
Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI) was a British chemical company. It was, for much of its history, the largest manufacturer in Britain. Its headquarters were at Millbank in London. ICI was a constituent of the FT 30 and later the FTSE 100 indices.

The chemical industry comprises the companies and other organizations that develop and produce industrial, specialty and other chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials into commodity chemicals for industrial and consumer products. It includes industries for petrochemicals such as polymers for plastics and synthetic fibers; inorganic chemicals such as acids and alkalis; agricultural chemicals such as fertilizers, pesticides and herbicides; and other categories such as industrial gases, speciality chemicals and pharmaceuticals.

Teesside is a built-up area around the River Tees in northern England, split between County Durham and North Yorkshire. The area contains the towns of Middlesbrough, Stockton-on-Tees, Billingham, Redcar, Thornaby-on-Tees, and Ingleby Barwick. Teesside's economy was once dominated by heavy manufacturing until deindustrialisation in the latter half of the 20th century. Chemical production continues to contribute significantly to Teesside's economy.
Fusel alcohols or fuselol, also sometimes called fusel oils in Europe, are mixtures of several higher alcohols produced as a by-product of alcoholic fermentation. The word Fusel is German for "bad liquor".

Solutia Inc. was an American manufacturer of materials and specialty chemicals including polyvinyl butyral (PVB), ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA), and thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) interlayers for laminated glass, aftermarket window films, protective barrier and conductive films, and rubber processing chemicals. The company was formed on September 1, 1997, as a divestiture of the Monsanto Company chemical business. In July 2012, the company was acquired by Eastman Chemical Company.

Billingham is a town and civil parish in County Durham, England. The town is on the north side of the River Tees and is governed as part of the Borough of Stockton-on-Tees unitary authority. It had a population of 35,165 in the 2011 Census.
Green chemistry, similar to sustainable chemistry or circular chemistry, is an area of chemistry and chemical engineering focused on the design of products and processes that minimize or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. While environmental chemistry focuses on the effects of polluting chemicals on nature, green chemistry focuses on the environmental impact of chemistry, including lowering consumption of nonrenewable resources and technological approaches for preventing pollution.

Methyl acetate, also known as MeOAc, acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a carboxylate ester with the formula CH3COOCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a characteristically pleasant smell reminiscent of some glues and nail polish removers. Methyl acetate is occasionally used as a solvent, being weakly polar and lipophilic, but its close relative ethyl acetate is a more common solvent being less toxic and less soluble in water. Methyl acetate has a solubility of 25% in water at room temperature. At elevated temperature its solubility in water is much higher. Methyl acetate is not stable in the presence of strong aqueous bases or aqueous acids. Methyl acetate is not regulated as a volatile organic compound in the USA.
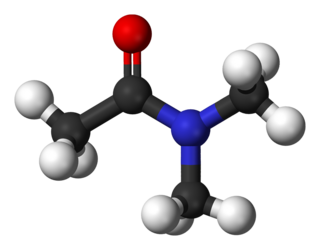
Dimethylacetamide (DMAc or DMA) is the organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)N(CH3)2. This colorless, water-miscible, high-boiling liquid is commonly used as a polar solvent in organic synthesis. DMA is miscible with most other solvents, although it is poorly soluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons.
The Distillers Company plc was a leading Scotch whisky company and, at one time, a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index. It was taken over in 1986 by Guinness & Co. and is now part of Diageo.
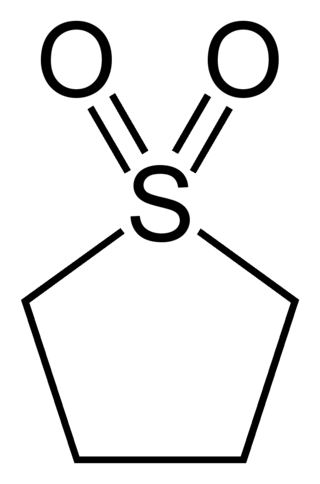
Sulfolane is an organosulfur compound, formally a cyclic sulfone, with the formula (CH2)4SO2. It is a colorless liquid commonly used in the chemical industry as a solvent for extractive distillation and chemical reactions. Sulfolane was originally developed by the Shell Oil Company in the 1960s as a solvent to purify butadiene. Sulfolane is a polar aprotic solvent, and it is miscible with water.

Isoamyl acetate, also known as isopentyl acetate, is an ester formed from isoamyl alcohol and acetic acid, with the molecular formula C7H14O2. It is a colorless liquid that is only slightly soluble in water, but very soluble in most organic solvents. Isoamyl acetate has a strong odor which is described as similar to both banana and pear. Pure isoamyl acetate, or mixtures of isoamyl acetate, amyl acetate, and other flavors in ethanol may be referred to as banana oil or pear oil.

Salt End or Saltend is a hamlet in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, in an area known as Holderness. It is situated on the north bank of the Humber Estuary just outside the Hull eastern boundary on the A1033 road. It forms part of the civil parish of Preston.

Acetone–butanol–ethanol (ABE) fermentation, also known as the Weizmann process, is a process that uses bacterial fermentation to produce acetone, n-butanol, and ethanol from carbohydrates such as starch and glucose. It was developed by chemist Chaim Weizmann and was the primary process used to produce acetone, which was needed to make cordite, a substance essential for the British war industry during World War I.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH. Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. It has been used, as a component of vinegar, throughout history from at least the third century BC.
Isopropyl alcohol is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.
The North East of England Process Industry Cluster (NEPIC) is an economic cluster developed in accordance with Michael Porter's theories and strategies regarding industrial clusters. The chemistry-using sectors in North East England, where more than 1,400 businesses are headquartered in the industry's supply chain, formed this Process Industry Cluster. In the north-east of England, the industry employs approximately 35,000 direct workers and around 190,000 indirect workers, who collectively account for more than one-third of the area's industrial economy. Companies in the cluster produce 35% of the pharmaceuticals and 50% of the petrochemicals used in the UK, making this area the only net exporter of goods from the country. The area has more than £13 billion in exports.
Specialty chemicals are particular chemical products which provide a wide variety of effects on which many other industry sectors rely. Some of the categories of speciality chemicals are adhesives, agrichemicals, cleaning materials, colors, cosmetic additives, construction chemicals, elastomers, flavors, food additives, fragrances, industrial gases, lubricants, paints, polymers, surfactants, and textile auxiliaries. Other industrial sectors such as automotive, aerospace, food, cosmetics, agriculture, manufacturing, and textiles are highly dependent on such products.

Chemische Werke Kluthe GmbH is a German-based chemical company headquartered in Heidelberg. The Kluthe group has 23 German and 39 international marketing bases and produces a total of 160,000 tons of goods to supply in 51 countries.
Harwich refinery is a 500,000 tonnes per year refining, processing, blending and storage facility near the port of Harwich in the UK. The refinery was commissioned in 1964 to process petroleum-based feedstocks into specialist hydrocarbon solvents.












