
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration; smaller varieties may be mechanically similar to some automobiles. Commercial trucks can be very large and powerful and may be configured to be mounted with specialized equipment, such as in the case of refuse trucks, fire trucks, concrete mixers, and suction excavators. In American English, a commercial vehicle without a trailer or other articulation is formally a "straight truck" while one designed specifically to pull a trailer is not a truck but a "tractor".

A tire or tyre is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively.

A garbage truck is a truck specially designed to collect municipal solid waste and transport it to a solid waste treatment facility, such as a landfill or transfer station. Other common names for this type of truck include trash truck in the United States, and refuse truck, dustcart, rubbish truck, junk truck, bin wagon, dustbin lorry, bin lorry or bin van elsewhere. Technical names include waste collection vehicle and refuse collection vehicle (RCV). These trucks are a common sight in most urban areas.
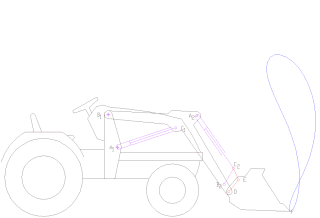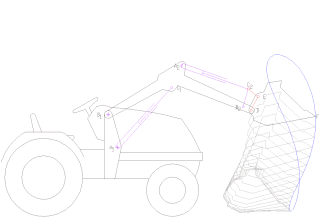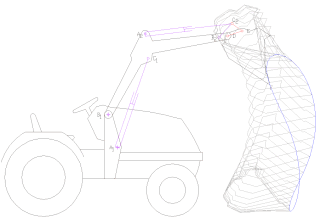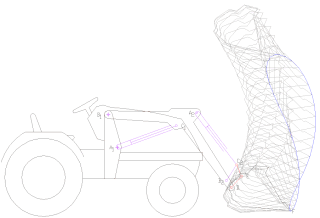
A loader is a heavy equipment machine used in construction to move aside or load materials such as asphalt, demolition debris, dirt, snow, feed, gravel, logs, raw minerals, recycled material, rock, sand, woodchips, etc. into or onto another type of machinery. There are many types of loader, which, depending on design and application, are called by various names, including bucket loader, front loader, front-end loader, payloader, scoop, shovel, skip loader, wheel loader, or skid-steer.

Heavy equipment or heavy machinery refers to heavy-duty vehicles, specially designed for executing construction tasks, most frequently ones involving earthwork operations or other large construction tasks. Heavy equipment usually comprises five equipment systems: implementation, traction, structure, power train, control and information.

A dump truck, known also as a dumper truck or tipper truck, is used for taking dumps for construction as well as coal. A typical dump truck is equipped with an open-box bed, which is hinged at the rear and equipped with hydraulic rams to lift the front, allowing the material in the bed to be deposited ("dumped") on the ground behind the truck at the site of delivery. In the UK, Australia and India the term applies to off-road construction plant only, and the road vehicle is known as a tipper lorry, tip-truck, tip-trailer, tipper truck, or tipper.

A dumper is a vehicle designed for carrying bulk material, often on building sites. Dumpers are distinguished from dump trucks by configuration: a dumper is usually an open 4-wheeled vehicle with the load skip in front of the driver, while a dump truck has its cab in front of the load. The skip can tip to dump the load; this is where the name "dumper" comes from. They are normally diesel powered. A towing eye is fitted for secondary use as a site tractor. Dumpers with rubber tracks are used in special circumstances and provide a more even distribution of weight compared to tires. Continuous tracks allow the operator to carry heavier payload on slick, snowy, or muddy surfaces, and are popular in some countries.

Snow removal or snow clearing is the job of removing snow after a snowfall to make travel easier and safer. This is done by both individual households and by governments and institutions.

In civil engineering, a wheel tractor-scraper is a piece of heavy equipment used for earthmoving. The rear part of the scraper has a vertically moveable hopper with a sharp horizontal front edge which can be raised or lowered. The front edge cuts into the soil, like a carpenter's plane cutting wood, and fills the hopper. When the hopper is full it is raised, closed, and the scraper can transport its load to the fill area where it is dumped. With a type called an 'elevating scraper' a conveyor belt moves material from the cutting edge into the hopper.

The Caterpillar 797 is a series of off-highway, ultra class, two-axle, mechanical powertrain haul trucks developed and manufactured in the United States by Caterpillar Inc. specifically for high-production mining and heavy-duty construction applications worldwide. In production since 1998, the 797 series represents Caterpillar’s largest, highest capacity haul trucks. The current, third-generation model, the 797F, offers one of the largest haul truck payload capacities in the world, up to 400 short tons (363 t) and has the highest payload capacity among mechanical drive haul trucks.

A semi-trailer is a trailer without a front axle. In the United States, the term is also used to refer to the combination of a truck and a semi-trailer, a tractor-trailer.

The Euclid Company of Ohio was a company specialized in heavy equipment for earthmoving, namely dump trucks and wheel tractor-scrapers, that operated from the United States of America from the 1920s to the 1950s, then it was purchased and converted into a section of General Motors and later on by Hitachi Construction Machinery.
Hydraulic hooklift hoists are mounted on heavy duty trucks to enable hauliers to change out flatbeds, dumpster bodies, and similar containers. Primarily used in conjunction with tilt frame bodies and specialised containers, generally designed for the transportation of materials in the waste, recycling, scrap and demolition industries.

A flatbed truck is a type of truck which can be either articulated or rigid. As the name suggests, its bodywork is just an entirely flat, level 'bed' with no sides or roof. This allows for quick and easy loading of goods, and consequently they are used to transport heavy loads that are not delicate or vulnerable to rain, and also for abnormal loads that require more space than is available on a closed body.

A grapple truck is a truck that has a grapple loader mounted to its frame which is used for loading and sometimes hauling bulky waste. A grapple loader is defined by ANSI Z245.1 as:
“a hydro-mechanical device able to rotate on an axis with a grapple or bucket attached at the end of the boom, which is intended for the collection of waste that due to size and/or weight is impractical to containerize.”

An articulated hauler, articulated dump truck (ADT), or sometimes a dump hauler, is a very large heavy duty type of dump truck used to transport loads over rough terrain, and occasionally on public roads. The vehicle usually has all-wheel drive and consists of two basic units: the front section, generally called the tractor, and the rear section that contains the dump body, called the hauler or trailer section. Steering is made by pivoting the front in relation to the back by hydraulic rams. This way, all wheels follow the same path, making it an excellent off-road vehicle.

A live bottom trailer is a semi-trailer used for hauling loose material such as asphalt, grain, potatoes, sand and gravel. A live bottom trailer is the alternative to a dump truck or an end dump trailer. The typical live bottom trailer has a conveyor belt on the bottom of the trailer tub that pushes the material out of the back of the trailer at a controlled pace. Unlike the conventional dump truck, the tub does not have to be raised to deposit the materials.

In North America, a roll-off is a usually open top dumpster characterized by a rectangular footprint, utilizing wheels to facilitate rolling the dumpster in place. The container is designed to be transported by special roll-off trucks. Roll-offs are commonly used to contain loads of construction and demolition waste or other waste types. While most roll-off containers have a swinging door on the end for easier disposal of waste, some roll-off containers are not open top and are used with commercial or industrial trash compactors.

Rear-Eject Haul Truck Bodies are an alternative haul truck body style developed for quarry, road-building, steel mill, landfill and underground mining applications. Instead of lifting the bed vertically, the hydraulic cylinder pushes a ram-face horizontally through the body to eject the hauled load.



















