
The AAI RQ-2 Pioneer is an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that was used by the United States Navy, Marine Corps, and Army, and deployed at sea and on land from 1986 until 2007. Initially tested aboard USS Iowa, the RQ-2 Pioneer was placed aboard Iowa-class battleships to provide gunnery spotting, its mission evolving into reconnaissance and surveillance, primarily for amphibious forces.

Sri Lanka is a popular tourist destination. Tourism is a key industry that attracts international tourists yearly. Foreigners visit Sri Lanka to see nature, wildlife, historical monuments, and indigenous culture. In 2018, tourist arrivals peaked at 2.5 million, who spent a total of US$5.6 billion in the country. However, the COVID-19 pandemic caused tourist numbers to decrease by 92% in 2020. As of 2022, tourist numbers have not rebounded from the pre-crisis high. The government is attempting to attract foreign investment in the country's tourism industry, which began in earnest after the end of the Sri Lankan Civil War in 2009.

The Eastern Province is one of the nine provinces of Sri Lanka, the first level administrative division of the country. The provinces have existed since the 19th century but did not have any legal status until 1987 when the 13th Amendment to the Constitution of Sri Lanka established provincial councils. Between 1988 and 2006 the province was temporarily merged with the Northern Province to form the North Eastern Province. The capital of the province is Trincomalee. Kalmunai is the largest and most populous city of Eastern Province.

Hambantota is the main town in Hambantota District, Southern Province, Sri Lanka.

The Sri Lanka Navy (SLN) is the naval arm of the Sri Lanka Armed Forces and is classed as the country's most vital defence force due to its island geography. It is responsible for the maritime defence of the Sri Lankan nation and its interests. The role of the Sri Lanka Navy is to conduct operations at sea for the defence of the nation and its interests and conduct prompt and sustainable combat operations at sea in accordance with the national policies.

The Sri Lanka Air Force is the air arm and the youngest of the Sri Lanka Armed Forces. It was founded in 1951 as the Royal Ceylon Air Force (RCyAF) with the assistance of the Royal Air Force (RAF). The SLAF played a major role throughout the Sri Lankan Civil War. The SLAF operates more than 160 aircraft.

Japan–Sri Lanka relations refers to the bilateral relations between the Sri Lanka and Japan.

The Sri Lanka Armed Forces is the overall unified military of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka encompassing the Sri Lanka Army, the Sri Lanka Navy, and the Sri Lanka Air Force; they are governed by the Ministry of Defence (MoD). The three services have around 346,700 active personnel; conscription has never been imposed in Sri Lanka. As of 2021 it is the 14th largest military in the world, with 1.46% of the Sri Lankan population actively serving.

Johnston Xavier Fernando is a Sri Lankan politician, former Cabinet Minister, Chief Government Whip and a current member of the Parliament of Sri Lanka from the Kurunegala District. He belongs to the Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna. He is considered a leader of the Rajapaksa loyalist mobs that carried out violent attacks against peaceful protestors during the 9 May 'Black Monday' incident of the 2022 Sri Lankan Protests.
The Ministry of Finance, Economic Stabilization and National Policies is a cabinet ministry of the Government of Sri Lanka responsible for developing and executing the government's public finance policy, economic policy and long term fiscal planning. The Treasury is housed at the General Treasury Building in Fort.

Iran and Sri Lanka have had official diplomatic relations since 1961.
Kulappu Arachchige Don Dhammika Perera, commonly known as Dhammika Perera, is a Sri Lankan billionaire businessman and politician. A top corporate leader, he is one of the wealthiest people in Sri Lanka, controlling 23 listed companies on the Colombo Stock Exchange. Perera owns a controlling stake in the conglomerates Hayleys and Vallibel One, a company he founded. Through Hayleys, Perera controls Amaya Leisure, The Kingsbury and Singer while Royal Ceramics, LB Finance, and Lanka Tiles are controlled by Vallibel One. Perera has been closely linked to the former President Mahinda Rajapaksa, having served as chairman of the Board of Investment of Sri Lanka from 2007 to 2010 and Transport Secretary from 2011 to 2015. He was appointed a Member of Parliament in the National List in June 2022, succeeding Basil Rajapaksa from the Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna, briefly serving President Gotabaya Rajapaksa as his Minister of Investment Promotion from June to July 2022.

Sri Lanka Marine Corps was formed in 2016 under the assistance of the 11th Marine Expeditionary Unit of the United States Marine Corps in November 2016 and received further training from the Commando Regiment of Sri Lanka Army.
The Sri Lankan Armed Forces have established numerous academies and staff colleges across Sri Lanka for the purpose of training professional soldiers in military sciences, warfare command and strategy, and associated technologies.
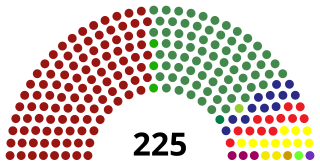
The 16th Parliament of Sri Lanka was the meeting of the Parliament of Sri Lanka with its membership determined by the results of the 2020 parliamentary election held on 5 August 2020. The parliament met for the first time on 20 August 2020 and was dissolved on 24 September 2024.

The Lihiniya MK 1 is an unmanned aerial vehicle under development by the Sri Lanka Air Force (SLAF) and the Centre for Research and Development (CRD) as an experimental platform to test technologies for its indigenous UAV program.
Lihiniya MK II is a medium range unmanned aerial vehicle developed by the Sri Lanka Air Force (SLAF) and the Centre for Research and Development (CRD) as a tactical UAV system for the national defence requirements.
Environmental Foundation Limited (EFL) is a public interest litigation and environmental conservation organisation in Sri Lanka. Established in 1981, EFL seeks to protect and conserve the natural environment through litigation, advocacy, awareness and youth-engagement.

UVision Air Ltd. is an Israeli defense technology company established in 2011. It engaged in the development, manufacturing and sales of advance missiles and loitering munition systems for land, air, and naval military forces. The company’s products, called HERO, are designed for targeted attacks against a variety of threats at various ranges.
Wanniarachchige Senali Koshila Fonseka (Sinhala: වන්නිආරච්චිගේ සෙනාලි කෝෂිලා ෆොන්සේකා, popularly known as Senali Fonseka, is an actress in Sri Lankan cinema, theatre and television. Her first appeared film was Siri Parakum as Sirimal Ethana. Senali became more popular with her role as Paatali "Sudu Chooti" in Sri Lankan television series Nadagamkarayo.














