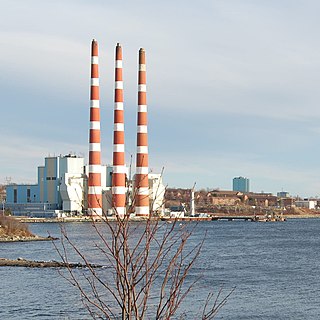Citadel Hill is a hill that is a National Historic Site in Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. Four fortifications have been constructed on Citadel Hill since the city was founded by the English in 1749, and were referred to as Fort George—but only the third fort was officially named Fort George. According to General Orders of October 20, 1798, it was named after King George III. The first two and the fourth and current fort, were officially called the Halifax Citadel. The last is a concrete star fort.

Point Pleasant Park is a large, mainly forested municipal park at the southern tip of the Halifax peninsula. It once hosted several artillery batteries, and still contains the Prince of Wales Tower - the oldest Martello tower in North America (1796). The park is a popular recreational spot for Haligonians, as it hosts forest walks and affords views across the harbour and out toward the Atlantic.

Halifax Harbour is a large natural harbour on the Atlantic coast of Nova Scotia, Canada, located in the Halifax Regional Municipality.

Halifax, Nova Scotia, was originally inhabited by the Mi'kmaq. The first European settlers to arrive in the future Halifax region were French, in the early 1600s, establishing the colony of Acadia. The British settled Halifax in 1749, which sparked Father Le Loutre's War. To guard against Mi'kmaw, Acadian, and French attacks on the new Protestant settlements, British fortifications were erected in Halifax (1749), Bedford (1749), Dartmouth (1750), and Lawrencetown (1754). St. Margaret's Bay was first settled by French-speaking Foreign Protestants at French Village, Nova Scotia, who migrated from Lunenburg, Nova Scotia, during the American Revolution. All of these regions were amalgamated into the Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM) in 1996. While all of the regions of HRM developed separately over the last 250 years, their histories have also been intertwined.

McNabs Island is the largest island in Halifax Harbour located in Halifax Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia, Canada. It played a major role in defending Halifax Harbour and is now a provincial park. The island was settled by Britons in the 1750s and later by Peter McNab, and McNab family members lived on the island until 1934.

Duncan's Cove is a small rural community on the Chebucto Peninsula in the Halifax Regional Municipality on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean on the Ketch Harbour Road, 19 kilometers from Halifax. The community is located beside Chebucto Head, the prominent coastal headland.
Dartmouth founded in 1750, is a Metropolitan Area and former city in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

The Chebucto Community Net (CCN) is a Canadian FreeNet operating in Nova Scotia's Halifax Regional Municipality (HRM). It is registered as a non-profit society under Nova Scotia's Registry of Joint Stocks using the name Chebucto Community Net Society. The name "Chebucto" comes from the local l'nu word for Halifax Harbour meaning "big water".

Sambro Island Lighthouse is a landfall lighthouse located at the entrance to Halifax Harbour, Nova Scotia, on an island near the community of Sambro in the Halifax Regional Municipality. It is the oldest surviving lighthouse in North America and its construction is a National Historic Event.

HMCS Esquimalt was a Bangor-class minesweeper that served in the Royal Canadian Navy during the Second World War. She saw service in the Battle of the Atlantic and in the Battle of the St. Lawrence. She was sunk in 1945, the last Canadian warship to suffer that fate. She was named for Esquimalt, British Columbia.

The Halifax Shipyard Limited is a Canadian shipbuilding company located in Halifax, Nova Scotia.

CFAV Firebird is a Fire-class fireboat in the Royal Canadian Navy designed by Robert Allan Ltd.. Firebird is based in CFB Halifax, in Halifax, Nova Scotia. Her sister ship CFAV Firebrand is based in CFB Esquimalt.
Kitano was a Japanese container ship. She was delivered in Japan in 1990 to Japanese container line NYK and scrapped in China in November 2011.

CCGS Sambro is a Canadian Coast Guard motor lifeboat homeported in Sambro, Nova Scotia.

Louisbourg Lighthouse is an active Canadian lighthouse in Louisbourg, Nova Scotia. The current tower is the fourth in a series of lighthouses that have been built on the site, the earliest was the first lighthouse in Canada.
CCGS Earl Grey is a Samuel Risley-class light icebreaker and buoy tender in the Canadian Coast Guard. Constructed in 1986, the vessel serves a variety of roles, including light ice-breaking and buoy tending, as well as being strengthened for navigation in ice to perform tasking along the shores off the Atlantic coast of Canada. Like her sister ship, CCGS Samuel Risley, she carries a large and powerful crane on her long low afterdeck for manipulating buoys. Earl Grey is the second icebreaker in Canadian service to carry the name.
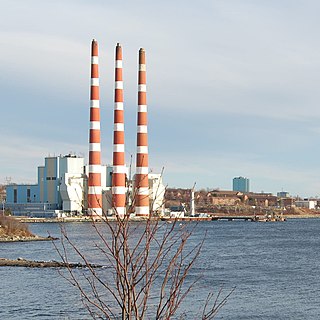
Tufts Cove is an urban neighbourhood in the Dartmouth area of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada. It is situated on the eastern shore of Halifax Harbour in the North End of Dartmouth. The neighbourhood boundaries of Tufts Cove are approximately from Albro Lake Road in the south to Highway 111 in the north, and from Victoria Road in the east with the harbour to the west.

Cape d'Or is a headland located near Advocate, Cumberland County, on the Bay of Fundy coast of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Nova Scotia: