
Proportional representation (PR) refers to any type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to political divisions among voters. The essence of such systems is that all votes cast – or almost all votes cast – contribute to the result and are effectively used to help elect someone. Under other election systems, a bare plurality or a scant majority are all that are used to elect candidates. PR systems provide balanced representation to different factions, reflecting how votes are cast.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 7, 2000. Republican nominee, Governor George W. Bush of Texas, the eldest son of George H. W. Bush, narrowly defeated incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore. It was the fourth of five U.S. presidential elections, and the first since 1888, in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest U.S. presidential elections, with long-standing controversy about the result. Gore conceded the election on December 13 after the Supreme Court issued its decision.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 5, 1996. Incumbent Democratic President Bill Clinton and his running mate, incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore were re-elected to a second and final term, defeating the Republican ticket of former Senate Majority Leader Bob Dole and former Secretary of Housing and Urban Development Jack Kemp and the Reform ticket of businessman Ross Perot and economist Pat Choate.
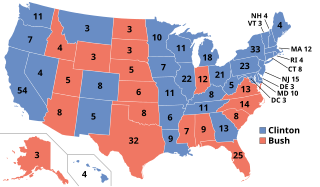
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 3, 1992. Democratic governor Bill Clinton of Arkansas defeated incumbent Republican president George H. W. Bush and independent businessman Ross Perot of Texas. The election marked the beginning of a period of Democratic dominance and the end of a period of Republican dominance in American presidential politics that began in 1968, and also marked the end of 12 years of Republican rule of the White House, as well as the end of the Greatest Generation's 32-year American rule and the beginning of the baby boomers' decades-long dominance lasting through the present day.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 7, 1848. Held in the aftermath of the Mexican–American War, General Zachary Taylor of the Whig Party defeated Senator Lewis Cass of the Democratic Party.
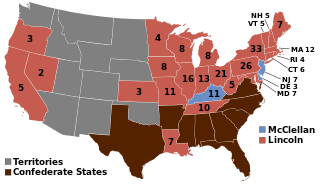
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1864, near the end of the American Civil War. Incumbent President Abraham Lincoln of the National Union Party easily defeated the Democratic nominee, former General George B. McClellan, by a wide margin of 212–21 in the electoral college, with 55% of the popular vote. For the election, the Republican Party and some Democrats created the National Union Party, especially to attract War Democrats.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 1920. Republican senator Warren G. Harding of Ohio defeated Democratic governor James M. Cox of Ohio. It was the first election held after the end of the First World War, and the first election after the ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment which gave equal votes to men and women. It was the third presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state, and the last time that the state was not New York. It was the first presidential election to have its results broadcast by radio. Coincidentally, the election was held on Harding's 55th birthday.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 4, 1924. Incumbent Republican President Calvin Coolidge won election to a full term. Coolidge was the second vice president, after Theodore Roosevelt, to ascend to the presidency and then win a full term.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 1932. Against the backdrop of the Great Depression, incumbent Republican President Herbert Hoover was defeated in a landslide by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt, the governor of New York and the vice presidential nominee of the 1920 presidential election. Roosevelt was the first Democrat in 80 years to simultaneously win an outright majority of the electoral college and popular vote, a feat last accomplished by Franklin Pierce in 1852, as well as the first Democrat in 56 years to win a majority of the popular vote, which was last achieved by Samuel J. Tilden in 1876. Roosevelt was the last sitting governor to be elected president until Bill Clinton in 1992. Hoover became the first incumbent president to lose an election to another term since William Howard Taft in 1912, the last to do so until Gerald Ford lost 44 years later, and the last elected incumbent president to do so until Jimmy Carter lost 48 years later. The election marked the effective end of the Fourth Party System, which had been dominated by Republicans. It was the first time since 1916 that a Democrat was elected president.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 3, 1936. In the midst of the Great Depression, incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican governor Alf Landon of Kansas in a landslide victory. Roosevelt won the highest share of the popular vote (60.8%) and the electoral vote since the largely uncontested 1820 election. The sweeping victory consolidated the New Deal Coalition in control of the Fifth Party System.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 7, 1972. Incumbent Republican President Richard Nixon defeated Democratic Senator George McGovern in a landslide victory. With 60.7% of the popular vote, Richard Nixon won the largest share of the popular vote for the Republican Party in any presidential election.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 4, 2008. The Democratic ticket of Barack Obama, the junior senator from Illinois, and Joe Biden, the senior senator from Delaware, defeated the Republican ticket of John McCain, the senior senator from Arizona, and Sarah Palin, the governor of Alaska. Obama became the first African American to be elected to the presidency. This was the first election since 1952 in which neither the incumbent president nor vice president was on the ballot, as well as the first election since 1928 in which neither ran for the nomination.

The Samajwadi Party is a socialist political party in India. It was founded on 4 October 1992 by former Janata Dal politician Mulayam Singh Yadav and is headquartered in New Delhi. The Samajwadi Party is currently led by former Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh, Akhilesh Yadav.
In the politics of the United States, elections are held for government officials at the federal, state, and local levels. At the federal level, the nation's head of state, the president, is elected indirectly by the people of each state, through an Electoral College. Today, these electors almost always vote with the popular vote of their state. All members of the federal legislature, the Congress, are directly elected by the people of each state. There are many elected offices at state level, each state having at least an elective governor and legislature. There are also elected offices at the local level, in counties, cities, towns, townships, boroughs, and villages; as well as for special districts and school districts which may transcend county and municipal boundaries.
An electoral swing analysis shows the extent of change in voter support, typically from one election to another, expressed as a positive or negative percentage. A multi-party swing is an indicator of a change in the electorate's preference between candidates or parties, often between major parties in a two-party system. A swing can be calculated for the electorate as a whole, for a given electoral district or for a particular demographic.
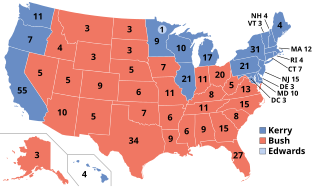
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 2004. Incumbent Republican President George W. Bush and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Dick Cheney, were re-elected to a second term. They narrowly defeated the Democratic ticket of John Kerry, a senator from Massachusetts, and his running mate John Edwards, a senator from North Carolina.
An independent, non-partisan politician, or non-affiliated politician is a politician not affiliated with any political party or bureaucratic association. There are numerous reasons why someone may stand for office as an independent.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 6, 2012. Incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Joe Biden, were elected to a second term. They defeated the Republican ticket of former Governor of Massachusetts Mitt Romney and U.S. Representative Paul Ryan of Wisconsin, who later became Speaker of the House of Representatives.

Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket of former secretary of state and former first lady Hillary Clinton and Virginia junior senator Tim Kaine, in what was considered one of the biggest political upsets in American history. It was the fifth and most recent presidential election in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote. It was also the sixth and most recent presidential election in U.S. history in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state; the others have been in 1860, 1904, 1920, 1940, and 1944.

The election of the president and for vice president of the United States is an indirect election in which citizens of the United States who are registered to vote in one of the fifty U.S. states or in Washington, D.C., cast ballots not directly for those offices, but instead for members of the Electoral College. These electors then cast direct votes, known as electoral votes, for president and for vice president. The candidate who receives an absolute majority of electoral votes is then elected to that office. If no candidate receives an absolute majority of the votes for president, the House of Representatives elects the president; likewise if no one receives an absolute majority of the votes for vice president, then the Senate elects the vice president.
















