Decompression sickness is a medical condition caused by dissolved gases emerging from solution as bubbles inside the body tissues during decompression. DCS most commonly occurs during or soon after a decompression ascent from underwater diving, but can also result from other causes of depressurisation, such as emerging from a caisson, decompression from saturation, flying in an unpressurised aircraft at high altitude, and extravehicular activity from spacecraft. DCS and arterial gas embolism are collectively referred to as decompression illness.

Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure higher than atmospheric pressure, and therapeutic recompression for decompression illness, intended to reduce the injurious effects of systemic gas bubbles by physically reducing their size and providing improved conditions for elimination of bubbles and excess dissolved gas.

Saturation diving is diving for periods long enough to bring all tissues into equilibrium with the partial pressures of the inert components of the breathing gas used. It is a diving mode that reduces the number of decompressions divers working at great depths must undergo by only decompressing divers once at the end of the diving operation, which may last days to weeks, having them remain under pressure for the whole period. A diver breathing pressurized gas accumulates dissolved inert gas used in the breathing mixture to dilute the oxygen to a non-toxic level in their tissues, which can cause decompression sickness if permitted to come out of solution within the body tissues; hence, returning to the surface safely requires lengthy decompression so that the inert gases can be eliminated via the lungs. Once the dissolved gases in a diver's tissues reach the saturation point, however, decompression time does not increase with further exposure, as no more inert gas is accumulated.

A Canadian Forces base or CFB is a military installation of the Canadian Armed Forces. For a facility to qualify as a Canadian Forces base, it must station one or more major units.
Wilbur Rounding Franks, OBE was a Canadian scientist, notable as the inventor of the anti-gravity suit or G-suit, and for his work in cancer research.

Diving medicine, also called undersea and hyperbaric medicine (UHB), is the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of conditions caused by humans entering the undersea environment. It includes the effects on the body of pressure on gases, the diagnosis and treatment of conditions caused by marine hazards and how relationships of a diver's fitness to dive affect a diver's safety. Diving medical practitioners are also expected to be competent in the examination of divers and potential divers to determine fitness to dive.

Survival, Evasion, Resistance, and Escape (SERE) is a training program, best known by its military acronym, that prepares U.S. military personnel, U.S. Department of Defense civilians, and private military contractors to survive and "return with honor" in survival scenarios. The curriculum includes survival skills, evading capture, application of the military code of conduct, and techniques for escape from captivity. Formally established by the U.S. Air Force at the end of World War II and the start of the Cold War, it was extended to the Navy and United States Marine Corps and consolidated within the Air Force during the Korean War with greater focus on "resistance training."

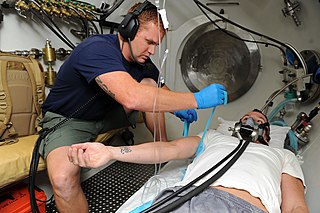
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of breathing gas for the occupants.

CFB Edmonton is a Canadian Forces base located in Sturgeon County adjacent to the City of Edmonton in Alberta, Canada. It is also known as Edmonton Garrison or "Steele Barracks".

Canadian Forces Base Winnipeg, is a Royal Canadian Air Force base located within the City of Winnipeg, Manitoba. Co-located at the Winnipeg James Armstrong Richardson International Airport, CFB Winnipeg is home to many flight operations support divisions, as well as several training schools. Its primary RCAF lodger unit is 17 Wing, commonly referred to as 17 Wing Winnipeg.

The Canadian Forces Health Services Group is a formation of the Canadian Forces within the Military Personnel Command. It includes personnel from both the Royal Canadian Medical Service and the Royal Canadian Dental Corps, fulfills all military health system functions from education and clinical services to research and public health, and is composed of health professionals from over 40 occupations and specialties in over 120 units and detachments across Canada and abroad.

The 336th Training Group is the combat survival training group of the United States Air Force. The group is located at Fairchild Air Force Base, Washington, with one subordinate unit at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida, and one at Eielson Air Force Base, Alaska.
Springer Lake is a lake in central North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada, about 170 kilometres (110 mi) north east of the city of Winnipeg. It is situated in Nopiming Provincial Park.

A Special Amphibious Reconnaissance Corpsman (SARC) is a United States Navy hospital corpsman who provides MARSOC and other USSOCOM units advanced trauma management associated with combatant diving and parachute entry. Traditionally, they are attached to the Marine Corps Force Reconnaissance companies to help support the Command Element of the Marine Air-Ground Task Force in special reconnaissance missions.

Colonel William Paul Fife USAF (Ret) was a United States Air Force officer that first proved the feasibility for U.S. Air Force Security Service airborne Communications Intelligence (COMINT) collection and Fife is considered the "Father of Airborne Intercept". Fife was also a hyperbaric medicine specialist who was known for his pioneering research on pressurized environments ranging from high altitude to underwater habitats. Fife was a Professor Emeritus at Texas A&M University.
Captain Albert Richard Behnke Jr. USN (ret.) was an American physician, who was principally responsible for developing the U.S. Naval Medical Research Institute. Behnke separated the symptoms of Arterial Gas Embolism (AGE) from those of decompression sickness and suggested the use of oxygen in recompression therapy.

Hyperbaric treatment schedules or hyperbaric treatment tables, are planned sequences of events in chronological order for hyperbaric pressure exposures specifying the pressure profile over time and the breathing gas to be used during specified periods, for medical treatment. Hyperbaric therapy is based on exposure to pressures greater than normal atmospheric pressure, and in many cases the use of breathing gases with oxygen content greater than that of air.

The United States Air Force School of Aerospace Medicine (USAFSAM) is the United States Air Force (USAF) organization focused on education, research, and operational consultation in aerospace and operational medicine. USAFSAM was founded in 1918 to conduct research into the medical and physiologic domains related to human flight, and as a school for medical officers trained to support military aviation operations, later coined as flight surgeons. The school supported early military aviation from World War I through the evolution of aviation and into the modern era. USAFSAM conducted medical research and provided medical support for the initial US space operations beginning in 1947 through the establishment of NASA in 1958. After the creation of NASA, USAFSAM continued to actively support civilian and military manned space missions through clinical and physiologic research. USAFSAM is one of the oldest continually operating school for flight surgeons and other operational medical personnel of its kind in the world. USAFSAM is located in Dayton, Ohio at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, and is part of the 711th Human Performance Wing and the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL).
The Diving Medical Advisory Council (DMAC) is an independent organisation of diving medical specialists, mostly from across Northern Europe which exists to provide expert advice about medical and some safety aspects of commercial diving. The advice is published in the form of guidance documents, which are made available for download.