Related Research Articles

Okaloosa County is located in the northwestern portion of the U.S. state of Florida, extending from the Gulf of Mexico to the Alabama state line. As of the 2010 census, the population was 180,822. Its county seat is Crestview. Okaloosa County is included in the Crestview-Fort Walton Beach-Destin, FL Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Eglin Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force base in the western Florida Panhandle, located about three miles (5 km) southwest of Valparaiso in Okaloosa County.

Crestview is a city in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States. The population was 20,978 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Okaloosa County. With an elevation of 235 feet (72 m) above sea level, it is one of the highest points in the state; it receives 65 inches (1,700 mm) of rainfall annually, the second-most of any city in the state of Florida, after Fort Walton Beach with 69 inches.

Destin is a city located in Okaloosa County, Florida. It is a principal city of the Crestview–Fort Walton Beach–Destin, Florida, metropolitan area.

Fort Walton Beach is a city in southern Okaloosa County, Florida, United States. As of 2010, the population estimate for Fort Walton Beach was 19,510 recorded by the U.S. Census Bureau. It is the principal city of the Fort Walton Beach−Crestview−Destin Metropolitan Statistical Area.
Shalimar is a town in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States. The population was 717 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Fort Walton Beach–Crestview–Destin Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Valparaiso is a city in Okaloosa County, Florida, United States. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 5,036. According to the U.S. Census Bureau's 2018 estimates, the city had a population of 5,195. It is part of the Fort Walton Beach–Crestview–Destin Metropolitan Statistical Area.

The Northwest Florida Daily News is a daily newspaper published in Fort Walton Beach, Florida. It was founded in 1946 and is owned by Gannett.
State Road 123 is a north–south state highway that bypasses the stretch of State Road 85 through Niceville, Florida. The highway is a more direct route to Fort Walton Beach from points north. With flyover ramps at both intersections of SR 85 now completed, the highway has been widened into a 4-lane divided highway.

Destin Executive Airport, also known as Coleman Kelly Field, is a public use airport owned by and located in Okaloosa County, Florida. The airport is one nautical mile (2 km) east of the central business district of Destin, Florida. It is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, which categorized it as a general aviation facility.

The Okaloosa darter is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish, a darter from the subfamily Etheostomatinae, part of the family Percidae, which also contains the perches, ruffes and pikeperches. It is indigenous to freshwater streams and tributary systems in Okaloosa and Walton Counties in northwest Florida.
State Road 85 is a north–south state highway that runs from US 98 in Fort Walton Beach, Florida north to State Route 55 at the Florida/Alabama state line. In its earliest inception, it was just a clayed road over graded sandy soil, and was known early in the twentieth century as the Georgia, Alabama and Florida Highway.

Choctawhatchee Bay is a bay in the Emerald Coast region of the Florida Panhandle. The bay, located within Okaloosa and Walton counties, has a surface area of 334 square kilometres (129 sq mi). It is an inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, connected to it through East Pass. It also connects to Santa Rosa Sound in Fort Walton Beach, Florida to the west and to St. Andrews Bay in Bay County to the east, via the Gulf Intracoastal Waterway. East Pass is the only outlet of the bay flowing directly into the Gulf of Mexico. The Choctawhatchee River flows into Choctawhatchee Bay, as do several smaller rivers and streams. The Mid-Bay Bridge crosses the bay, connecting the city of Destin to Niceville, Florida.

The Eglin Air Force Base Railroad was a 45-mile military railroad at Eglin Air Force Base in Florida. It was created in 1951, and was operational until the late 1970s.

The Pensacola and Atlantic Railroad (P&A) was a company incorporated by an act of the Florida Legislature on March 4, 1881, to run from Pensacola to the Apalachicola River near Chattahoochee, a distance of about 160 miles (260 km). No railroad had ever been built across the sparsely populated panhandle of Florida, which left Pensacola isolated from the rest of the state. William D. Chipley and Frederick R. De Funiak, both of whom are commemorated in the names of towns later built along the P&A line, were among the founding officers of the railroad company.
Eglin Air Force Base, a United States Air Force base located southwest of Valparaiso, Florida, was established in 1935 as the Valparaiso Bombing and Gunnery Base. It is named in honor of Lieutenant Colonel Frederick I. Eglin (1891–1937), who was killed in a crash of his Northrop A-17 pursuit aircraft on a flight from Langley to Maxwell Field, Alabama.

Major General Grandison Gardner, USAF, Air Corp service number O-10193 / Air Force service number: 12A, was an American military officer involved with weapons systems development and evaluation.
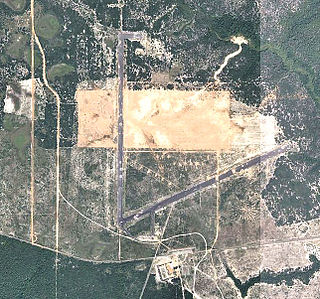
Baldsiefen Field,, is a closed United States Air Force field. It is located 10.2 miles east of Valparaiso, Florida.
Search for Paradise is a 1957 American documentary film shot in Cinerama. It was directed by Otto Lang and produced by Lowell Thomas with distribution by Cinerama Releasing Corp.
James E. Plew was a successful Chicago businessman whose early interest in the development of aviation eventually led him to acquire the initial leasehold in 1934 on the Valparaiso, Florida property that would evolve into Eglin Air Force Base.
References
- ↑ Angell, Joseph W., "History of the Army Air Forces Proving Ground Command - Part One - Historical Outline 1933-1944", The Historical Branch, Army Air Forces Proving Ground Command, Eglin Field, Florida, 1944, reprint by Office of History, Munitions Systems Division, Eglin AFB, Florida, 1989, page 36.
- ↑ Angell, page 37.
- ↑ Hutchinson, Leonard Patrick, "History of the Playground Area of Northwest Florida", Great Outdoors Publishing Co., St. Petersburg, Florida, 1st ed., 1961, no Library of Congress card number, no ISBN, page 69.
- ↑ Dobson, Henry Allen, "A History of Okaloosa County, Florida", A Thesis Presented to the Graduate Faculty of Southeastern Louisiana University, June 1974, page 86.
- ↑ Dobson, page 84.
- ↑ Dobson, page 84.
- ↑ Crestview, Florida, Okaloosa News-Journal, Friday 3 July 1931, page 1.
- ↑ Dobson, page 86
- ↑ Fort Walton, Florida, "Eglin Keeps 'Em Rolling, Too, On Rails", Playground Daily News, Thursday 11 December 1952, Volume 7, Number 45, page 1.