Acetobacter is a genus of acetic acid bacteria. Acetic acid bacteria are characterized by the ability to convert ethanol to acetic acid in the presence of oxygen. Of these, the genus Acetobacter is distinguished by the ability to oxidize lactate and acetate into carbon dioxide and water. Bacteria of the genus Acetobacter have been isolated from industrial vinegar fermentation processes and are frequently used as fermentation starter cultures.
The Aquificota phylum is a diverse collection of bacteria that live in harsh environmental settings. The name Aquificota was given to this phylum based on an early genus identified within this group, Aquifex, which is able to produce water by oxidizing hydrogen. They have been found in springs, pools, and oceans. They are autotrophs, and are the primary carbon fixers in their environments. These bacteria are Gram-negative, non-spore-forming rods. They are true bacteria as opposed to the other inhabitants of extreme environments, the Archaea.

Halomonadaceae is a family of halophilic Pseudomonadota.

Campylobacterota are a phylum of bacteria. All species of this phylum are Gram-negative.
Mycolicibacterium aubagnense is a species of the phylum Actinomycetota, belonging to the genus Mycolicibacterium.
Mycobacterium monacense is a yellow-pigmented, non-photochromogenic species of mycobacterium named after Monacum, the Latin name of the German city Munich where the first strain was isolated. It grows in less than a week on solid medium.

Zhou's box turtle is a species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. The species is apparently endemic to China.

Cronobacter is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, oxidase-negative, catalase-positive, rod-shaped bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Several Cronobacter species are desiccation resistant and persistent in dry products such as powdered infant formula. They are generally motile, reduce nitrate, use citrate, hydrolyze esculin and arginine, and are positive for L-ornithine decarboxylation. Acid is produced from D-glucose, D-sucrose, D-raffinose, D-melibiose, D-cellobiose, D-mannitol, D-mannose, L-rhamnose, L-arabinose, D-trehalose, galacturonate and D-maltose. Cronobacter spp. are also generally positive for acetoin production and negative for the methyl red test, indicating 2,3-butanediol rather than mixed acid fermentation. The type species of the genus Cronobacter is Cronobacter sakazakii comb. nov.
Eugyrinus is an extinct genus of dendrerpetontid temnospondyl. It was originally named Hylonomus wildi in 1891 by Arthur Smith Woodward.

Cadlina is a genus of sea slugs, dorid nudibranchs, shell-less marine gastropod mollusks historically classified in the family Chromodorididae. Recent research by R.F. Johnson in 2011 has shown that Cadlina does not belong to the family Chromodorididae. She has therefore brought back the name Cadlinidae from synonymy with Chromodorididae. The family Cadlinidae also includes the genus AldisaBergh, 1878.
Pinguiochrysidaceae is a family of marine Heterokontophyta. It is the only family in the order Pinguiochrysidales, which is the only order in the class Pinguiophyceae. It includes five species of unicellular organisms with high concentration of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the cytoplasm. The other common features are the lack of cell wall and the tendency for flagella loss even on the stage of zoospore, which is unusual for heterokonts. One species inhabits benthic substates and is able to produce lorica with one or more tubular necks. The other species live in the plankton.
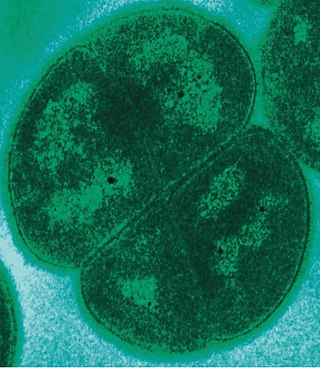
Deinococcus is in the monotypic family Deinococcaceae, and one genus of three in the order Deinococcales of the bacterial phylum Deinococcota highly resistant to environmental hazards. These bacteria have thick cell walls that give them Gram-positive stains, but they include a second membrane and so are closer in structure to Gram-negative bacteria. Deinococcus survive when their DNA is exposed to high doses of gamma and UV radiation. Whereas other bacteria change their structure in the presence of radiation, such as by forming endospores, Deinococcus tolerate it without changing their cellular form and do not retreat into a hardened structure. They are also characterized by the presence of the carotenoid pigment deinoxanthin that give them their pink color. They are usually isolated according to these two criteria. In August 2020, scientists reported that bacteria from Earth, particularly Deinococcus bacteria, were found to survive for three years in outer space, based on studies conducted on the International Space Station. These findings support the notion of panspermia, the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed in various ways, including space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids or contaminated spacecraft.
Lentisphaerota is a phylum of bacteria closely related to Chlamydiota and Verrucomicrobiota.

The Haemoproteidae are a family of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Polynucleobacter is a genus of bacteria, originally established by Heckmann and Schmidt (1987) to exclusively harbor obligate endosymbionts of ciliates belonging to the genus Euplotes.
Streptomyces guanduensis is an acidophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from pine forest soil from Guandu in the Yunnan Province in China.
Streptomyces paucisporeus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from acidic soil from the Yunnan Province in China.
Streptomyces rubidus is an acidophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a pine forest in Yanglin in the Yunnan province in China.
Streptomyces yanglinensis is an acidophilic bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from a pine forest in Yanglin in the Yunnan province in China.
Cerasicoccus arenae is a Gram-negative, obligately aerobic and non-spore-forming bacterium from the genus of Cerasicoccus which has been isolated from marine sand from Kamaishi. Cerasicoccus arenae can produce carotenoid.






