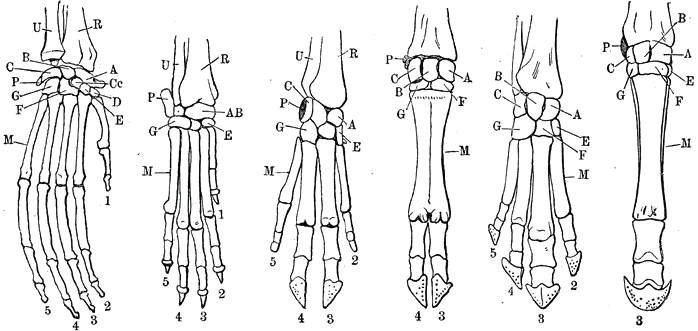The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

The carpal bones are the eight small bones that make up the wrist (carpus) that connects the hand to the forearm. The terms "carpus" and "carpal" are derived from the Latin carpus and the Greek καρπός (karpós), meaning "wrist". In human anatomy, the main role of the carpal bones is to articulate with the radial and ulnar heads to form a highly mobile condyloid joint, to provide attachments for thenar and hypothenar muscles, and to form part of the rigid carpal tunnel which allows the median nerve and tendons of the anterior forearm muscles to be transmitted to the hand and fingers.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as (1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and; (3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The trapezoid bone is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.

In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, also known as the "palm bones", are the appendicular bones that form the intermediate part of the hand between the phalanges (fingers) and the carpal bones, which articulate with the forearm. The metacarpal bones are homologous to the metatarsal bones in the foot.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew nut.

The capitate bone is a bone in the human wrist found in the center of the carpal bone region, located at the distal end of the radius and ulna bones. It articulates with the third metacarpal bone and forms the third carpometacarpal joint. The capitate bone is the largest of the carpal bones in the human hand. It presents, above, a rounded portion or head, which is received into the concavity formed by the scaphoid and lunate bones; a constricted portion or neck; and below this, the body. The bone is also found in many other mammals, and is homologous with the "third distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.
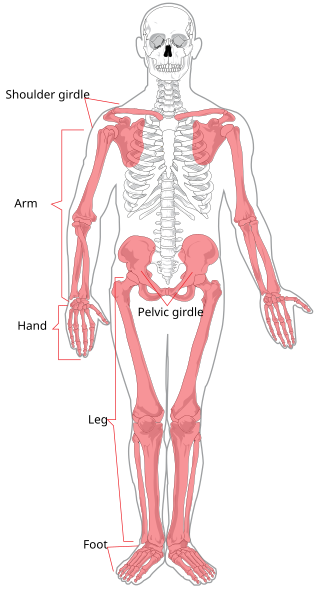
The appendicular skeleton is the portion of the vertebrate endoskeleton consisting of the bones, cartilages and ligaments that support the paired appendages. In most terrestrial vertebrates, the appendicular skeleton and the associated skeletal muscles are the predominant locomotive structures.

The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.

The upper limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, lifting and manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg.
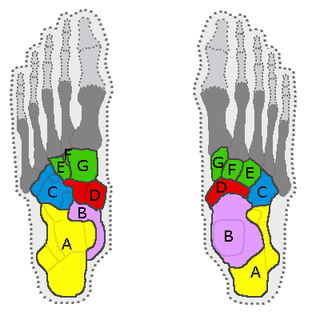
In the human body, the tarsus is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot and hindfoot.

The talus, talus bone, astragalus, or ankle bone is one of the group of foot bones known as the tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.

The intercarpal joints can be subdivided into three sets of joints : Those of the proximal row of carpal bones, those of the distal row of carpal bones, and those of the two rows with each other.

The midcarpal joint is formed by the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones in the proximal row, and the trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate bones in the distal row. The distal pole of the scaphoid articulates with two trapezial bones as a gliding type of joint. The proximal end of the scaphoid combines with the lunate and triquetrum to form a deep concavity that articulates with the convexity of the combined capitate and hamate in a form of diarthrodial, almost condyloid joint.
A limb is a jointed, muscled appendage of a tetrapod vertebrate animal used for weight-bearing, terrestrial locomotion and physical interaction with other objects. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods, who use their limbs for walking, running and jumping, swimming, climbing, grasping, touching and striking.

A hand is a prehensile, multi-fingered appendage located at the end of the forearm or forelimb of primates such as humans, chimpanzees, monkeys, and lemurs. A few other vertebrates such as the koala are often described as having "hands" instead of paws on their front limbs. The raccoon is usually described as having "hands" though opposable thumbs are lacking.

An accessory bone or supernumerary bone is a bone that is not normally present in the body, but can be found as a variant in a significant number of people. It poses a risk of being misdiagnosed as bone fractures on radiography.

Hand-foot-genital syndrome (HFGS) is characterized by limb malformations and urogenital defects. Mild bilateral shortening of the thumbs and great toes, caused primarily by shortening of the distal phalanx and/or the first metacarpal or metatarsal, is the most common limb malformation and results in impaired dexterity or apposition of the thumbs. Urogenital abnormalities include abnormalities of the ureters and urethra and various degrees of incomplete Müllerian fusion in females and hypospadias of variable severity with or without chordee in males. Vesicoureteral reflux, recurrent urinary tract infections, and chronic pyelonephritis are common; fertility is normal.

The muscles of the thumb are nine skeletal muscles located in the hand and forearm. The muscles allow for flexion, extension, adduction, abduction and opposition of the thumb. The muscles acting on the thumb can be divided into two groups: The extrinsic hand muscles, with their muscle bellies located in the forearm, and the intrinsic hand muscles, with their muscles bellies located in the hand proper.