
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion does not always result in fire, because a flame is only visible when substances undergoing combustion vaporize, but when it does, a flame is a characteristic indicator of the reaction. While activation energy must be supplied to initiate combustion, the heat from a flame may provide enough energy to make the reaction self-sustaining.
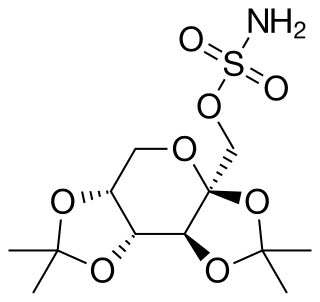
Topiramate, sold under the brand name Topamax among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and prevent migraines. It has also been used in alcohol dependence and essential tremor. For epilepsy this includes treatment for generalized or focal seizures. It is taken orally.
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test, or arterial blood gas analysis (ABGA) measures the amounts of arterial gases, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. An ABG test requires that a small volume of blood be drawn from the radial artery with a syringe and a thin needle, but sometimes the femoral artery in the groin or another site is used. The blood can also be drawn from an arterial catheter.

Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. When the foreskin is also affected, the proper term is balanoposthitis. Balanitis on boys still in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis. The word balanitis is from the Greek βάλανοςbalanos, literally meaning 'acorn', used because of the similarity in shape to the glans penis.
The control of ventilation is the physiological mechanisms involved in the control of breathing, which is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Ventilation facilitates respiration. Respiration refers to the utilization of oxygen and balancing of carbon dioxide by the body as a whole, or by individual cells in cellular respiration.

Sankey diagrams are a data visualisation technique or flow diagram that emphasizes flow/movement/change from one state to another or one time to another, in which the width of the arrows is proportional to the flow rate of the depicted extensive property.
EcoHomes was an environmental rating scheme for homes in the United Kingdom. It was the domestic version of the Building Research Establishment's Environmental Assessment Method BREEAM, which could also be applied to a variety of non-residential buildings. It was replaced by the Code for Sustainable Homes in April 2008.
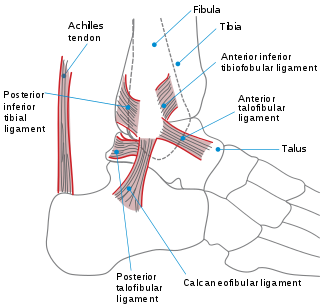
A sprained ankle is an injury where sprain occurs on one or more ligaments of the ankle. It is the most commonly occurring injury in sports, mainly in ball sports such as basketball, volleyball, football, and tennis.

Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are a class of pharmaceuticals that suppress the activity of carbonic anhydrase. Their clinical use has been established as anti-glaucoma agents, diuretics, antiepileptics, in the management of mountain sickness, gastric and duodenal ulcers, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, neurological disorders, or osteoporosis.
The Undersea and Hyperbaric Medical Society (UHMS) is an organization based in the US which supports research on matters of hyperbaric medicine and physiology, and provides a certificate of added qualification for physicians with an unrestricted license to practice medicine and for limited licensed practitioners, at the completion of the Program for Advanced Training in Hyperbaric Medicine. They support an extensive library and are a primary source of information for diving and hyperbaric medicine physiology worldwide.

Soil carbon is the solid carbon stored in global soils. This includes both soil organic matter and inorganic carbon as carbonate minerals. It is vital to the soil capacity in our ecosystem. Soil carbon is a carbon sink in regard to the global carbon cycle, playing a role in biogeochemistry, climate change mitigation, and constructing global climate models. Natural variation such as organisms and time has affected the management of carbon in the soils. The major influence has been that of human activities which has caused a massive loss of soil organic carbon. An example of human activity includes fire which destroys the top layer of the soil and the soil therefore get exposed to excessive oxidation.
Carbonic anhydrase 14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA14 gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 5B, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA5B gene.

Carbonic anhydrase 7 (CA7) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CA7 gene.
Blood gas tension refers to the partial pressure of gases in blood. There are several significant purposes for measuring gas tension. The most common gas tensions measured are oxygen tension (PxO2), carbon dioxide tension (PxCO2) and carbon monoxide tension (PxCO). The subscript x in each symbol represents the source of the gas being measured: "a" meaning arterial, "A" being alveolar, "v" being venous, and "c" being capillary. Blood gas tests (such as arterial blood gas tests) measure these partial pressures.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.

Carbon farming is a name for a variety of agricultural methods aimed at sequestering atmospheric carbon into the soil and in crop roots, wood and leaves. The aim of carbon farming is to increase the rate at which carbon is sequestered into soil and plant material with the goal of creating a net loss of carbon from the atmosphere. Increasing a soil's organic matter content can aid plant growth, increase total carbon content, improve soil water retention capacity and reduce fertilizer use. Carbon farming is one component of climate-smart agriculture.

Carbonic anhydrase 5A, mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CA5A gene.

Kenneth Karl Mikael Möllersten is a Swedish researcher. He holds a PhD in chemical engineering and an MSc in mechanical engineering, both from the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH), Stockholm, Sweden. Möllersten is a consultant and researcher at IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute, was previously affiliated as a researcher with Mälardalen University and is currently affiliated with KTH.













