
Ephesus was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, three kilometres southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of the former Arzawan capital by Attic and Ionian Greek colonists. During the Classical Greek era, it was one of twelve cities that were members of the Ionian League. The city came under the control of the Roman Republic in 129 BC.

Celsus was a 2nd-century Greek philosopher and opponent of early Christianity. He is known for his literary work, The True Word, which survives exclusively in quotations from it in Contra Celsum, a refutation written in 248 by Origen of Alexandria. The True Word is the earliest known comprehensive criticism of Christianity. It was written between about 175 and 177, shortly after the death of Justin Martyr, and was probably a response to his work.

Aulus Cornelius Celsus was a Roman encyclopaedist, known for his extant medical work, De Medicina, which is believed to be the only surviving section of a much larger encyclopedia. The De Medicina is a primary source on diet, pharmacy, surgery and related fields, and it is one of the best sources concerning medical knowledge in the Roman world. The lost portions of his encyclopedia likely included volumes on agriculture, law, rhetoric, and military arts. He made contributions to the classification of human skin disorders in dermatology, such as Myrmecia, and his name is often occurring in medical terms about the skin, e.g., kerion celsi and area celsi.

Tiberius Julius Abdes Pantera was a Roman-Phoenician soldier born in Sidon, whose tombstone was found in Bingerbrück, Germany, in 1859. A historical connection from this soldier to Jesus has long been hypothesized by numerous scholars, based on the claim of the ancient Greek philosopher Celsus, who, according to Christian writer Origen in his "Against Celsus", was the author of a work entitled The True Word.

Saints Nazarius and Celsus were two martyrs of whom nothing is known except the discovery of their bodies by Saint Ambrose.

Against Celsus, preserved entirely in Greek, is a major apologetics work by the Church Father Origen of Alexandria, written in around 248 AD, countering the writings of Celsus, a pagan philosopher and controversialist who had written a scathing attack on Christianity in his treatise Logos Alēthēs. Among a variety of other charges, Celsus had denounced many Christian doctrines as irrational and criticized Christians themselves as uneducated, deluded, unpatriotic, close-minded towards reason, and too accepting of sinners. He had accused Jesus of performing his miracles using black magic rather than actual divine powers and of plagiarizing his teachings from Plato. Celsus had warned that Christianity itself was drawing people away from traditional religion and claimed that its growth would lead to a collapse of traditional, conservative values.

The Library of Celsus is an ancient Roman building in Ephesus, Anatolia, now part of Selçuk, Turkey. The building was commissioned in the 110s A.D. by a consul, Gaius Julius Aquila, as a funerary monument for his father, former proconsul of Asia Tiberius Julius Celsus Polemaeanus, and completed during the reign of Hadrian, sometime after Aquila's death. The library is considered an architectural marvel, and is one of the only remaining examples of a library from the Roman Empire. The Library of Celsus was the third-largest library in the Roman world behind only Alexandria and Pergamum, believed to have held around twelve thousand scrolls. Celsus is buried in a crypt beneath the library in a decorated marble sarcophagus. The interior measured roughly 180 square metres.
Events from the year 1119 in Ireland.
Publius Juventius Celsus Titus Aufidius Hoenius Severianus — the son of a little-known jurist of the same name, hence also Celsus filius — was, together with Julian, the most influential ancient Roman jurist of the High Classical era.
Events from the year 1129 in Ireland.
The True Word is a lost treatise in which the ancient Greek philosopher Celsus addressed many principal points of Early Christianity and refuted or argued against their validity. In The True Word, Celsus attacked Christianity in three ways: by refuting its philosophical claims, by marking it as a phenomenon associated with the uneducated and lower class, and by cautioning his audience that it was a danger to the Roman Empire. All information concerning the work exists only in the extensive quotations from it in the Contra Celsum written some seventy years later by the Christian Origen. These are believed to be accurate as far as they go, but may not give a fully comprehensive picture of the original work.

Isopogon ceratophyllus, commonly known as the horny cone-bush or wild Irishman, is a plant of the family Proteaceae that is endemic to the coast in Victoria, South Australia and on the Furneaux Group of islands in Tasmania. It is a small woody shrub that grows to 100 cm high with prickly foliage. It is extremely sensitive to dieback from the pathogen Phytophthora cinnamomi

Ceratophyllus gallinae, known as the hen flea in Europe or the European chicken flea elsewhere, is an ectoparasite of birds. This flea was first described by the German botanist and entomologist Franz von Paula Schrank in 1803.

Tiberius Julius Celsus Polemaeanus, commonly known as Celsus, was an Ancient Greek Roman citizen who became a senator, and served as suffect consul as the colleague of Lucius Stertinius Avitus. Celsus Polemaeanus was a wealthy and popular citizen and benefactor of Ephesus, and was buried in a sarcophagus beneath the famous Library of Celsus, which was built as a mausoleum in his honor by his son Tiberius Julius Aquila Polemaeanus.

Ceratophyllus is a widespread genus of fleas found in temperate climates. Some of its members include the chicken flea, Ceratophyllus gallinae, and the poultry flea, Ceratophyllus niger.
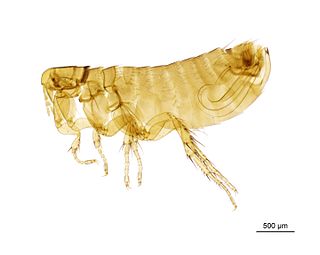
Ceratophyllus columbae is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Gervais in 1844.
Ceratophyllus phrillinae is a species of flea in the family Ceratophyllidae. It was described by Smit in 1976.
Aulus Marius Celsus was a Roman senator who held several offices in the emperor's service during the first century AD, as well as playing a role in the Year of Four Emperors. He was suffect consul of the nundinium of July to August 69 as the colleague of Gnaeus Arrius Antoninus.
Panthera is the name of a soldier said by Celsus to be Jesus' real father and referred to in passages on Jesus in the Talmud and the Toledot Yeshu.









