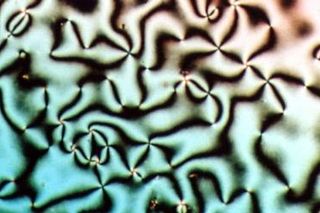
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal can flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a common direction as in a solid. There are many types of LC phases, which can be distinguished by their optical properties. The contrasting textures arise due to molecules within one area of material ("domain") being oriented in the same direction but different areas having different orientations. An LC material may not always be in an LC state of matter.

In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge. The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds.

Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CaCO3. It is a common substance found in rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skeletons and pearls. Materials containing much calcium carbonate or resembling it are described as calcareous. Calcium carbonate is the active ingredient in agricultural lime and is produced when calcium ions in hard water react with carbonate ions to form limescale. It has medical use as a calcium supplement or as an antacid, but excessive consumption can be hazardous and cause hypercalcemia and digestive issues.
Vitrification is the full or partial transformation of a substance into a glass, that is to say, a non-crystalline amorphous solid. Glasses differ from liquids structurally and glasses possess a higher degree of connectivity with the same Hausdorff dimensionality of bonds as crystals: dimH = 3. In the production of ceramics, vitrification is responsible for their impermeability to water.

Soft matter or soft condensed matter is a type of matter that can be deformed or structurally altered by thermal or mechanical stress of the magnitude of thermal fluctuations. The science of soft matter is a subfield of condensed matter physics. Soft materials include liquids, colloids, polymers, foams, gels, granular materials, liquid crystals, flesh, and a number of biomaterials. These materials share an important common feature in that predominant physical behaviors occur at an energy scale comparable with room temperature thermal energy, and that entropy is considered the dominant factor. At these temperatures, quantum aspects are generally unimportant. When soft materials interact favorably with surfaces, they become squashed without an external compressive force. Pierre-Gilles de Gennes, who has been called the "founding father of soft matter," received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1991 for discovering that methods developed for studying order phenomena in simple systems can be generalized to the more complex cases found in soft matter, in particular, to the behaviors of liquid crystals and polymers.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used as a filler in the manufacture of powdered home laundry detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping for making highly alkaline sulfides.

Thermochromism is the property of substances to change color due to a change in temperature. A mood ring is an excellent example of this phenomenon, but thermochromism also has more practical uses, such as baby bottles which change to a different color when cool enough to drink, or kettles which change color when water is at or near boiling point. Thermochromism is one of several types of chromism.

In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that determines how long an observer has to wait before the new phase or self-organized structure appears. For example, if a volume of water is cooled below 0 °C, it will tend to freeze into ice, but volumes of water cooled only a few degrees below 0 °C often stay completely free of ice for long periods (supercooling). At these conditions, nucleation of ice is either slow or does not occur at all. However, at lower temperatures nucleation is fast, and ice crystals appear after little or no delay.
In chemistry and materials science, impurities are chemical substances inside a confined amount of liquid, gas, or solid. They differ from the chemical composition of the material or compound. Firstly, a pure chemical should appear in at least one chemical phase and can also be characterized by its phase diagram. Secondly, a pure chemical should prove to be homogeneous. The perfect pure chemical will pass all attempts to separate and purify it further. Thirdly, and here we focus on the common chemical definition, it should not contain any trace of any other kind of chemical species. In reality, there are no absolutely 100% pure chemical compounds, as there is always some small amount of contamination.
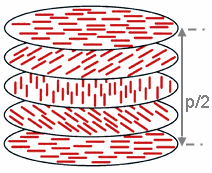
A cholesteric liquid-crystal display (ChLCD) is a display containing a liquid crystal with a helical structure and which is therefore chiral. Cholesteric liquid crystals are also known as chiral nematic liquid crystals. They organize in layers with no positional ordering within layers, but a director axis which varies with layers. The variation of the director axis tends to be periodic in nature. The period of this variation is known as the pitch, p. This pitch determines the wavelength of light which is reflected.

In chemistry, fractional crystallization is a stage-wise separation technique that relies on the liquid-solid phase change. It fractionates via differences in crystallization temperature and enables the purification of multi-component mixtures, as long as none of the constituents can act as solvents to the others. Due to the high selectivity of the solid – liquid equilibrium, very high purities can be achieved for the selected component.

Georges Friedel was a French mineralogist and crystallographer.

Cholesteryl nonanoate, also called cholesteryl pelargonate, 3β-cholest-5-en-3-ol nonaoate or cholest-5-ene-3-β-yl nonanoate, is an ester of cholesterol and nonanoic acid. It is a liquid crystal material forming cholesteric liquid crystals with helical structure. It forms spherulite crystals.

Cholesteryl benzoate, also called 5-cholesten-3-yl benzoate, is an organic chemical, an ester of cholesterol and benzoic acid. It is a liquid crystal material forming cholesteric liquid crystals with helical structure.

Cholesteryl chloride, also called 3-chlorocholest-5-ene or 3β-chlorocholest-5-ene, is an organic chemical, an organochloride derivate cholesterol. It is a liquid crystal material forming clockwise cholesteric liquid crystals. It is a transparent liquid, or a soft crystalline material with melting point around 94-96 °C.

Friedrich Richard Reinitzer was an Austrian botanist and chemist. In late 1880s, experimenting with cholesteryl benzoate, he discovered properties of liquid crystals.
A blue phase mode LCD is a liquid crystal display (LCD) technology that uses highly twisted cholesteric phases in a blue phase. It was first proposed in 2007 to obtain a better display of moving images with, for example, frame rates of 100–120 Hz to improve the temporal response of LCDs. This operational mode for LCDs also does not require anisotropic alignment layers and thus theoretically simplifies the LCD manufacturing process.
The term liquid chalk, or sharkchalk, refers to several different kinds of liquified chalk including liquid-chalk marking pens, liquid-chalk mixtures, and liquid-chalk hobby-craft paints made of cornstarch and food coloring. Some forms of "liquid chalk" contain no actual chalk.

Temperature sensitive glass is a glass material that reacts to ambient temperatures radiated off of other surfaces, e.g. hands or water. The liquid crystals beneath the glass surface impact color upon temperature. There are three main phases of these crystals: nematic, smectic, and chiral.

A carbonate fluoride, fluoride carbonate, fluorocarbonate or fluocarbonate is a double salt containing both carbonate and fluoride. The salts are usually insoluble in water, and can have more than one kind of metal cation to make more complex compounds. Rare-earth fluorocarbonates are particularly important as ore minerals for the light rare-earth elements lanthanum, cerium and neodymium. Bastnäsite is the most important source of these elements. Other artificial compounds are under investigation as non-linear optical materials and for transparency in the ultraviolet, with effects over a dozen times greater than Potassium dideuterium phosphate.

















