
Candidiasis is a fungal infection due to any type of Candida. When it affects the mouth, in some countries it is commonly called thrush. Signs and symptoms include white patches on the tongue or other areas of the mouth and throat. Other symptoms may include soreness and problems swallowing. When it affects the vagina, it may be referred to as a yeast infection or thrush. Signs and symptoms include genital itching, burning, and sometimes a white "cottage cheese-like" discharge from the vagina. Yeast infections of the penis are less common and typically present with an itchy rash. Very rarely, yeast infections may become invasive, spreading to other parts of the body. This may result in fevers along with other symptoms depending on the parts involved.

Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constitute 1% of all described fungal species.
Candida, or Cándida (Spanish), may refer to:

Candida albicans is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usually a commensal organism, but it can become pathogenic in immunocompromised individuals under a variety of conditions. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida that causes the human infection candidiasis, which results from an overgrowth of the fungus. Candidiasis is, for example, often observed in HIV-infected patients. C. albicans is the most common fungal species isolated from biofilms either formed on (permanent) implanted medical devices or on human tissue. C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, and C. glabrata are together responsible for 50–90% of all cases of candidiasis in humans. A mortality rate of 40% has been reported for patients with systemic candidiasis due to C. albicans. By one estimate, invasive candidiasis contracted in a hospital causes 2,800 to 11,200 deaths yearly in the US. Nevertheless, these numbers may not truly reflect the true extent of damage this organism causes, given new studies indicating that C. albicans can cross the blood brain barrier.

Candida is a genus of yeasts and is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of hosts including humans; however, when mucosal barriers are disrupted or the immune system is compromised they can invade and cause disease, known as an opportunistic infection. Candida is located on most of mucosal surfaces and mainly the gastrointestinal tract, along with the skin. Candida albicans is the most commonly isolated species and can cause infections in humans and other animals. In winemaking, some species of Candida can potentially spoil wines.

Terconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat vaginal yeast infection. It comes as a lotion or a suppository and disrupts the biosynthesis of fats in a yeast cell. It has a relatively broad spectrum compared to azole compounds but not triazole compounds. Testing shows that it is a suitable compound for prophylaxis for those that suffer from chronic vulvovaginal candidiasis.

Saccharomycotina is a subdivision (subphylum) of the division (phylum) Ascomycota in the Kingdom Fungi. It comprises most of the ascomycete yeasts. The members of Saccharomycotina reproduce by budding and they do not produce ascocarps.
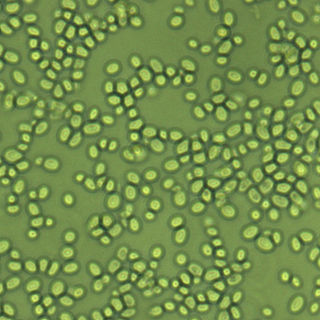
Candida glabrata is a species of haploid yeast of the genus Candida, previously known as Torulopsis glabrata. Despite the fact that no sexual life cycle has been documented for this species, C. glabrata strains of both mating types are commonly found. C. glabrata is generally a commensal of human mucosal tissues, but in today's era of wider human immunodeficiency from various causes, C. glabrata is often the second or third most common cause of candidiasis as an opportunistic pathogen. Infections caused by C. glabrata can affect the urogenital tract or even cause systemic infections by entrance of the fungal cells in the bloodstream (Candidemia), especially prevalent in immunocompromised patients.

Candida lusitaniae is a species of yeast in the genus Candida.
A killer yeast is a yeast, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is able to secrete one of a number of toxic proteins which are lethal to susceptible cells. These "killer toxins" are polypeptides that kill sensitive cells of the same or related species, often functioning by creating pores in target cell membranes. These yeast cells are immune to the toxic effects of the protein due to an intrinsic immunity. Killer yeast strains can be a problem in commercial processing because they can kill desirable strains. The killer yeast system was first described in 1963. Study of killer toxins helped to better understand the secretion pathway of yeast, which is similar to those of more complex eukaryotes. It also can be used in treatment of some diseases, mainly those caused by fungi.
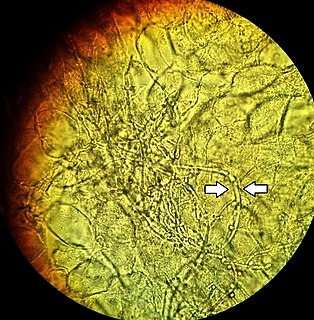
Vaginal yeast infection, also known as candidal vulvovaginitis and vaginal thrush, is excessive growth of yeast in the vagina that results in irritation. The most common symptom is vaginal itching, which may be severe. Other symptoms include burning with urination, a thick, white vaginal discharge that typically does not smell bad, pain during sex, and redness around the vagina. Symptoms often worsen just before a woman's period.
Starmerella is a genus of fungi within the Saccharomycetales order. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the order is unknown, and it has not yet been placed with certainty into any family. Several members of the Starmerella clade are associated with flowers and flower-visiting insects like bees and bumblebees; these yeasts cope well with high sugar niches. Many strains (species) of the Starmerella clade, including Starmerella bombicola and Candida apicola are known to produce sophorolipids which are carbohydrate-based, amphiphilic biosurfactants.

Herman Jan Phaff was a scientist who specialised in yeast ecology. He was born in the Netherlands before moving to California at age of 26. He was active in Californian universities until his death. During his career he accumulated thousands of strains of yeast from the wild, and described 60 new taxa of yeast.
Candida blankii is a species of budding yeast (Saccharomycotina) in the family Saccharomycetaceae. The yeast may be a dangerous pathogen and resistant to treatment in human hosts. Research on the fungi has therapeutic, medical and industrial implications.
Candida humilis is a species of yeast in the genus Candida. It commonly occurs in sourdough and kefir cultures, along with different species of lactic acid bacteria. Candida humilis is the most representative yeast species found in type I sourdough ecosystems. The effects of electric field strength, pulse width and frequency, or pulse shape is significant on the membranes of Candida humilis, but not very noticeable.

Candida auris is a species of fungus that grows as yeast. It is one of the few species of the genus Candida which cause candidiasis in humans. Often, candidiasis is acquired in hospitals by patients with weakened immune systems. C. auris can cause invasive candidiasis (fungemia) in which the bloodstream, the central nervous system, and internal organs are infected. It has attracted widespread attention because of its multiple drug resistance. Treatment is also complicated because it is easily misidentified as other Candida species.
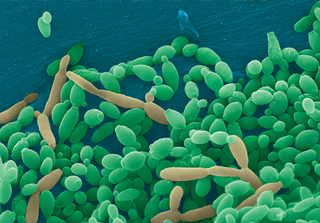
Candida tropicalis is a species of yeast in the genus Candida. It is a common pathogen in neutropenic hosts, in whom it may spread through the bloodstream to peripheral organs. For invasive disease, treatments include amphotericin B, echinocandins, or extended-spectrum triazole antifungals.
Candida hypersensitivity is a pseudoscientific disease promoted by William G. Crook, M.D. It is spuriously claimed that chronic yeast infections are responsible for many common disorders and non-specific symptoms including fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dizziness, muscle and joint pain, asthma, and others.

Fungal DNA barcoding is the process of identifying species of the biological kingdom Fungi through the amplification and sequencing of specific DNA sequences and their comparison with sequences deposited in a DNA barcode database such as the ISHAM reference database, or the Barcode of Life Data System (BOLD). In this attempt, DNA barcoding relies on universal genes that are ideally present in all fungi with the same degree of sequence variation. The interspecific variation, i.e., the variation between species, in the chosen DNA barcode gene should exceed the intraspecific (within-species) variation.











