The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is one of the 27 institutes and centers that make up the National Institutes of Health (NIH), an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). NIAID's mission is to conduct basic and applied research to better understand, treat, and prevent infectious, immunologic, and allergic diseases.
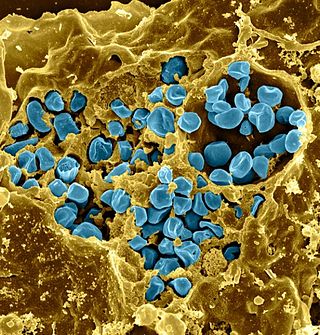
Francisella tularensis is a pathogenic species of Gram-negative coccobacillus, an aerobic bacterium. It is nonspore-forming, nonmotile, and the causative agent of tularemia, the pneumonic form of which is often lethal without treatment. It is a fastidious, facultative intracellular bacterium, which requires cysteine for growth. Due to its low infectious dose, ease of spread by aerosol, and high virulence, F. tularensis is classified as a Tier 1 Select Agent by the U.S. government, along with other potential agents of bioterrorism such as Yersinia pestis, Bacillus anthracis, and Ebola virus. When found in nature, Francisella tularensis can survive for several weeks at low temperatures in animal carcasses, soil, and water. In the laboratory, F. tularensis appears as small rods, and is grown best at 35–37 °C.
The Immune Epitope Database and Analysis Resource (IEDB) is a project hosted by scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology (LIAI), with support from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The focus is dissemination of immune epitope information to facilitate the generation of new research tools, diagnostic techniques, vaccines and therapeutics.
The Bioinformatics Resource Centers (BRCs) are a group of five Internet-based research centers established in 2004 and funded by NIAID The BRCs were formed in response to the threats posed by emerging and re-emerging pathogens, particularly Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Category A, B, and C pathogens, and their potential use in bioterrorism. The intention of NIAID in funding these bioinformatics centers is to assist researchers involved in the experimental characterization of such pathogens and the formation of drugs, vaccines, or diagnostic tools to combat them.

Rocky Mountain Laboratories (RML) is part of the NIH Intramural Research Program and is located in Hamilton, Montana. Operated by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, RML conducts research on maximum containment pathogens such as Ebola as well as research on prions and intracellular pathogens such as Coxiella burnetti and Francisella tularensis. RML operates one of the few Biosafety level 4 laboratories in the United States, as well as Biosafety level 3 and ABSL3/4 laboratories.

The Vaccine Research Center (VRC), is an intramural division of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). The mission of the VRC is to discover and develop both vaccines and antibody-based products that target infectious diseases.
Pathema was one of the eight bioinformatics resource centers funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a component of the National Institute of Health (NIH), which is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services.
Barton Ford Haynes is an American physician and immunologist internationally recognized for work in T-cell immunology, retrovirology, and HIV vaccine development. Haynes is a Frederic M. Hanes Professor of Medicine and Immunology at Duke University Medical Center. He is the director of the Duke Human Vaccine Institute and the Duke Center for HIV/AIDS Vaccine Immunology and Immunogen Discovery (CHAVI-ID), which was funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) in 2012. In addition, Haynes directs the B-cell Lineage Envelope Design Study, the Centralized Envelope Phase I Study, and the Role of IgA in HIV-1 Protection Study as part of the Collaboration for AIDS Vaccine Discovery (CAVD), which was funded by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation in 2006.

Kathryn C. Zoon is a U.S.-based immunologist, elected to the U.S. Institute of Medicine in 2002 for her research on human interferons. She is the former scientific director of the Division of Intramural Research at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Institutes of Health (NIH) in Bethesda, Maryland. From 1992 to 2002, Zoon was director of the FDA Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER).
In 1990, the Duke Human Vaccine Institute (DHVI), located in Durham, North Carolina, was formed to support interdisciplinary efforts across Duke University School of Medicine to develop vaccines and therapeutics for HIV and other emerging infections that threaten the health of people living in the United States and the world. Since 1990, DHVI investigators have been at the forefront in the battle against AIDS and specifically in the quest for an HIV vaccine.

Julie E. Ledgerwood is an American allergist and immunologist, who is the chief medical officer and serves as chief of the Clinical Trials Program at the Vaccine Research Center (VRC) of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health in Bethesda, Maryland. She is a Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine.

Sonja Marie Best is an Australian-American virologist. She is chief of the innate immunity and pathogenesis section at the Rocky Mountain Laboratories. Best researches interactions between pathogenic viruses and the host immune response using flavivirus as a model.

Andrea Marzi is a German-American virologist. She is chief of the immunobiology and molecular virology unit at the Rocky Mountain Laboratories. Marzi investigates the pathogenesis of filoviruses and vaccine development. She received the Loeffler-Frosch medal in recognition of her research.

Vanessa M. Hirsch is a Canadian-American veterinary pathologist and scientist. She is a senior investigator and chief of the nonhuman primate virology section at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Hirsch researches AIDS pathogenesis, the evolution and origins of primate lentiviruses, and HIV vaccine development.

Silvana Romina Goldszmid is an Argentine-American biologist researching tumor immunology. She is an NIH Stadtman Investigator at the National Cancer Institute.

Dr. Michael J. Lenardo, is the chief of the Molecular Development and Immune System Section and the founder and co-Director of the Clinical Genomics Program at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (NIAID), National Institutes of Health (NIH). Trained as a geneticist, molecular biologist, and immunologist, his research examines how cells of the immune system defend themselves against various pathogens, including viruses and bacteria. His research has investigated genetic abnormalities in the immune system, mechanisms of cell death, genetic diseases of immune homeostasis and autoimmunity, and development of novel diagnostics and therapeutics for diseases of the immune system. Lenardo's contributions to science and medicine have shown the possibilities of genomic research in developing precision medicine diagnoses and treatments for disease in humans. In 2006 he was appointed Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (O.B.E.) by Queen Elizabeth II. In 2019 he was inducted into the National Academies of Sciences and the National Academy of Medicine, considered among the highest honors awarded to a U.S scientist and medical researcher respectively.

John Ring La Montagne was a Mexican-American biomedical scientist who served as the deputy director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases from 1998 to 2004. He specialized in viral vaccines, HIV/AIDS research, and oversaw NIH's biodefense research after the September 11 attacks.

Hilary D. Marston is an American physician-scientist and global health policy advisor specializing in pandemic preparedness. She is the Chief Medical Officer of the Food and Drug Administration.

John R. Mascola is an American physician-scientist, immunologist and infectious disease specialist. He was the director of the Vaccine Research Center (VRC), part of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Institutes of Health (NIH). He also served as a principal advisor to Anthony Fauci, director of NIAID, on vaccines and biomedical research affairs.
Shabaana A. Khader is an Indian-American microbiologist who is the Theodore and Berta Endowed Professor of Molecular Microbiology at the Washington University in St. Louis. She is also Chair of the Department of Microbiology. In an effort to design new vaccines and therapeutic strategies, Khader studies host-pathogen interactions in infectious disease.













