Thurston Island is an ice-covered, glacially dissected island, 215 km (134 mi) long, 90 km (56 mi) wide and 15,700 km2 (6,062 sq mi) in area, lying a short way off the northwest end of Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. It is the third largest island of Antarctica, after Alexander Island and Berkner Island.

Cape Disappointment is a cape which marks the tip of the ice-covered Akra Peninsula lying between Exasperation Inlet and Scar Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land. It was discovered in 1902 by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, under Otto Nordenskiöld, and so named by him because he encountered many difficult crevasses in approaching the cape.

Cape Longing is a rocky cape on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica, forming the south end of a large ice-covered promontory which marks the west side of the south entrance to Prince Gustav Channel. It was discovered by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld in 1902, and so named by him because from the position of his winter hut on Snow Hill Island the cape lay in the direction of his "land of longing" which he was anxious to explore.
Cape Irizar is a bold rocky headland that forms the northern end of Lamplugh Island, off the coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott. He named it for Captain Julián Irízar, of the Argentine Navy's schooner Uruguay, who rescued the shipwrecked members of the Swedish Antarctic Expedition of 1901–04.
Blackface Point is a rocky and precipitous headland 3 nautical miles (6 km) northwest of Cape Freeman on the east coast of Graham Land. The point was photographed by the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and mapped by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, 1947–48. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in description of the extremely black rock exposed at the end of the point.

Mount Cloos is a dome-shaped mountain probably over 915 metres (3,000 ft) high, standing at the north side of Girard Bay and 2.3 miles (3.7 km) northeast of Cape Cloos, on the northwest coast of Kiev Peninsula in Graham Land. It was discovered by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–99 under Gerlache. It was named in association with Cape Cloos by the French Antarctic Expedition of 1908–10 under Jean-Baptiste Charcot.

Nuñez Point is a point forming the west extremity of Takaki Promontory on Barison Peninsula on Graham Coast, Graham Land, in Antarctica. Discovered by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05, and named by Charcot for Captain Nuñez, Argentine Navy.

Crume Glacier is a tributary glacier, 5 nautical miles (9 km) long, flowing east to enter Ommanney Glacier near the north coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. The geographical feature was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for William R. Crume, AS1, U.S. Navy, Support Equipment Maintenance Supervisor with Squadron VX-6 at McMurdo Station, Hut Point Peninsula, Ross Island, during Operation Deep Freeze 1968. The glacier lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare.
Smith Peaks is a group of peaks standing close south of Mount Hordern in the David Range of the Framnes Mountains. Mapped by Norwegian cartographers from aerial photographs taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition, 1936-37. Remapped by ANARE, 1957–60, and named by Antarctic Names Committee of Australia (ANCA) for F.A. Smith, diesel mechanic at Mawson Station, 1957.

Duyvis Point is the point forming the southeast side of the entrance to Urovene Cove situated 11 nautical miles (20 km) south-southeast of Cape Garcia and 2.65 km southeast of Laskar Point, on the southwest coast of Felipe Solo (Obligado) Peninsula, Graham Land in Antarctica. It was first roughly charted by the British Graham Land Expedition under John Rymill, 1934–37. It was mapped more accurately by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey from photos taken by Hunting Aerosurveys Ltd in 1956–57, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for F. Donker Duyvis, a Dutch documentalist who was Secretary of the International Federation for Documentation.

Erebus Bay is a bay about 24 kilometres (13 nmi) wide between Cape Evans and Hut Point Peninsula, on the west side of Ross Island. The bay was explored by the British National Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Robert Falcon Scott. It was named by Scott's second expedition, the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13, which built its headquarters on Cape Evans; the feature is surmounted by Mount Erebus.
Framnes Head is a small rock point in Sandefjord Cove on the west side of Peter I Island. It was charted and named by a Norwegian expedition in the Norvegia under Nils Larsen, who made the first landing on Peter I Island at this point in February 1929.
Goodwin Glacier is a glacier flowing west into Flandres Bay southward of Pelletan Point on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was charted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition under Gerlache, 1897–99. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1960 for Hannibal Goodwin, an American pastor who invented the first transparent nitrocellulose flexible photographic roll-film in 1887.
Mason Inlet is an ice-filled inlet which recedes 28 kilometres (15 nmi) southwest between Cape Mackintosh and the coastline south of Cape Herdman, along the east coast of Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was first seen and photographed from the air in December 1940 by members of the United States Antarctic Service, and during 1947 was photographed from the air by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition, who in conjunction with the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) charted it from the ground. The inlet was named by the FIDS for D.P. Mason, their surveyor on the joint British–American sledge journey during the charting of this coast in 1947.
Cape Kinnes is a cape which forms the western extremity of Joinville Island, off the northeast end of the Antarctic Peninsula. It was named by members of the Dundee whaling expedition 1892–93, for Robert Kinnes, sponsor of the expedition.
Småtind Peak is a small peak close southeast of Fasettfjellet, near the east end of the Borg Massif in Queen Maud Land. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition of 1958–59 and named Småtind.
Thomas Mountains is a separate cluster of rocky mountains, about 5 nautical miles (9 km) long, standing 15 nautical miles (28 km) northeast of Mount Horne in Palmer Land. Discovered by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition (RARE), 1947–48, under Ronne, who named these mountains for noted author and radio commentator Lowell Thomas, a supporter of the expedition.
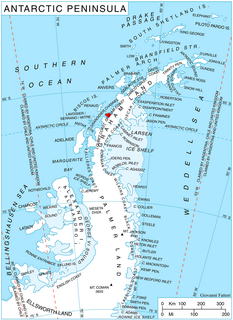
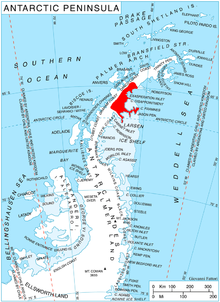
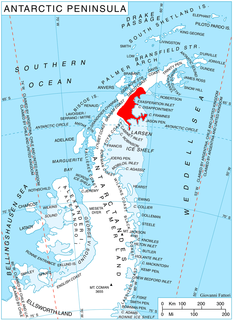
Rossa Point is a point 2 nautical miles (3.7 km) northeast of Ferin Head on Velingrad Peninsula, the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1959 for Anders Rossa, a Jokkmokk Sami who, with Pava Tuorda, accompanied A.E. Nordenskjold to Greenland in 1883 and first demonstrated the possibilities of skis for polar travel.

Leay Glacier is a glacier flowing northwest into Girard Bay to the west of Hotine Glacier, on Kiev Peninsula, on the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Petra Searle of the Directorate of Overseas Surveys, who has contributed to the work of mapping the Antarctic Peninsula area.