Related Research Articles

Strategic Air Command (SAC) was a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile components of the United States military's strategic nuclear forces from 1946 to 1992. SAC was also responsible for strategic reconnaissance aircraft; airborne command posts; and most of the USAF's aerial refueling aircraft.
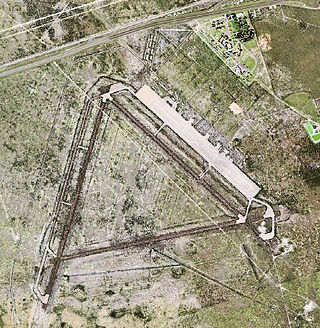
Pyote Air Force Base was a World War II United States Army Air Forces training airbase. It was on 2,745 acres (1,111 ha) a mile from the town of Pyote, Texas, on U.S. Highway 80, 20 miles west of Monahans,` 230 miles (370 km) east of El Paso.

Mather Air Force Base was a United States Air Force Base, which was closed in 1993 pursuant to a post-Cold War BRAC decision. It was located 12 miles (19 km) east of Sacramento, on the south side of U.S. Route 50 in Sacramento County, California. Mather Field was one of 32 Air Service training camps established after the United States entry into World War I in April 1917.

The Alaskan Air Command (AAC) is an inactive United States Air Force Major Command originally established in 1942 under the United States Army Air Forces. Its mission was to organize and administer the air defense system of Alaska, exercise direct control of all active measures, and coordinate all passive means of air defense. In addition, the command also supported Strategic Air Command elements operating through and around Alaska. It was redesignated Eleventh Air Force on 9 August 1990 and, concurrently, status changed from a major command of the United States Air Force to a subordinate organization of Pacific Air Forces.

Norton Air Force Base (1942–1994) was a United States Air Force facility 2 miles (3.2 km) east of downtown San Bernardino in San Bernardino County, California.

The 1st Combat Evaluation Group was a Strategic Air Command (SAC) unit. It was formed on 1 August 1961 to merge the 3908th Strategic Standardization Group for SAC aircrew evaluation with the 1st Radar Bomb Scoring Group that had originated from the 263rd Army Air Force Base Unit which transferred from 15th AF to directly under Strategic Air Command c. 1946. The 1CEVG formed after SAC switched to low-level tactics to counter Soviet surface-to-air missiles and SAC had "developed a Radar Bomb Scoring field kit for use in NIKE Systems" in early 1960 for scoring SAC training missions against US Hercules SAM sites. The 1CEVG headquarters included an Office of History and a "standardization and evaluation school" for command examiners.

Cross City Air Force Station is a former United States Air Force facility, located 1.6 miles (2.6 km) east of Cross City, Florida.

Las Vegas Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located 26.5 miles (42.6 km) west-northwest of Las Vegas, Nevada. It was closed by the Air Force in 1969 and turned over to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). The site is now data-tied into the Joint Surveillance System (JSS).

Winslow Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located in Coconino County, Arizona, 8.7 miles (14.0 km) west-northwest of Winslow, Arizona. It was closed in 1963.
Ground Equipment Facility J-36A is a Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) radar station of the Joint Surveillance System (JSS) in the Western Air Defense Sector (WADS) of NORAD.

Madera Air Force Station is a closed United States Air Force General Surveillance Radar station. It is located 5.2 miles (8.4 km) north-northeast of Madera, California. It was closed in 1966.
Radar Bomb Scoring is a combat aviation ground support operation used to evaluate Cold War aircrews' effectiveness with simulated unguided bomb drops near radar stations of the United States Navy, the USAF Strategic Air Command, and Army Project Nike units. USAF RBS used various ground radar, computers, and other electronic equipment such as jammers to disrupt operations of the bomber's radar navigator, AAA/SAM simulators to require countermeasures from the bomber, and Radar Bomb Scoring Centrals for estimating accuracy of simulated bombings. Scores for accuracy and electronic warfare effectiveness were transmitted from radar sites such as those at Strategic Range Training Complexes.
RBS Express railroad trains were 3 mobile United States Air Force radar stations for 1CEVG Radar Bomb Scoring (RBS) of Strategic Air Command bomber crews beginning in March 1961. Electronic equipment included the "MSQ-39, TLQ-11, MPS-9, and the IFF/SIF for the MSQ-39" along with support railcars, and the trains were temporarily used at various rail sites with the radar antennas emplaced using hoists built onto flatcars. Pulled by a "contracted locomotive" that left the train at the site, and a North American B-25 Mitchell was used for calibration of the radar station.

The Badlands Bombing Range (BBR) refers to Rapid City Army Air Base target ranges for World War II which included the current Air Force Retained Area, an inactive 2,486-acre (10.06 km2) United States Air Force site "20 miles southeast" of Scenic, South Dakota. The retained area is the remainder of 341,726 acres (1,382.92 km2) federally acquired in 1942 under eminent domain at the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation. In addition to use by World War II aircraft, BBR was used for a post-war Army National Guard gunnery range and a Cold War Radar Bomb Scoring site.
The AN/MPQ-2 Close Cooperation Control Unit was a truck-mounted pautomatic tracking radar/computer/communication system for aircraft command guidance, e.g., missile tracking, and for Radar Bomb Scoring. It was introduced shortly after the end of World War II. For ground directed bombing (GDB), an operator would manually plot a target on the "Blind Bombing Plotting Sheet", then use the manual "E6B computer and bombing tables" to plot the release point for striking the target, after which a radar operator used the AN/MPQ-2 to acquire a track of the bomber near an initial point during which allowed ground control of the bomb run to the release point.

The 99th Range Group is an inactive United States Air Force (USAF) unit. It was last stationed at Nellis AFB, Nevada, where it was responsible for the Nevada Test and Training Range (NTTR).
The Stockton Ordance Depot was a World War II vehicle repair facility, supply depot, and camp for German and Italian prisoners of war. The installation was also used as a USAF radar station and a DLA Defense Distribution Center.
The Interior Radar Bomb Scoring Site opened in August 1960 on Hurley Butte, adjacent to the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation and a few miles from Interior, South Dakota. The Interior RBSS is a Formerly Used Defense Site, that closed in 1968.
The 3903rd Radar Bomb Scoring Group was a military evaluation unit under direct command of Strategic Air Command (SAC) headquarters for scoring simulated bomb runs using automatic tracking radar stations. Initially an Army Air Forces Base Unit (AAFBU) and then a squadron, the 3903rd RBS Group was personnel, assets, and detachments were redesignated the 1st Radar Bomb Scoring Group and then the 1CEVG Radar Bomb Scoring Division when the RBS Group merged with the 3908th Strategic Standardization Group in 1961, the year RBS Express trains began to be used for low-altitude Boeing B-52 Stratofortress operations..
Genesee Mountain Park Training Annex (1955–70) was a U.S. Air Force radar station, an outstation of Lowry Air Force Base. It is a Formerly Used Defense Site of 3 acres (1.2 ha) at Genesee Park (Colorado)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Historic California Posts, Stations and Airfields, Cheli Air Force Station". californiamilitaryhistory.org. The California State Military Museum. Archived from the original on 17 March 2016. Retrieved 11 September 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ Shaw, Frederick J. (2004). Locating Air Force Base Sites: History's Legacy (PDF). Air Force History and Museums Program. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2011. Retrieved 14 June 2012.
- ↑ Dtic.mil: Cheli AFS
- 1 2 Map of flight path between Sacramento and Santa Barbara on pdf page 56
- ↑ oreanwar.org: Cheli AFS RBS
- 1 2 Cevga.com
- ↑ Ancestry.com: Lt Col James O. McHan
- ↑ Trabuca Bombing Range history Archived 17 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ Patton United States Army Reserve Center, 5340 Bandini Boulevard, Bell CA
- ↑ "Cheli Air Force Station". Historic California Posts, Stations and Airfields. The California State Military Museum . Retrieved 14 June 2012.