
The Pacific cod is a species of ray-finned fish in the family Gadidae. It is a bottom-dwelling fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean, mainly on the continental shelf and upper slopes, to depths of about 900 m (3,000 ft). It can grow to a length of a meter or so and is found in large schools. It is an important commercial food species and is also known as gray cod or grey cod, and grayfish or greyfish. Fishing for this species is regulated with quotas being allotted for hook and line fishing, pots, and bottom trawls. Fossils have been found in Canada near a Steller Sea lion fossil dating to the Pleistocene.

The snailfishes or sea snails are a family of marine ray-finned fishes. These fishes make up the Liparidae, which is classified within the order Scorpaeniformes.

The sea toads and coffinfishes are a family of deep-sea anglerfishes known as the Chaunacidae.
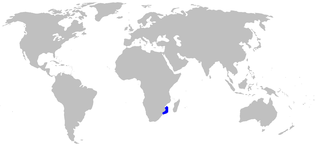
The balloon shark is a species of catshark, and part of the family Scyliorhinidae, endemic to the southwestern Indian Ocean off South Africa and Mozambique. Benthic in nature, it is found over sandy and muddy flats at depths of 40–600 m (130–1,970 ft). This thick-bodied species has a broad, flattened head and a short tail; its distinguishing traits include narrow, lobe-like skin flaps in front of the nostrils, and a dorsal color pattern of faint darker saddles on a light grayish background.

The viper dogfish or viper shark is a rare species of dogfish shark in the family Etmopteridae, and the only extant member of its genus. It has been found in the Pacific Ocean off southern Japan, the Bonin Islands, Pacific Ocean off northern Taitung County and the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands. This species inhabits upper continental slopes and seamounts. It may migrate vertically, shifting between bottom waters 270–360 m (890–1,180 ft) deep during the day and upper waters less than 150 m (490 ft) deep at night. A slender, black shark reaching 54 cm (21 in) in length, the viper dogfish can be recognized by its narrow, triangular jaws and well-spaced, fang-like teeth. It also has two spined dorsal fins, dermal denticles with faceted crowns, and numerous light-emitting photophores concentrated on its ventral surface.

The quagga catshark is a species of catshark, belonging to the family Scyliorhinidae. A small, slim-bodied shark reaching 37 cm (15 in) in length, it has a distinctive color pattern of narrow, dark brown vertical bars, which resemble those of the quagga. Its head is short and flattened, with a pointed snout tip that is not upturned.
Bathyraja maculata, the white-blotched skate, is a species of skate from the western North Pacific Ocean. An adult is approximately 1 meter in length, and is found at depths of up to 1 kilometer. Unlike any other known member of the genus Bathyraja, the white-blotched skate has white blotches on a grey to brown dorsal surface, while the ventral side is lighter in color with darker blotches. Dorsal side is rough with spines, while the ventral side is smooth.

Phyllorhinichthys is a genus of dreamers. Like other oneirodids, they are small, bathypelagic fish with bioluminescent lures. Phyllorhinichthys is unique amongst the deep-sea anglerfish in having a pair of fleshy, leaf-like structures on its snout.
Notoliparis antonbruuni is a species of snailfish. It was described in 2005 from a single poorly preserved specimen collected in 1966 from the hadal zone off Callao, Peru.

Careproctus is a genus of snailfishes found in benthic and benthopelagic habitats in the Atlantic, Pacific, Arctic and Southern Oceans. Whether they truly are absent from the Indian Ocean is unknown and might be an artifact of limited sampling. They range from shallow coastal seas in the far north of their range to the abyssal zone, at depths of 6 to 5,459 m (20–17,910 ft). In the Northern Hemisphere they mostly live shallower than Paraliparis, but this pattern is reversed in the Southern Hemisphere. Although almost entirely restricted to very cold waters, a single species, C. hyaleius, lives at hydrothermal vents.
Careproctus pallidus is a species of snailfish found around Tierra del Fuego in the far south of South America.

Liparis fabricii, commonly known as the gelatinous seasnail or gelatinous snailfish, is a benthopelagic species of snailfish from the Arctic Ocean. It has a tadpole-like body with a maximum length of about 20 cm (7.9 in). It is brown to black in coloration with a distinctive dark peritoneum. It preys on small crustaceans and marine worms. It is not commercially important, though it is a valuable food source for predatory fish and seabirds in the Arctic region.
Bathyraja panthera, the leopard skate, is a species of cartilaginous fish in the family Arhynchobatidae. It was first described as a new species in 2011, having been discovered in the Aleutian Islands at depths between 50 and 258 m. It is a moderately large species with a short snout and wide mouth. The dorsal surface is pale greenish-brown, with speckling, round black spots and yellow blotches, giving it its specific name panthera from its resemblance to a leopard skin. It is an egg-bearing species, the eggs being enclosed in egg capsules with horns at the corners.
Allocareproctus is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Liparidae, the snailfishes. These fish are found in the northern Pacific Ocean.
The hardhead snailfish is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Liparidae, the snailfishes. This species is found in the northern Pacific Ocean where a single specimen was collected in June 2000 from near the Aleutian Islands at a depth of 285 m (935 ft). The length of the fish was 3.3 cm (1.3 in) SL. This species is the only member of the monospecific genus Lopholiparis. The specific name honors the collector of the holotype, William C. Flerx of the National Marine Fisheries Service.

The redbanded rockfish, also known as the bandit, barber pole, flag rockfish, Spanish flag, Hollywood, convict, and canary, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the northern Pacific Ocean.

Sebastes reedi the yellowmouth rockfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Sebastinae, the rockfishes, part of the family Scorpaenidae. It is found in the Eastern Pacific.

Careproctus ovigerus, commonly known as the abyssal snailfish, is a species of snailfish found in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. It is found at depths of 1,920–2,910 m (6,300–9,550 ft) off northern British Columbia and off Washington state.
Careproctus spiraki, or pimpled snailfish, is a small, marine, bottom-dwelling snailfish. The type specimen was collected in a bottom trawl 457 meters deep in Seguam Pass in the Aleutian Islands. The species was first described to science by J. W. Orr in 2021.

James Wilder Orr is an American fisheries biologist, ichthyologist, and systematist best known for his studies of skates, rockfishes, snailfishes, and flatfishes. He has described 32 new species and two new genera of fishes, and is the author or co-author of more than 130 scientific and popular articles, including three books. His work has focused primarily on the phylogenetic relationships, zoogeography, reproductive biology, and behavior of marine teleosts, particularly deep-water benthic taxa. He has spent most of his career at the Alaska Fisheries Science Center, National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), in Seattle, as a Research Fisheries Biologist. At the same time, he has served as an Affiliate Professor at the School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences, and Affiliate Curator of Fishes at the Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture, University of Washington, Seattle. For his lifetime of service, Orr was presented with a National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Distinguished Career Award in 2022.













