Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism, liver dysfunction, or biliary-tract obstruction. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare, while jaundice in babies is common, with an estimated 80% affected during their first week of life. The most commonly associated symptoms of jaundice are itchiness, pale feces, and dark urine.

Bilirubin (BR) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the destruction of aged or abnormal red blood cells. In the first step of bilirubin synthesis, the heme molecule is stripped from the hemoglobin molecule. Heme then passes through various processes of porphyrin catabolism, which varies according to the region of the body in which the breakdown occurs. For example, the molecules excreted in the urine differ from those in the feces. The production of biliverdin from heme is the first major step in the catabolic pathway, after which the enzyme biliverdin reductase performs the second step, producing bilirubin from biliverdin.
Liver function tests, also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT), albumin, bilirubin, and others. The liver transaminases aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase are useful biomarkers of liver injury in a patient with some degree of intact liver function. Most liver diseases cause only mild symptoms initially, but these diseases must be detected early. Hepatic (liver) involvement in some diseases can be of crucial importance. This testing is performed on a patient's blood sample. Some tests are associated with functionality, some with cellular integrity, and some with conditions linked to the biliary tract. Because some of these tests do not measure function, it is more accurate to call these liver chemistries or liver tests rather than liver function tests. Several biochemical tests are useful in the evaluation and management of patients with hepatic dysfunction. These tests can be used to detect the presence of liver disease. They can help distinguish among different types of liver disorders, gauge the extent of known liver damage, and monitor the response to treatment. Some or all of these measurements are also carried out on individuals taking certain medications, such as anticonvulsants, to ensure that these medications are not adversely impacting the person's liver.

Kernicterus is a bilirubin-induced brain dysfunction. The term was coined in 1904 by Schmorl. Bilirubin is a naturally occurring substance in the body of humans and many other animals, but it is neurotoxic when its concentration in the blood is too high, a condition known as hyperbilirubinemia. Hyperbilirubinemia may cause bilirubin to accumulate in the grey matter of the central nervous system, potentially causing irreversible neurological damage. Depending on the level of exposure, the effects range from clinically unnoticeable to severe brain damage and even death.

Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a syndrome in which the liver of affected individuals processes bilirubin more slowly than the majority. Many people never have symptoms. Occasionally jaundice may occur.

Hemolytic anemia or haemolytic anaemia is a form of anemia due to hemolysis, the abnormal breakdown of red blood cells (RBCs), either in the blood vessels or elsewhere in the human body (extravascular). This most commonly occurs within the spleen, but also can occur in the reticuloendothelial system or mechanically. Hemolytic anemia accounts for 5% of all existing anemias. It has numerous possible consequences, ranging from general symptoms to life-threatening systemic effects. The general classification of hemolytic anemia is either intrinsic or extrinsic. Treatment depends on the type and cause of the hemolytic anemia.

Enterohepatic circulation refers to the circulation of biliary acids, bilirubin, drugs or other substances from the liver to the bile, followed by entry into the small intestine, absorption by the enterocyte and transport back to the liver. Enterohepatic circulation is an especially important concept in the field of toxicology as many lipophilic xenobiotics undergo this process causing repeated liver damage.

Neonatal jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the white part of the eyes and skin in a newborn baby due to high bilirubin levels. Other symptoms may include excess sleepiness or poor feeding. Complications may include seizures, cerebral palsy, or kernicterus.

Dubin–Johnson syndrome is a rare, autosomal recessive, benign disorder that causes an isolated increase of conjugated bilirubin in the serum. Classically, the condition causes a black liver due to the deposition of a pigment similar to melanin. This condition is associated with a defect in the ability of hepatocytes to secrete conjugated bilirubin into the bile, and is similar to Rotor syndrome. It is usually asymptomatic, but may be diagnosed in early infancy based on laboratory tests. No treatment is usually needed.

Urobilinogen is a colorless by-product of bilirubin reduction. It is formed in the intestines by bacterial action on bilirubin. About half of the urobilinogen formed is reabsorbed and taken up via the portal vein to the liver, enters circulation and is excreted by the kidney.
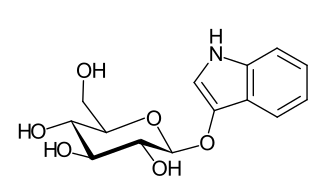
Indican is a colourless organic compound, soluble in water, naturally occurring in Indigofera plants. It is a precursor of indigo dye.

Crigler–Najjar syndrome is a rare inherited disorder affecting the metabolism of bilirubin, a chemical formed from the breakdown of the heme in red blood cells. The disorder results in a form of nonhemolytic jaundice, which results in high levels of unconjugated bilirubin and often leads to brain damage in infants. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. The annual incidence is estimated at 1 in 1,000,000.

Rotor syndrome is a rare cause of mixed direct (conjugated) and indirect (unconjugated) hyperbilirubinemia, relatively benign, autosomal recessive bilirubin disorder characterized by non-hemolytic jaundice due to the chronic elevation of predominantly conjugated bilirubin.

Stercobilinogen is a chemical created by bacteria in the gut. It is made of broken-down hemoglobin. It is further processed to become the chemical that gives feces its brown color.

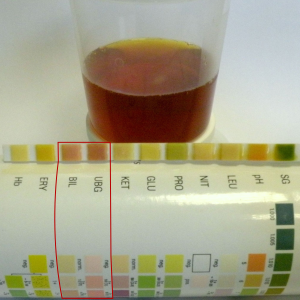
A urine test strip or dipstick is a basic diagnostic tool used to determine pathological changes in a patient's urine in standard urinalysis.
Cholestatic pruritus is the sensation of itch due to nearly any liver disease, but the most commonly associated entities are primary biliary cholangitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, obstructive choledocholithiasis, carcinoma of the bile duct, cholestasis, and chronic hepatitis C viral infection and other forms of viral hepatitis.
Acholia is pallor of the faeces, which lack their normal brown colour, as a result of impaired bile secretion into the bowel. It can also be referred to as hypocholia. Acholia is a sign pointing to reduced or lacking flow of conjugated bilirubin into the bowel, as a result of a problem in the liver itself or in the biliary tree.

Bilirubin glucuronide is a water-soluble reaction intermediate over the process of conjugation of indirect bilirubin. Bilirubin glucuronide itself belongs to the category of conjugated bilirubin along with bilirubin di-glucuronide. However, only the latter one is primarily excreted into the bile in the normal setting.
Hemolytic jaundice, also known as prehepatic jaundice, is a type of jaundice arising from hemolysis or excessive destruction of red blood cells, when the byproduct bilirubin is not excreted by the hepatic cells quickly enough. Unless the patient is concurrently affected by hepatic dysfunctions or is experiencing hepatocellular damage, the liver does not contribute to this type of jaundice.
Hyperbilirubinemia is a clinical condition describing an elevation of blood bilirubin level due to the inability to properly metabolise or excrete bilirubin, a product of erythrocytes breakdown. In severe cases, it is manifested as jaundice, the yellowing of tissues like skin and the sclera when excess bilirubin deposits in them. The US records 52,500 jaundice patients annually. By definition, bilirubin concentration of greater than 3 mg/ml is considered hyperbilirubinemia, following which jaundice progressively develops and becomes apparent when plasma levels reach 20 mg/ml. Rather than a disease itself, hyperbilirubinemia is indicative of multifactorial underlying disorders that trace back to deviations from regular bilirubin metabolism. Diagnosis of hyperbilirubinemia depends on physical examination, urinalysis, serum tests, medical history and imaging to identify the cause. Genetic diseases, alcohol, pregnancy and hepatitis viruses affect the likelihood of hyperbilirubinemia. Causes of hyperbilirubinemia mainly arise from the liver. These include haemolytic anaemias, enzymatic disorders, liver damage and gallstones. Hyperbilirubinemia itself is often benign. Only in extreme cases does kernicterus, a type of brain injury, occur. Therapy for adult hyperbilirubinemia targets the underlying diseases but patients with jaundice often have poor outcomes.