
ASCII art is a graphic design technique that uses computers for presentation and consists of pictures pieced together from the 95 printable characters defined by the ASCII Standard from 1963 and ASCII compliant character sets with proprietary extended characters. The term is also loosely used to refer to text-based visual art in general. ASCII art can be created with any text editor, and is often used with free-form languages. Most examples of ASCII art require a fixed-width font such as Courier for presentation.
The keyboard for IBM PC-compatible computers is standardized. However, during the more than 30 years of PC architecture being frequently updated, many keyboard layout variations have been developed.

Roguelike is a style of role-playing game traditionally characterized by a dungeon crawl through procedurally generated levels, turn-based gameplay, grid-based movement, and permanent death of the player character. Most roguelikes are based on a high fantasy narrative, reflecting their influence from tabletop role-playing games such as Dungeons & Dragons.

Rogue is a dungeon crawling video game by Michael Toy and Glenn Wichman with later contributions by Ken Arnold. Rogue was originally developed around 1980 for Unix-based minicomputer systems as a freely distributed executable. It was later included in the Berkeley Software Distribution 4.2 operating system (4.2BSD). Commercial ports of the game for a range of personal computers were made by Toy, Wichman, and Jon Lane under the company A.I. Design and financially supported by the Epyx software publishers. Additional ports to modern systems have been made since by other parties using the game's now-open source code.

Pool of Radiance is a role-playing video game developed and published by Strategic Simulations, Inc (SSI) in 1988. It was the first adaptation of TSR's Advanced Dungeons & Dragons (AD&D) fantasy role-playing game for home computers, becoming the first episode in a four-part series of D&D computer adventure games. The other games in the "Gold Box" series used the game engine pioneered in Pool of Radiance, as did later D&D titles such as the Neverwinter Nights online game. Pool of Radiance takes place in the Forgotten Realms fantasy setting, with the action centered in and around the port city of Phlan.

The Monochrome Display Adapter is IBM's standard video display card and computer display standard for the IBM PC introduced in 1981. The MDA does not have any pixel-addressable graphics modes, only a single monochrome text mode which can display 80 columns by 25 lines of high-resolution text characters or symbols useful for drawing forms.

Code page 437 is the character set of the original IBM PC. It is also known as CP437, OEM-US, OEM 437, PC-8, or DOS Latin US. The set includes all printable ASCII characters as well as some accented letters (diacritics), Greek letters, icons, and line-drawing symbols. It is sometimes referred to as the "OEM font" or "high ASCII", or as "extended ASCII".

Eamon, sometimes known as The Wonderful World of Eamon, is a game creation system and a role-playing adventure game series created by Donald Brown and released for the Apple II in 1980. The game is a text adventure similar to other early titles like Adventure (1976) or Zork (1980) and to later text-based multi-user dungeons (MUDs), though with many role-playing elements not available in other interactive fiction. Eamon software is non-commercial and is freely available in the public domain.

Odyssey: The Compleat Apventure was a video game written by Robert Clardy and released by Synergistic Software in 1980. It was created for the Apple II platform and is considered one of the first microcomputer-based role-playing video games. The title was intentionally misspelled; Apventure is a reference to the Apple computer while "Compleat" is simply an Archaic spelling of the word "complete" meant to match the feel and setting of the game.
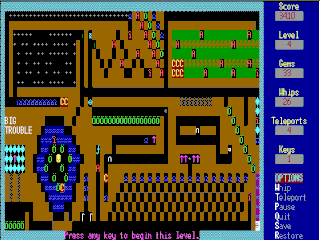
Kroz is a series of Roguelike video games created by Scott Miller for IBM PC compatibles. The first episode in the series, Kingdom of Kroz, was released in 1987 as Apogee Software's first game. It was also published on Big Blue Disk #20. Kroz introduced the scheme of the first episode being free and charging money for additional episodes, a technique which defined the business model for Apogee and was adopted by other MS-DOS shareware publishers.

Dungeon Hack is a 1993 role-playing video game developed by DreamForge Intertainment and published by Strategic Simulations for DOS and NEC PC-9801.

King's Quest: Quest for the Crown is an adventure game developed by Sierra On-Line and published originally for the IBM PCjr in 1984 and later for several other systems between 1984 and 1989. The game was originally titled King's Quest; the subtitle was added to the games box art in the 1987 re-release, but did not appear in the game.
Several 8-bit character sets (encodings) were designed for binary representation of common Western European languages, which use the Latin alphabet, a few additional letters and ones with precomposed diacritics, some punctuation, and various symbols. These character sets also happen to support many other languages such as Malay, Swahili, and Classical Latin.
A text game or text-based game is an electronic game that uses a text-based user interface, that is, the user interface employs a set of encodable characters, such as ASCII, instead of bitmap or vector graphics.

Twin Kingdom Valley is a text adventure game with animated pictures for the BBC Micro, Acorn Electron, Commodore 64, Commodore 16, and ZX Spectrum. It was released in 1983 by Bug-Byte.

Zyll is a text-based role-playing video game published by IBM for the IBM PCjr in 1984. It was written by Marshal Linder and Scott Edwards, two IBM employees, and marketed as an adventure game.

Adventureland is a text adventure video game for microcomputers, released by Scott Adams in 1978. The game has no plot but simply involves searching for thirteen lost artifacts in a fantasy setting. Its success led Adams to form Adventure International, which went on to publish thirteen similar games in the Adventure series, each in different settings.

The Prisoner is an adventure game for the Apple II published by Edu-Ware in 1980. It is loosely based on the 1960s television series The Prisoner and incorporates that show's themes about the loss of individuality in a technological, controlling society. The player's role is that of an intelligence agent who has resigned from his job for reasons known only to himself, and who has been abducted to an isolated island community that seems designed to be his own personal prison. The island's authorities will use any means—including coercion, disorientation, deception, and frustration—to learn why their prisoner has resigned, and every character, location, and apparent escape route seem to be part of a grand scheme to trick the player into revealing a code number representing the prisoner's reason for resigning. The game occasionally breaks the fourth wall by acknowledging that a game is being played.

Ghost of Lion Castle is a 1984 adventure module for the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy roleplaying game. Its module code is BSOLO, and it was written by Merle M. Rasmussen with cover art by Bob Maurus.

Game-Maker is an MS-DOS-based suite of game design tools, accompanied by demonstration games, produced between 1991 and 1995 by the Amherst, New Hampshire based Recreational Software Designs and sold through direct mail in the US by KD Software. Game-Maker also was sold under various names by licensed distributors in the UK, Korea, and other territories including Captain GameMaker and Create Your Own Games With GameMaker!. Game-Maker is notable as one of the first complete game design packages for DOS-based PCs, for its fully mouse-driven graphical interface, and for its early support for VGA graphics, Sound Blaster sound, and full-screen four-way scrolling.



















