Related Research Articles

Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor.
Chapter 7 of Title 11 U.S. Code is the bankruptcy code that governs the process of liquidation under the bankruptcy laws of the U.S. In contrast to bankruptcy under Chapter 11 and Chapter 13, which govern the process of reorganization of a debtor, Chapter 7 bankruptcy is the most common form of bankruptcy in the U.S.
A lien is a form of security interest granted over an item of property to secure the payment of a debt or performance of some other obligation. The owner of the property, who grants the lien, is referred to as the lienee and the person who has the benefit of the lien is referred to as the lienor or lien holder.
A creditor or lender is a party that has a claim on the services of a second party. It is a person or institution to whom money is owed. The first party, in general, has provided some property or service to the second party under the assumption that the second party will return an equivalent property and service. The second party is frequently called a debtor or borrower. The first party is called the creditor, which is the lender of property, service, or money.
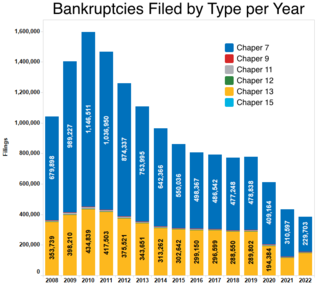
In the United States, bankruptcy is largely governed by federal law, commonly referred to as the "Bankruptcy Code" ("Code"). The United States Constitution authorizes Congress to enact "uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States". Congress has exercised this authority several times since 1801, including through adoption of the Bankruptcy Reform Act of 1978, as amended, codified in Title 11 of the United States Code and the Bankruptcy Abuse Prevention and Consumer Protection Act of 2005 (BAPCPA).
Hypothec, sometimes tacit hypothec, is a term used in civil law systems or to refer to a registered real security of a creditor over real estate, but under some jurisdictions it may additionally cover ships only, as opposed to other collaterals, including corporeal movables other than ships, securities or intangible assets such intellectual property rights, covered by a different type of right (pledge). Common law has two main equivalents to the term: mortgages and non-possessory lien.
A guarantee is a form of transaction in which one person, to obtain some trust, confidence or credit for another, agrees to be answerable for them. It may also designate a treaty through which claims, rights or possessions are secured. It is to be differentiated from the colloquial "personal guarantee" in that a guarantee is a legal concept which produces an economic effect. A personal guarantee, by contrast, is often used to refer to a promise made by an individual which is supported by, or assured through, the word of the individual. In the same way, a guarantee produces a legal effect wherein one party affirms the promise of another by promising to themselves pay if default occurs.
The act of cession is the assignment of property to another entity. In international law it commonly refers to land transferred by treaty. Ballentine's Law Dictionary defines cession as "a surrender; a giving up; a relinquishment of jurisdiction by a board in favor of another agency." In contrast with annexation, where property is forcibly seized, cession is voluntary or at least apparently so.
A bankruptcy discharge is a court order that releases an individual or business from specific debts and obligations they owe to creditors. In other words, it's a legal process that eliminates the debtor's liability to pay certain types of debts they owe before filing the bankruptcy case.
In finance, a security interest is a legal right granted by a debtor to a creditor over the debtor's property which enables the creditor to have recourse to the property if the debtor defaults in making payment or otherwise performing the secured obligations. One of the most common examples of a security interest is a mortgage: a person borrows money from the bank to buy a house, and they grant a mortgage over the house so that if they default in repaying the loan, the bank can sell the house and apply the proceeds to the outstanding loan.
Antichresis, under civil law and Roman law, is a contract whereby a debtor pledges real property to a creditor, allowing the use and occupation of the pledged property, in lieu of interest on the loan.
The history of Roman law can be divided into three systems of procedure: that of legis actiones, the formulary system, and cognitio extra ordinem. Though the periods in which these systems were in use overlapped one another and did not have definitive breaks, the legis actio system prevailed from the time of the XII Tables until about the end of the 2nd century BC, the formulary procedure was primarily used from the last century of the Republic until the end of the classical period, and cognitio extra ordinem was in use in post-classical times.
Ogden v. Saunders, 25 U.S. 213 (1827), was a United States Supreme Court case that determined the scope of a bankruptcy law in relation to a clause of the Constitution of the United States. It is notable for its era in producing multiple opinions from the justices. Justice William Johnson delivered the majority opinion. Chief Justice John Marshall, Justice Gabriel Duvall, and Justice Joseph Story concurred in part and dissented in part to the Court's judgment, while Justices Bushrod Washington, Smith Thompson, and Robert Trimble dissented.
Sturges v. Crowninshield, 17 U.S. 122 (1819), dealt with the constitutionality of New York creating bankruptcy laws and retroactively applying those laws.
A pledge is a bailment that conveys title to property owned by a debtor to a creditor to secure repayment for some debt or obligation and to the mutual benefit of both parties. The term is also used to denote the property which constitutes the security. The pledge is a type of security interest. Pledge is the pignus of Roman law, from which most of the modern European-based law on the subject is derived, but is generally a feature of even the most basic legal systems. A pledge of personal property is known as a pawn.
Flagg Bros., Inc. v. Brooks, 436 U.S. 149 (1978), was a case decided by the Supreme Court of the United States wherein the constitutionality of New York's Uniform Commercial Code provision, which allows a warehouse to enforce a lien upon repossessed goods by selling said goods, was challenged under the Fourteenth Amendment. The Court held that the state-allowed re-sale provision did not constitute state action, and thus, the plaintiff did not possess a colorable federal due process claim.
Attachment is a legal process by which a court of law, at the request of a creditor, designates specific property owned by the debtor to be transferred to the creditor, or sold for the benefit of the creditor. A wide variety of legal mechanisms are employed by debtors to prevent the attachment of their assets.
Consensu or obligatio consensu or obligatio consensu contracta or obligations ex consensu or contractus ex consensu or contracts consensu or consensual contracts or obligations by consent are, in Roman law, those contracts which do not require formalities.
The history of bankruptcy law begins with the first legal remedies available for recovery of debts. Bankruptcy is the legal status of a legal person unable to repay debts.
Debt relief, or debt forgiveness, has been practiced in many societies since antiquity. Periodic debt remission was institutionalised in the Ancient Near East and contributed to the stability of its societies. In ancient Greece and Rome the laws were more creditor-friendly and debt cancellation was one of the major demands of the poor, only occasionally implemented by the government. Medieval canon law contained provisions for the annulment of debts owed by borrowers in distress, which influenced modern personal bankruptcy law.
References
- ↑ W. Pakter, The origins of bankruptcy in medieval canon and Roman law, in Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress of Medieval Canon Law, 1984, ed. P. Linehan, Vatican City, 1988, 485–506.
- ↑ Erskine, John (1860). The Principles of the Law of Scotland (3 ed.). p. 720.
- ↑ One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain : Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Cessio Bonorum". Encyclopædia Britannica . Vol. 5 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 768.
- ↑ Ogden v. Saunders , 25 U.S. (12 Wheat. ) 213, 215 (1827) (appellant argument).
- ↑ Sturges v. Crowninshield , 17 U.S. (4 Wheat. ) 122, 129 (1819) (appellant argument).
- ↑ Blackstone, William (1775). Commentaries on the Laws of England. Vol. 2 (7 ed.). p. 473.
[In] the law of cession, [...] if a debtor ceded, or yielded up all his fortune to his creditors, he was secured from being dragged to a gaol, omni quoque corporali cruciatu semoto.
- ↑ Black, Henry C. (1910). A Law Dictionary (2 ed.). p. 185.