
A castellated beam is a beam style where an I-beam is subjected to a longitudinal cut along its web following a specific pattern.
The purpose is to divide and reassemble the beam with a deeper web by taking advantage of the cutting pattern. [1]

A castellated beam is a beam style where an I-beam is subjected to a longitudinal cut along its web following a specific pattern.
The purpose is to divide and reassemble the beam with a deeper web by taking advantage of the cutting pattern. [1]

Reinforced concrete (RC), also called reinforced cement concrete (RCC) and ferroconcrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ductility. The reinforcement is usually, though not necessarily, steel bars (rebar) and is usually embedded passively in the concrete before the concrete sets. However, post-tensioning is also employed as a technique to reinforce the concrete. In terms of volume used annually, it is one of the most common engineering materials. In corrosion engineering terms, when designed correctly, the alkalinity of the concrete protects the steel rebar from corrosion.

Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. While typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser most commonly through optics. The laser optics and CNC is used to direct the laser beam to the material. A commercial laser for cutting materials uses a motion control system to follow a CNC or G-code of the pattern to be cut onto the material. The focused laser beam is directed at the material, which then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish.

Glued laminated timber, commonly referred to as glulam, is a type of structural engineered wood product constituted by layers of dimensional lumber bonded together with durable, moisture-resistant structural adhesives so that all of the grain runs parallel to the longitudinal axis. In North America, the material providing the laminations is termed laminating stock or lamstock.

A plate girder bridge is a bridge supported by two or more plate girders.

Falsework consists of temporary structures used in construction to support a permanent structure until its construction is sufficiently advanced to support itself. For arches, this is specifically called centering. Falsework includes temporary support structures for formwork used to mold concrete in the construction of buildings, bridges, and elevated roadways.

An I-beam, also known as H-beam, w-beam, universal beam (UB), rolled steel joist (RSJ), or double-T, is a beam with an I or H-shaped cross-section. The horizontal elements of the I are flanges, and the vertical element is the "web". I-beams are usually made of structural steel and are used in construction and civil engineering.

Steel frame is a building technique with a "skeleton frame" of vertical steel columns and horizontal I-beams, constructed in a rectangular grid to support the floors, roof and walls of a building which are all attached to the frame. The development of this technique made the construction of the skyscraper possible.

A girder is a support beam used in construction. It is the main horizontal support of a structure which supports smaller beams. Girders often have an I-beam cross section composed of two load-bearing flanges separated by a stabilizing web, but may also have a box shape, Z shape, or other forms. Girders are commonly used to build bridges.

Structural steel is a category of steel used for making construction materials in a variety of shapes. Many structural steel shapes take the form of an elongated beam having a profile of a specific cross section. Structural steel shapes, sizes, chemical composition, mechanical properties such as strengths, storage practices, etc., are regulated by standards in most industrialized countries.

The M5 is an expressway in the City of Cape Town Metropolitan Municipality, South Africa. It connects Milnerton on the Western Seaboard in the north to Muizenberg in the south, and crosses both the N1 and the N2. For part of its length, from the N1 interchange to Plumstead, it is a limited-access freeway (motorway). From Mowbray to Muizenberg, it is parallel to the M4 Main Road.

A girder bridge is a bridge that uses girders as the means of supporting its deck. The two most common types of modern steel girder bridges are plate and box.
The staggered truss system is a type of structural steel framing used in high-rise buildings. The system consists of a series of story-high trusses spanning the total width between two rows of exterior columns and arranged in a staggered pattern on adjacent column lines. William LeMessurier, the founder Cambridge, Massachusetts engineering firm LeMessurier Consultants has been credited in developing this award winning system as part of his research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
The Micromechanical Flying Insect (MFI) is a miniature UAV composed of a metal body, two wings, and a control system. Launched in 1998, it is currently being researched at University of California, Berkeley. The MFI is among a group of UAVs that vary in size and function. The MFI is proving to be a practical approach for specific situations. The US Office of Naval Research and Defense Advanced Research Project Agency are funding the project. The Pentagon hopes to use the robots as covert "flies on the wall" in military operations. Other prospective uses include space exploration and search and rescue.
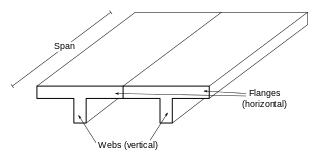
A T-beam, used in construction, is a load-bearing structure of reinforced concrete, wood or metal, with a T-shaped cross section. The top of the T-shaped cross section serves as a flange or compression member in resisting compressive stresses. The web of the beam below the compression flange serves to resist shear stress. When used for highway bridges the beam incorporates reinforcing bars in the bottom of the beam to resist the tensile stresses which occur during bending.
The structural channel, also known as a C-channel or Parallel Flange Channel (PFC), is a type of beam, used primarily in building construction and civil engineering. Its cross section consists of a wide "web", usually but not always oriented vertically, and two "flanges" at the top and bottom of the web, only sticking out on one side of the web. It is distinguished from I-beam or H-beam or W-beam type steel cross sections in that those have flanges on both sides of the web.
This glossary of structural engineering terms pertains specifically to structural engineering and its sub-disciplines. Please see glossary of engineering for a broad overview of the major concepts of engineering.

The Leavers machine is a lacemaking machine that John Levers adapted from Heathcoat's Old Loughborough machine. It was made in Nottingham in 1813. The name of the machine was the Leavers machine. The original machine made net but it was discovered that the Jacquard apparatus could be adapted to it. From 1841 lace complete with pattern, net and outline could be made on the Leavers machine.

The lace curtain machine is a lace machine invented by John Livesey in Nottingham in 1846. It was an adaptation of John Heathcoat's bobbinet machine. It made the miles of curtaining which screened Victorian and later windows.
Cellular beam is a further development of the traditional castellated beam. The advantage of the steel beam castellation process is that it increases strength without adding weight, making both versions an inexpensive solution to achieve maximum structural load capacity in building construction.