Related Research Articles

Poḷonnaruwa, also referred as Pulathisipura and Vijayarajapura in ancient times, is the main town of Polonnaruwa District in North Central Province, Sri Lanka. The modern town of Polonnaruwa is also known as New Town, and the other part of Polonnaruwa remains as the royal ancient city of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa.

Lilavati was the fourth woman in Sri Lankan history to rule as sovereign in her own right. Lilavati rose to prominence as the wife of Parakramabahu I, king of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa. Being of royal descent herself, she then ruled as sole monarch on three occasions in the near-anarchy following Parakramabahu's death, with the backing of various generals. The primary source for her life is the Culavamsa, specifically chapter LXXX.
Kalinga Magha or Gangaraja Kalinga Vijayabahu was an invader from the Kingdom of Kalinga who usurped the throne from Parakrama Pandyan II of Polonnaruwa in 1215. A massive migration followed of Sinhalese people to the south and west of Sri Lanka, and into the mountainous interior, as they attempted to escape his power. Magha was the last ruler to have his seat in the traditional northern seat of native power on the island, known as Rajarata; so comprehensive was his destruction of Sinhalese power in the north that all of the successor kingdoms to Rajarata existed primarily in the south of the island.

Parākramabāhu I, or Parakramabahu the Great, was the king of Polonnaruwa from 1153 to 1186. He oversaw the expansion and beautification of his capital, constructed extensive irrigation systems, reorganised the country's army, reformed Buddhist practices, encouraged the arts and undertook military campaigns in South India and Burma. The adage, "Not even a drop of water that comes from the rain must flow into the ocean without being made useful to man" is one of his most famous utterances."
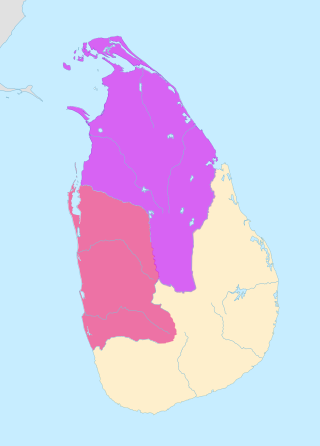
The Kingdom of Polonnaruwa was the Sinhalese kingdom that expanded across the island of Sri Lanka and several overseas territories, from 1070 until 1232. The kingdom started expanding its overseas authority during the reign of Parakramabahu the Great.
Vikramabahu was a medieval king of Sri Lanka. Following the death of his father in 1029, Vikramabahu led the resistance movement against the Chola invaders of the country, ruling from the southern principality of Ruhuna from 1029 to 1041. He spent a number of years building up his forces to drive out the Chola, but died before he could launch his military campaign.

Vijayabahu I, also known as Vijayabahu the Great, was a medieval king of Sri Lanka. Born to a royal bloodline, Vijayabahu grew up under Chola occupation. He assumed rulership of the Ruhuna principality in the southern parts of the country in 1055. Following a seventeen-year-long campaign, he successfully drove the Cholas out of the island in 1070, reuniting the country for the first time in over a century. During his reign, he re-established Buddhism in Sri Lanka and repaired much of the damage caused to infrastructure during the wars. He offered the Thihoshin Pagoda(Lord of Sri Lanka Buddha image) to Burma king Alaungsithu and it is now still in Pakokku.

The Anuradhapura period was a period in the history of Sri Lanka of the Anuradhapura Kingdom from 377 BCE to 1017 CE. The period begins when Pandukabhaya, King of Upatissa Nuwara moved the administration to Anuradhapura, becoming the kingdom's first monarch. Anuradhapura is heralded as an ancient cosmopolitan citadel with diverse populations.
Parakrama Pandyan II, also Pandu Parakramabahu of Polonnaruwa or Parakrama Pandu, was a Pandyan king who invaded the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa in the thirteenth century and ruled from 1212 to 1215 CE. His namesake royal Parakrama Pandyan I had ruled in Madurai fifty years earlier and had sought help from his contemporary Parakramabahu I of Polonnaruwa when faced with a Pandyan civil war. Parakrama Pandyan II came to the throne deposing Lilavati—ruling monarch, consort and successor of Parakramabahu I—as king of Polonnaruwa. He ruled for three years until Polonnaruwa was invaded and he was taken captive by Kalinga Magha, who succeeded him.
Vikramabahu II was King of Polonnaruwa in the twelfth century, who ruled in 1196, for three months. He succeeded his nephew Vira Bahu I as king of Polonnaruwa and was murdered and succeeded by another nephew Chodaganga, a son of his sister. He was the younger brother of Nissanka Malla.

Sahassa Malla was King of Polonnaruwa in the thirteenth century. He ruled the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa from 1200 to 1202. He succeeded Lilavati, who was removed from the throne by her co-ministers. He was deposed by General Ayasmantha and succeeded by Kalyanavati. He was the younger brother of Nissanka Malla.
Anikanga was King of Polonnaruwa in the thirteenth century, who ruled from 1209 to 1209. He succeeded his son Dharmasoka, who was installed as king of Polonnaruwa, and was succeeded by Queen Lilavati. He reigned for 17 days. He allied with the Cholas and invaded Polonnaruwa to capture the throne.
Dharmasoka was an infant King of Polonnaruwa in the thirteenth century, who ruled from 1208 to 1209. He was three months old and installed as king by General Ayasmantha succeeding Kalyanavati as king of Polonnaruwa and was succeeded by his father Anikanga.

Parakramabahu II, also known as Panditha Parakramabāhu, was the King of Dambadeniya in 13th century, whose reign lasted from 1236 to 1270. As a pioneer in literature, he was bestowed with the honorary title "Kalikala Sahitya Sarvagna Pandita". Parakramabahu's reign is notable for the creation of numerous Sinhalese literal works such as, Kausilumina, Pūjāvaliya, Pāli Vishuddḥi Mārgaya, Thūpavaṃsa and Sidhath Sangarāva. He launched a campaign against the Eastern Ganga invader Kalinga Magha, and successfully expelled him in 1255, unifying Sri Lanka under one rule. He succeeded his father Vijayabahu III as King of Dambadeniya, and was succeeded by his elder son, Vijayabahu IV, after his death.
Parakramabahu III was a medieval king of Dambadeniya, from 1302 to 1310. He succeeded his uncle Bhuvanaikabahu I as King of Dambadeniya and was succeeded by Bhuvanaikabahu II.

The Polonnaruwa period was a period in the history of Sri Lanka from 1017, after the Chola conquest of Anuradhapura and when the center of administration was moved to Polonnaruwa, to the end of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa in 1232.

Malayan invasions of Sri Lanka occurred in the mid-13th century, when the Malayan ruler Chandrabhanu Sridhamaraja of Tambralinga, invaded Sri Lanka twice during the reign of king Parakramabahu II of Dambadeniya. Both invasions were successfully repulsed by the Kingdom of Dambadeniya.
1157 Ruhuna Rebellion, also known as the Rebellion of Queen Sugala, was a revolt led-by Queen Sugala of Ruhuna against the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa ruled by Parakramabahu the Great. The rebellion was suppressed by the army of Parakramabahu, and the kingdom of Ruhuna was annexed as a part of Polonnaruwa in 1158.
Polonnaruwa is a town in Sri Lanka. Polonnaruwa may also refer to:
References
- ↑ Dikshit, Damodar Datta (1986). Agriculture, Irrigation, and Horticulture in Ancient Sri Lanka: From Earliest Times to 1186 A.D. : a Study Based on the Pāli Vaṃsa Literature of Sri Lanka. Bharatiya Vidya Prakashan. p. 40. ISBN 978-81-217-0000-9.
- ↑ Yamin, Mohammed. Cultural History of Odisha. Readworthy Publications. ISBN 978-93-5018-430-1.
