
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any species of the genus Candida. When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers, among other symptoms.
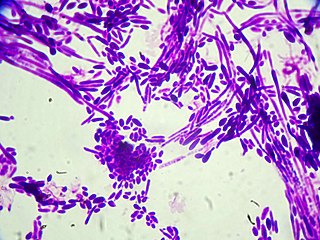
Candida dubliniensis is a fungal opportunistic pathogen originally isolated from AIDS patients. It is also occasionally isolated from immunocompetent individuals. It is of the genus Candida, very closely related to Candida albicans but forming a distinct phylogenetic cluster in DNA fingerprinting. It is most commonly isolated from oral cavities, and is also occasionally found in other anatomical sites.

An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally.

Candida is a genus of yeasts. It is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide and the largest genus of medically important yeasts.
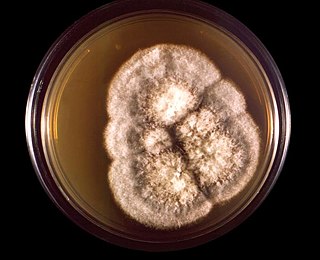
Coccidioides immitis is a pathogenic fungus that resides in the soil in certain parts of the southwestern United States, northern Mexico, and a few other areas in the Western Hemisphere.
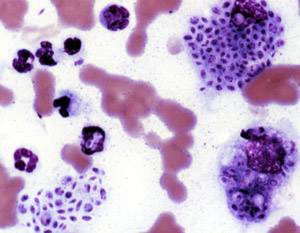
Sporotrichosis, also known as rose handler's disease, is a fungal infection that may be localised to skin, lungs, bone and joint, or become systemic. It presents with firm painless nodules that later ulcerate. Following initial exposure to Sporothrix schenckii, the disease typically progresses over a period of a week to several months. Serious complications may develop in people who have a weakened immune system.
Candida parapsilosis is a fungal species of yeast that has become a significant cause of sepsis and of wound and tissue infections in immunocompromised people. Unlike Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis, C. parapsilosis is not an obligate human pathogen, having been isolated from nonhuman sources such as domestic animals, insects and soil. C. parapsilosis is also a normal human commensal and it is one of the fungi most frequently isolated from human hands. There are several risk factors that can contribute to C. parapsilosis colonization. Immunocompromised individuals and surgical patients, particularly those undergoing surgery of the gastrointestinal tract, are at high risk for infection with C. parapsilosis. There is currently no consensus on the treatment of invasive candidiasis caused by C. parapsilosis, although the therapeutic approach typically includes the removal of foreign bodies such as implanted prostheses and the administration of systemic antifungal therapy. Amphotericin B and Fluconazole are often used in the treatment of C. parapsilosis infection.
Pichia kudriavzevii is a budding yeast involved in chocolate production. P. kudriavzevii is an emerging fungal nosocomial pathogen primarily found in the immunocompromised and those with hematological malignancies. It has natural resistance to fluconazole, a standard antifungal agent. It is most often found in patients who have had prior fluconazole exposure, sparking debate and conflicting evidence as to whether fluconazole should be used prophylactically. Mortality due to P. kudriavzevii fungemia is much higher than the more common C. albicans. Other Candida species that also fit this profile are C. parapsilosis, C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, C. guillermondii and C. rugosa.
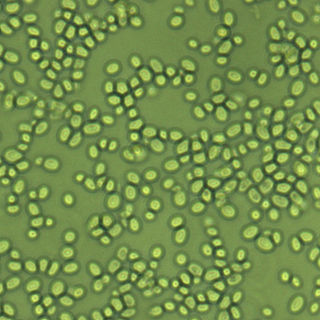
Nakaseomyces glabratus is a species of haploid yeast of the genus Nakaseomyces, previously known as Candida glabrata. Despite the fact that no sexual life cycle has been documented for this species, N. glabratus strains of both mating types are commonly found. N. glabrata is generally a commensal of human mucosal tissues, but in today's era of wider human immunodeficiency from various causes, N. glabratus is often the second or third most common cause of candidiasis as an opportunistic pathogen. Infections caused by N. glabratus can affect the urogenital tract or even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients.
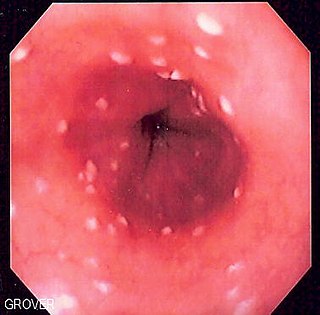
Esophageal candidiasis is an opportunistic infection of the esophagus by Candida albicans. The disease usually occurs in patients in immunocompromised states, including post-chemotherapy and in AIDS. However, it can also occur in patients with no predisposing risk factors, and is more likely to be asymptomatic in those patients. It is also known as candidal esophagitis or monilial esophagitis.

Clavispora lusitaniae, formerly also known by the anamorph name Candida lusitaniae, is a species of yeast in the genus Candida or Clavispora. The species name is a teleomorph name.

Echinocandins are a class of antifungal drugs that inhibit the synthesis of β-glucan in the fungal cell wall via noncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase. The class has been termed the "penicillin of antifungals," along with the related papulacandins, as their mechanism of action resembles that of penicillin in bacteria. β-glucans are carbohydrate polymers that are cross-linked with other fungal cell wall components, the fungal equivalent to bacterial peptidoglycan. Caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin are semisynthetic echinocandin derivatives with limited clinical use due to their solubility, antifungal spectrum, and pharmacokinetic properties.
Exophiala jeanselmei is a saprotrophic fungus in the family Herpotrichiellaceae. Four varieties have been discovered: Exophiala jeanselmei var. heteromorpha, E. jeanselmei var. lecanii-corni, E. jeanselmei var. jeanselmei, and E. jeanselmei var. castellanii. Other species in the genus Exophiala such as E. dermatitidis and E. spinifera have been reported to have similar annellidic conidiogenesis and may therefore be difficult to differentiate.
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. Although fungi are eukaryotic, many pathogenic fungi are microorganisms. Approximately 300 fungi are known to be pathogenic to humans; their study is called "medical mycology". Fungal infections are estimated to kill more people than either tuberculosis or malaria—about two million people per year.

Candida auris is a species of fungus that grows as yeast. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida which cause candidiasis in humans. Often, candidiasis is acquired in hospitals by patients with weakened immune systems. C. auris can cause invasive candidiasis (fungemia) in which the bloodstream, the central nervous system, and internal organs are infected. It has attracted widespread attention because of its multiple drug resistance. Treatment is also complicated because it is easily misidentified as other Candida species.

Rhodotorula glutinis is the type species of the genus Rhodotorula, a basidiomycetous genus of pink yeasts which contains 370 species. Heterogeneity of the genus has made its classification difficult with five varieties having been recognized; however, as of 2011, all are considered to represent a single taxon. The fungus is a common colonist of animals, foods and environmental materials. It can cause opportunistic infections, notably blood infection in the setting of significant underlying disease. It has been used industrially in the production of carotenoid pigments and as a biocontrol agent for post-harvest spoilage diseases of fruits.
Invasive candidiasis is an infection (candidiasis) that can be caused by various species of Candida yeast. Unlike Candida infections of the mouth and throat or vagina, invasive candidiasis is a serious, progressive, and potentially fatal infection that can affect the blood (fungemia), heart, brain, eyes, bones, and other parts of the body.
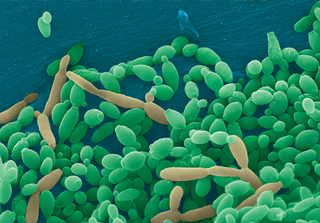
Candida tropicalis is a species of yeast in the genus Candida. It is a common pathogen in neutropenic hosts, in whom it may spread through the bloodstream to peripheral organs. For invasive disease, treatments include amphotericin B, echinocandins, or extended-spectrum triazole antifungals.

Trichosporon asteroides is an asexual basidiomycetous fungus first described from human skin but now mainly isolated from blood and urine. T. asteroides is a hyphal fungus with a characteristically yeast-like appearance due to the presence of slimy arthroconidia. Infections by this species usually respond to treatment with azoles and amphotericin B.
Microascus manginii is a filamentous fungal species in the genus Microascus. It produces both sexual (teleomorph) and asexual (anamorph) reproductive stages known as M. manginii and Scopulariopsis candida, respectively. Several synonyms appear in the literature because of taxonomic revisions and re-isolation of the species by different researchers. M. manginii is saprotrophic and commonly inhabits soil, indoor environments and decaying plant material. It is distinguishable from closely related species by its light colored and heart-shaped ascospores used for sexual reproduction. Scopulariopsis candida has been identified as the cause of some invasive infections, often in immunocompromised hosts, but is not considered a common human pathogen. There is concern about amphotericin B resistance in S. candida.













