
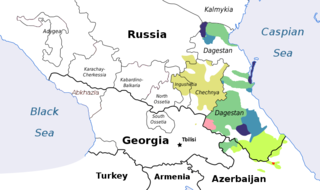
Chechnya, officially the Chechen Republic, is a republic of Russia. It is situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe, close to the Caspian Sea. The republic forms a part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia to its south; with the Russian republics of Dagestan, Ingushetia, and North Ossetia-Alania to its east, north, and west; and with Stavropol Krai to its northwest.
The Nakh languages are a group of languages within Northeast Caucasian family, spoken chiefly by the Chechens and Ingush in the North Caucasus.
The history of Chechnya may refer to the history of the Chechens, of their land Chechnya, or of the land of Ichkeria.

The Chechens, historically also known as Kisti and Durdzuks, are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group of the Nakh peoples native to the North Caucasus. They are the largest ethnic group in the region and refer to themselves as Nokhchiy. The vast majority of Chechens are Muslims and live in Chechnya, a republic of Russia.
Ingush, historically known as Durdzuks, Gligvi and Kists, are a Northeast Caucasian ethnic group mainly inhabiting Ingushetia in central Caucasus, but also inhabitanting Prigorodny District and town of Vladikavkaz of modern day North-Ossetia. The Ingush are predominantly Sunni Muslims and speak the Ingush language.
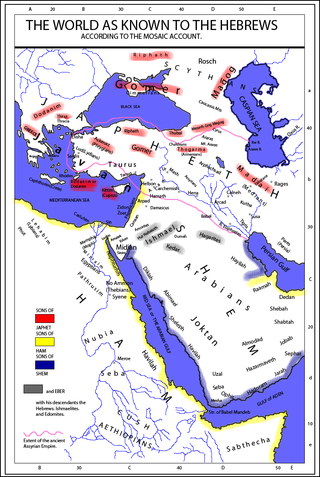
Togarmah is a figure in the "table of nations" in Genesis 10, the list of descendants of Noah that represents the peoples known to the ancient Hebrews. Togarmah is among the descendants of Japheth and is thought to represent some people located in Anatolia. Medieval sources claimed that Togarmah was the legendary ancestor of several peoples of the Caucasus.

Kartlos is the eponymous ancestor and legendary progenitor of the Georgians (Kartvelians) in Georgian mythology, more specifically of the nation of Kartli . Kartlos is introduced in the medieval Georgian Chronicles , presumably recorded from oral tradition by Leonti Mroveli in the 11th century.
Leonti Mroveli was the 11th-century Georgian chronicler, presumably an ecclesiastic. Mroveli is not his last name, but the adjective for the diocese of Ruisi, whose bishop he probably was. Hence, another modern English transliteration of his name is Leontius of Ruisi.

The Nakh peoples are a group of North Caucasian peoples identified by their use of the Nakh languages and other cultural similarities. These are chiefly the ethnic Chechen, Ingush and Bats peoples of the North Caucasus, including closely related minor or historical groups.
The Grozny riots of 1958 occurred between 23 and 27 August that year in Grozny. Although beginning as a small-scale event, it turned a major event in the history of the city, of Chechnya and of Russo-Chechen relations, starting a series of ethnic riots, to continue until 1965.

The deportation of the Chechens and Ingush, or Ardakhar Genocide, and also known as Operation Lentil, was the Soviet forced transfer of the whole of the Vainakh populations of the North Caucasus to Central Asia on 23 February 1944, during World War II. The expulsion was ordered by NKVD chief Lavrentiy Beria after approval by Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, as a part of a Soviet forced settlement program and population transfer that affected several million members of ethnic minorities in the Soviet Union between the 1930s and the 1950s.
The Vainakh peoples of the North Caucasus were Islamised comparatively late, during the early modern period, and Amjad Jaimoukha (2005) proposes to reconstruct some of the elements of their pre-Islamic religion and mythology, including traces of ancestor worship and funerary cults. The Nakh peoples, like many other peoples of the North Caucasus such as Circassians, practised tree worship, and believed that trees were the abodes of spirits. Vainakh peoples developed many rituals to serve particular kinds of trees. The pear tree held a special place in the faith of Vainakhs.

The Vainakh tower architecture, also called Nakh architecture, is a characteristic feature of ancient and medieval architecture of Chechnya and Ingushetia.
The Èrsh language was the language of the Èr or Èrs people, hypothetical Nakh-speaking people argued for by Amjad Jaimoukha in his book The Chechens: A Handbook.
During the 13th and 14th centuries, the Mongols launched two long, massive invasions of the territory of modern Chechnya and Ingushetia, which included the lands of Alania in the West, Simsir in the Northeast, and the Georgian-allied polity of Durdzuketia in the South. They caused massive destruction and human death for the Durdzuks, but also greatly shaped the people they became afterward. However, this came at great cost to them, and the states they had built were utterly destroyed, as were their previous organized systems. These invasions are among the most significant occurrences in Chechen and Ingush history, and have had long-ranging effects on Chechnya, Ingushetia and their peoples.
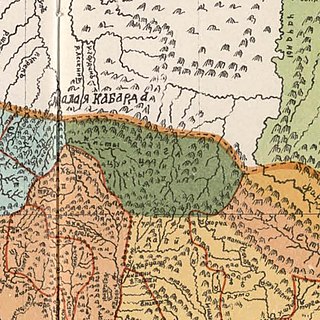
The Durdzuks, also known as Dzurdzuks, was a medieval exonym of the 9th-18th centuries used mainly in Georgian, Arabic, but also Armenian sources in reference to the Vainakh peoples.
Tusholi (Тушоли) is a goddess of Spring and fertility in Ingush and Chechen mythology and the daughter of the supreme god Dyala.
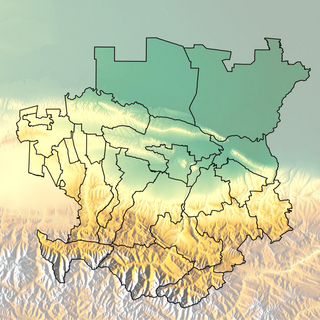
Vainakhia is a historical territory of Chechens and Ingush, is located in the Russian Caucasus. It includes the historic lands of Vainakh Chechnya, Ingushetia, the eastern part of North Ossetia and parts of north and west Dagestan. It has many historical sites. In 2004, rebels attempted to create a Vainakh republic by merging Chechnya and Ingushetia.
Revolt of Iberian nobles was the revolt of the Iberian nobles against Saurmag I that took place in Iberia during 3rd century BCE.

Ghalghai is the self-name (endonym) of the Ingush people.











