Fortaleza is the state capital of Ceará, located in Northeastern Brazil. It is Brazil's 4th largest city, having surpassed Salvador in 2022 census with a population of slightly over 2.4 million, and the 12th largest city by gross domestic product. It forms the core of the Fortaleza metropolitan area, which is home to almost 4 million people.

Ceará is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic coast. It is the eighth-largest Brazilian State by population and the 17th by area. It is also one of the main tourist destinations in Brazil. The state capital is the city of Fortaleza, the country's fourth most populous city. The state has 4.3% of the Brazilian population and produces 2.1% of the Brazilian GDP.

Natal is the capital and largest city of the state of Rio Grande do Norte, located in northeastern Brazil. According to IBGE's 2022 estimate, the city had a total population of 751,300, making it the 24th largest city in the country. Natal is a major tourist destination and an exporting hub of crustaceans, carnauba wax and fruits, mostly melon, sugar apple, cashew and papaya. Natal is Brazil's closest city to Africa and Europe, its Greater Natal International Airport connects the city with many Brazilian destinations and also operates some international flights. The city was one of the host cities of the 2014 FIFA World Cup.

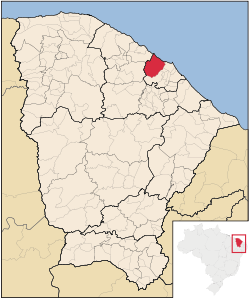
Acarape is a municipality in the north region of the state of Ceará, Brazil.

Crato is a city of 130,000 inhabitants on the banks of the river Granjeiro in the south of the state of Ceará, in the northeast of Brazil. It was founded on June 21, 1764 by the Capuchin friar Carlos Maria de Ferrara. Originally it was a small village in which the population were principally native Kariris, it gained official status as a city on October 17, 1817.
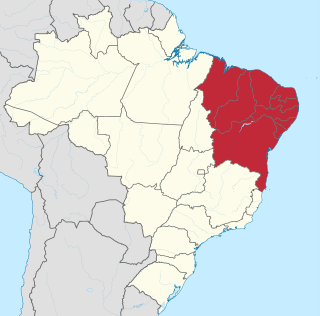
The Northeast Region of Brazil is one of the five official and political regions of the country according to the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. Of Brazil's twenty-six states, it comprises nine: Maranhão, Piauí, Ceará, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraíba, Pernambuco, Alagoas, Sergipe and Bahia, along with the Fernando de Noronha archipelago.

The Trans-Amazonian Highway was introduced on September 27, 1972. It is 4,000 km long, making it the third longest highway in Brazil. It runs through the Amazon forest and the Brazilian states of Paraíba, Ceará, Piauí, Maranhão, Tocantins, Pará and Amazonas, from the proximities of Saboeiro up until the town of Lábrea.
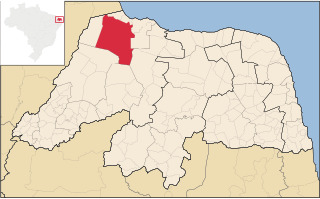
Mossoró is the second most populous city in the state of Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil, and also the largest municipality of that state. It is equidistant from Natal, the state capital of Rio Grande do Norte, and from Fortaleza, the capital of the state of Ceará. It is also in the heart of Brazil's salt production area. Situated in the Oeste Potiguar mesoregion, Mossoró is the country's largest land-based petroleum producer.

Canoa Quebrada, known as the pearl of the east coast of Ceará, Brazil, is an international tourist beach resort 164 km from Fortaleza, in the municipality of Aracati.

Pesqueira is a Brazilian municipality in the state of Pernambuco. It had an estimated population in 2020 according to the IBGE, of 67,735. Its area is 980.876 km2.

Guaramiranga is one of the smallest towns of the Northeastern state of Ceará in Brazil. It is located at an altitude of 865 m in the Serra de Baturité hills 110 km from the state capital of Fortaleza. Guaramiranga is known locally for its temperate climate and lush green scenery. The temperature in Guaramiranga varies between 15 and 23 degrees Celsius through the year.

Beberibe is a municipality in the state of Ceará in Brazil. Its estimated population in 2020 is 53,949.

The Metropolitan of Fortaleza, also known popularly as Metro of Fortaleza or Metrofor, is a system of metropolitan transport that operates in the Brazilian city of Fortaleza, operated by Companhia Cearense de Transportes Metropolitanos, company of social capital, captained by the Government of the State of Ceará, in Brazil, and has as current president Eduardo Hotz. Founded on May 2, 1997, the company is responsible for administration, construction and metro planning in the state of Ceará, being present in the systems of Sobral and Cariri, having its main activity in Fortaleza and its metropolitan region.

Aquiraz is the thirteenth largest city in the state of Ceará and is located on the nation's northeast coast. The municipality has a population of 80,935 with a population density of 150 inhabitants per square kilometer. Aquiraz is located 32 km (20 mi) from the state capital of Ceará, Fortaleza. It borders the municipalities of Maranguape, Caucaia, Pacatuba, Guaiuba, and Maracanau; the Atlantic Ocean makes up its northeast border. The Pacoti and Catu rivers cross Aquiraz and empty into the ocean.

Punta del Diablo is a village and seaside locality in Uruguay, Rocha Department, 298 kilometres (185 mi) east from the capital Montevideo. According to the 2011 census, its permanent population consisted of 823 inhabitants, mostly fishermen and artisans, while during high tourism season, the population swells to approximately 25,000, mostly with Argentinians, Brazilians and Europeans on holiday. As with the country it is located in, the primary language spoken in Punta del Diablo is Spanish. In 2008 it was named by the magazine "Lonely Planet" as one of the top 20 places to visit and invest.

Barbalha is a municipality in the state of Ceará in the Northeast region of Brazil. Barbalha covers 569.5 km2 (219.9 sq mi), and has a population of 61,228 with a population density of 100 inhabitants per square kilometer. It is located at the south of the state, 575 km (357 mi) from the state capital of Fortaleza. The eastern part of the Araripe-Apodi National Forest, established in 1946, is located in Barbalha. The city sits at the foot of the Chapada do Araripe, a large plateau on the border of Ceará and Pernambuco.
The Tapeba people are an indigenous people of Brazil, who formed from the remnant populations of tribes around the Village of Nossa Senhora dos Prazeres de Caucaia in Ceará, Brazil. They are native Portuguese-speakers and are also known as Tapebano and Perna-de-pau people.

The Tremembé or Teremembé people are an indigenous people in the states of Ceará and Maranhão in Brazil.

The BR-222 is a Brazilian federal highway that connects the cities of Fortaleza, in the state of Ceará, to Marabá, Pará. It has a total length of 1,819.8 km.

The history of Ceará began with the Portuguese colonization, characterized by the resistance of the natives and the difficulties the European had in adapting to the climatic conditions of the territory. Initially, a rural society was formed, based mainly on livestock and agriculture, which controlled almost every aspect of social life through its economic power and complex relations of parentage and patronage. The so-called "coronéis" kept many dependents on their properties who provided them with services or gave them part of their production in exchange for owning a plot of land, in a semi-feudal regime. The servitude of Africans, although of lesser importance, was practiced throughout the 17th and 18th centuries, especially in areas where agriculture flourished.