahim. This was one of the earliest battles involving gunpowder arms on the Indian subcontinent. The victory marked the beginning of Mughal rule in India.

Ghazni is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in southeastern Afghanistan. The province contains 19 districts, encompassing over a thousand villages and roughly 1.3 million people, making it the 5th most populous province. The city of Ghazni serves as the capital. It lies on the important Kabul–Kandahar Highway, and has historically functioned as an important trade center. The Ghazni Airport is located next to the city of Ghazni and provides limited domestic flights to Afghanistan's capital, Kabul.

The Battle of Khanwa was fought at Khanwa on 16 March 1527. It was fought between the invading Timurid forces of Babur and the Kingdom of Mewar led by Rana Sanga for supremacy of Northern India. The battle was a major event in Medieval Indian history although Timurids won at Panipat but at the time, the sultanate at Delhi was a spent force that was long crumbling. To the contrary, Kingdom of Mewar under the able rule of Rana Sanga and his predecessors, had turned into one of the strongest powers of northern India.The battle was among the most decisive battles in the Mughal conquest of northern India. It was among the earliest battles in Northern India where gunpowder was used to a great extent. The battle resulted in heavy casualties for both Timurids and Rajputs.

The Arghun dynasty ruled over the area adjoining Southern Afghanistan and then the Sindh Sultanate from the late 15th century to the early 16th century. Arghun rule can be divided into two branches: the Arghun branch of Dhu'l-Nun Beg Arghun that ruled until 1554, and the Tarkhan branch of Muhammad Isa Tarkhan that ruled until 1593.

Kamran Mirza was the second son of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first Mughal Emperor. Kamran Mirza was born in Kabul to Babur's wife Gulrukh Begum. He was half-brother to Babur's eldest son Humayun, who would go on and inherit the Mughal throne, but he was full-brother to Babur's third son, Askari. A divan written in Persian and Chagatai is attributed to him.
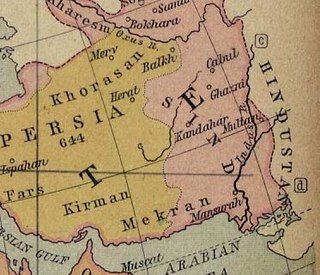
In 1504, Babur besieged Kabul and took the city from the Arghuns under Mukim Beg Arghun, to become the new king of Kabul and Ghazni regions. The territory gave him respite from his Uzbek troubles in Central Asia. It allowed him to build his nascent kingdom into a strong and formidable power in later years, enough to conquer northern India.

In January 1505, Babur set out from Kabul towards India and proceeding by way of Badam Cheshmeh and Jagdalak reached Adinapur (Jalalabad). Nasir Mirza, his younger brother, joined him here. As the Aimaqs of that neighborhood with their followers had moved down with all their families into Lamghanat for the purpose of wintering there, they waited for this group and others till they were joined by them after which the army went on to Kush Gumbez lower down than Jui Shahi. Nasir Mirza having made some provision for his dependents and followers from the country under his government stayed behind at Kush Gumbez promising to follow in two or three days.

Battle of Ab Darrah Pass was the battle that took place in 1511 in the place called Ab Darrah between Uzbeks and Babur of Timurids. The battle ended with the decisive Timurid victory which enabled Babur to regain Transoxiana and briefly reunite the whole of the ancestral part of the Timurid Empire. Such a decisive and significant battle is not mentioned in Babur’s Memoirs (Baburnama), in which there is a break from the year 1508 to the beginning of 1519.
Eastern Afghanistan Operations was when Uzbek Khan and Muhammad Shaybani surrounded Kandahar, Babur found his developing Kingdom of Kabul in danger. He feared that Kabul would be the next target of the Uzbeks.

Abu'l-Nasir Muhammad, better known by the sobriquet Hindal, was a Mughal prince and the youngest son of Emperor Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire and the first Mughal emperor. He was also the older brother of Gulbadan Begum, the younger half-brother of the second Mughal emperor Humayun, as well as the paternal-uncle and father-in-law of the third Mughal emperor Akbar.
Ruqaiya Sultan Begum was the first wife and one of the chief consorts of the third Mughal emperor, Akbar.
The First Campaign against Turkoman Hazaras was a Mughal Empire campaign against Hazaras in the 16th century. Following Babur's departure from Kabul for Qalat, the Hazaras took advantage of his absence to raid his territories. After Babur had returned to Kabul from his victory at the Battle of Qalat, he remained encamped in the Chaharbagh during the harsh winter of 1505 CE where he planned to make an excursion against them. He then went into Kabul city into the palace of Ulugh Beg Mirza, called Bostān-Serāi, prepared for the campaign and set out from there on December 28, 1505 CE.

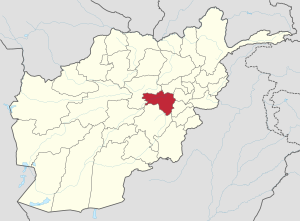
The Hazāra of Muḥammad Khwāja is one of the major tribes of the ethnic Hazara, originating and inhabiting mainly from Ghazni, Afghanistan.
Ulugh Beg II also known as Ulugh Beg Kabuli (d.1502) was the Timurid ruler of Kabul and Ghazni from 1461 to 1502.
Jahangir Mirza II was the second son of Umar Sheikh Mirza and half brother of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Empire. He was two years younger to Babur and his mother, Fatima Sultan, belonged to the clan of Mughal Tuman Begs.

The foreign relations of the Mughal Empire were characterized by competition with the Persian Empire to the west, the Marathas and others to the south, and the British to the east. Steps were taken by successive Mughal rulers to secure the western frontiers of India. The Khyber Pass along the Kabul- Qandahar route was the natural defence for India, and their foreign policy revolved around securing these outposts, as also balancing the rise of powerful empires in the region.
Sultan Masudi was a tribe of the Hazaras.