
Philip II, also known as Philip the Prudent, was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He was also jure uxoris King of England and Ireland from his marriage to Queen Mary I in 1554 until her death in 1558. He was also Duke of Milan from 1540. From 1555, he was Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands.

Fernando Álvarez de Toledo y Pimentel, 3rd Duke of Alba, known as the Grand Duke of Alba in Spain and Portugal and as the Iron Duke in the Netherlands, was a Spanish noble, general and diplomat. Alba achieved notoriety for his actions during the Eighty Years' War in the Spanish Netherlands, where his prolonged military campaigns and harsh repression failed to suppress the Dutch Revolt.

The Portuguese conquest of Ceuta took place on 21 August 1415, between Portuguese forces under the command of King John I of Portugal and the Marinid sultanate of Morocco at the city of Ceuta. The city's defenses fell under Portuguese control after a carefully prepared attack, and the successful capture of the city marked the beginning of the Portuguese Empire. Ceuta was held under Portuguese control until being transferred to Spain in 1668.

The Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) was an intermittent conflict between the Habsburg Kingdom of Spain and the Kingdom of England that was never formally declared. It began with England's military expedition in 1585 to what was then the Spanish Netherlands under the command of the Earl of Leicester, in support of the Dutch rebellion against Spanish Habsburg rule.

António, Prior of Crato, sometimes called "The Determined", "The Fighter", "The Independentist" or "The Resistant", was a grandson of King Manuel I of Portugal who claimed the Portuguese throne during the 1580 dynastic crisis. According to some historians, he was King of Portugal for 33 days in 1580. Philip II of Spain prevailed in the succession struggle, but António claimed the throne until 1583. He was a disciple of Bartholomew of Braga.

The Iberian Union is a historiographical term used to describe the dynastic union of the Monarchy of Spain, which in turn was itself a personal union of the crowns of Castile and Aragon, and the Kingdom of Portugal, and of their respective colonial empires, that existed between 1580 and 1640 and brought the entire Iberian Peninsula except Andorra, as well as Portuguese and Spanish overseas possessions, under the Spanish Habsburg monarchs Philip II, Philip III, and Philip IV. The union began after the Portuguese succession crisis of 1580 and the ensuing War of the Portuguese Succession, and lasted until the Portuguese Restoration War, during which the House of Braganza was established as Portugal's new ruling dynasty with the acclamation of John IV as the new king of Portugal.
This is a historical timeline of Portugal.
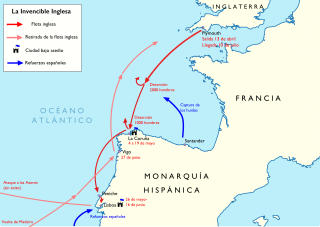
The English Armada, also known as the Counter Armada or the Drake–Norris Expedition, was an attack fleet sent against Spain by Queen Elizabeth I of England that sailed on 28 April 1589 during the undeclared Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604) and the Eighty Years' War. Led by Sir Francis Drake as admiral and Sir John Norris as general, it failed to drive home the advantage that England had gained resulting from the failure of the Spanish Armada in the previous year. The Spanish victory marked a revival of Philip II's naval power through the next decade.

Álvaro de Bazán y Guzmán, 1st Marquis of Santa Cruz, was a Spanish admiral and landlord. He took part, among others, in the seizure of the rock of Vélez de la Gomera (1564), the relief to the besieged during the Great Siege of Malta (1565), the quelling of the Alpujarras Rebellion (1569), the Battle of Lepanto (1571), the conquest of Tunis (1573), the incorporation of Portugal to the Hispanic monarchy (1580), and the conquest of Terceira (1582).

The naval Battle of Vila Franca do Campo, also known as Battle of Ponta Delgada and Naval Battle of Terceira Island, took place on 26 July 1582, off the coast of the island of São Miguel in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores, during the War of the Portuguese Succession. A combined corsair expedition, mainly French, sailed against a Spanish naval force made up of Portuguese and Castilian ships, to preserve control of the Azores under the pretender António, Prior of Crato and to defend the islands from incorporation into the Iberian Union, the largest French force sent overseas before the age of Louis XIV.

The Spanish Armada was a Spanish fleet that sailed from Lisbon in late May 1588, commanded by Alonso de Guzmán, Duke of Medina Sidonia, an aristocrat without previous naval experience appointed by Philip II of Spain. His orders were to sail up the English Channel, join with the Duke of Parma in Flanders, and escort an invasion force that would land in England and overthrow Elizabeth I. Its purpose was to reinstate Catholicism in England, end support for the Dutch Republic, and prevent attacks by English and Dutch privateers against Spanish interests in the Americas.

Sancho d'Avila was a Spanish general.

The War of the Portuguese Succession, a result of the extinction of the Portuguese royal line after the Battle of Alcácer Quibir and the ensuing Portuguese succession crisis of 1580, was fought from 1580 to 1583 between the two main claimants to the Portuguese throne: António, Prior of Crato, proclaimed in several towns as King of Portugal, and his first cousin Philip II of Spain, who eventually succeeded in claiming the crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.
Francisco de Portugal, also known as Francis II of Portugal, 3rd Count of Vimioso, was the eldest son and heir of the 2nd Count of Vimioso, Afonso de Portugal.
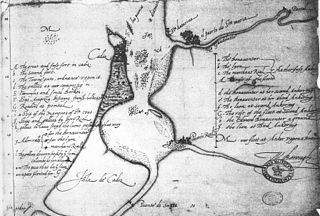
Singeing the King of Spain's Beard is the derisive name given to a series of attacks by the English privateer Francis Drake against the Spanish in the summer of 1587, beginning in April with a raid on Cádiz. This was an attack on the Spanish naval forces assembling in the Bay of Cádiz in preparation for the planned expedition against England. Much of the Spanish fleet was destroyed, and substantial supplies were destroyed or captured. There followed a series of raiding parties against several forts along the Portuguese coast. A Spanish treasure ship, returning from the Indies, was also captured. The damage caused by the English delayed Spanish preparations for the Armada by at least a year.

The Battle of Alcântara took place on 25 August 1580, near the brook of Alcântara, in the vicinity of Lisbon, Portugal, and was a victory of the Habsburg King Philip II over the other pretender to the Portuguese throne, Dom António, Prior of Crato.

The Sea Dogs were a group of English privateers and explorers authorised by Queen Elizabeth I to raid England's enemies, whether they were formally at war with them or not. Active from 1560 until Elizabeth's death in 1603, the Sea Dogs primarily attacked Spanish targets both on land and at sea, particularly during the Anglo-Spanish War. Members of the Sea Dogs, including Sir John Hawkins and Sir Francis Drake, also engaged in illicit slave trading with Spanish colonies in the Americas.

The Battle of Salga occurred on 25 July 1581, around the Bay of Salga and along the coastal part of the parish of Vila de São Sebastião, on the island of Terceira in the Portuguese Azores, between Spanish and Portuguese forces. The latter, in the name of António, Prior of Crato, successfully defended the island against the personal union with the Spanish crown during the War of the Portuguese Succession.

The Conquest of the Azores, but principally involving the conquest of the island of Terceira, occurred on 2 August 1583, in the Portuguese archipelago of the Azores, between forces loyal to the claimant D. António, Prior of Crato, supported by the French and English troops, and the Spanish and Portuguese forces loyal to King Philip II of Spain, commanded by the Admiral Don Álvaro de Bazán, Marquis of Santa Cruz, during the War of the Portuguese Succession. The victory of the Marquis of Santa Cruz resulted in the rapid Spanish conquest of the Azores, facilitating the integration of the Kingdom of Portugal and its colonial possessions into the Spanish Empire.

The Battle of the Gulf of Cádiz was a naval action which occurred on 7 August 1604, during the last days of the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604). The battle took place when a flotilla of two galleons commanded by Antonio de Oquendo engaged two English privateers who were plundering shipping lanes and villages around the Gulf of Cádiz. One of the English ships was captured and the other damaged. Oquendo's action off Cádiz is notable for having been fought just 21 days before the signing of the Treaty of London, which ended the protracted war between England and Spain.


















