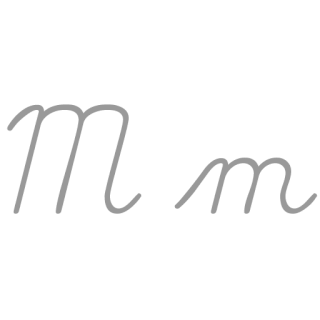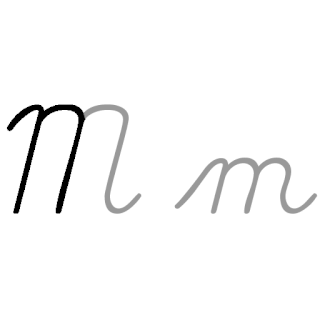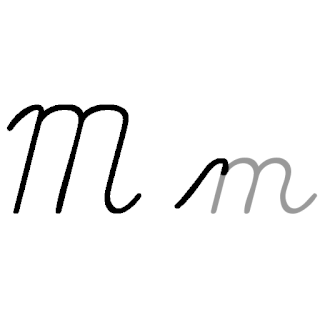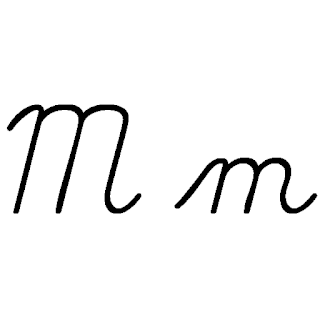A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing – no particles or even electromagnetic radiation such as light – can escape from it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. The boundary of no escape is called the event horizon. Although it has an enormous effect on the fate and circumstances of an object crossing it, it has no locally detectable features according to general relativity. In many ways, a black hole acts like an ideal black body, as it reflects no light. Moreover, quantum field theory in curved spacetime predicts that event horizons emit Hawking radiation, with the same spectrum as a black body of a temperature inversely proportional to its mass. This temperature is of the order of billionths of a kelvin for stellar black holes, making it essentially impossible to observe directly.

The cat is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is often referred to as the domestic cat to distinguish it from the wild members of the family. A cat can either be a house cat, a farm cat or a feral cat; the latter ranges freely and avoids human contact. Domestic cats are valued by humans for companionship and their ability to kill rodents. About 60 cat breeds are recognized by various cat registries.
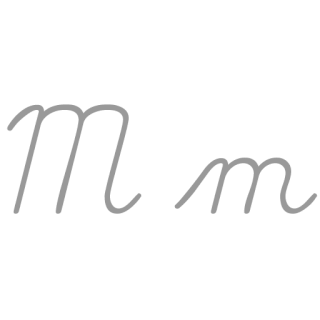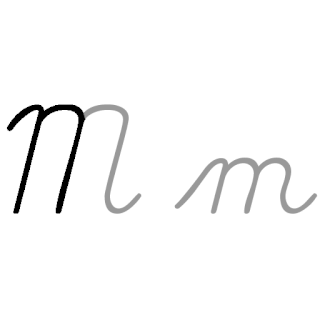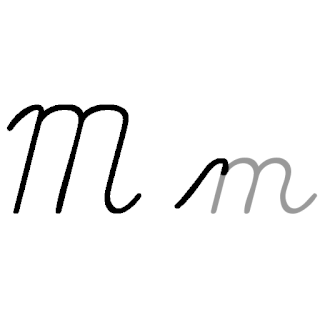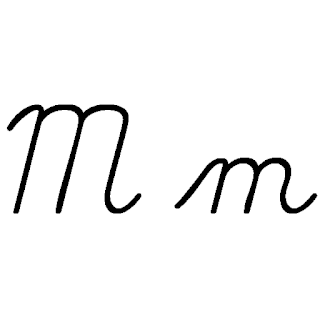
M, or m, is the thirteenth letter of the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is em, plural ems.

The M16 rifle is a family of military rifles adapted from the ArmaLite AR-15 rifle for the United States military. The original M16 rifle was a 5.56×45mm automatic rifle with a 20-round magazine.

The Solar System is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. The Solar System formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system are substantially larger and more massive than the terrestrials. The two largest, Jupiter and Saturn, are gas giants, being composed mainly of hydrogen and helium; the next two, Uranus and Neptune, are ice giants, being composed mostly of volatile substances with relatively high melting points compared with hydrogen and helium, such as water, ammonia and methane. All eight planets have nearly circular orbits that lie close to the plane of the Earth's orbit, called the ecliptic.

Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms.

The M1 Abrams is a third-generation American main battle tank designed by Chrysler Defense and named for General Creighton Abrams. Conceived for modern armored ground warfare and now one of the heaviest tanks in service at nearly 68 short tons, it introduced several innovative features, including a multifuel turbine engine, sophisticated Chobham composite armor, a computer fire control system, separate ammunition storage in a blow-out compartment, and NBC protection for crew safety. Initial models of the M1 were armed with a licensed-produced 105 mm Royal Ordnance L7 gun, while later variants feature a licensed Rheinmetall 120 mm L/44.

Messier 87 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy with several trillion stars in the constellation Virgo. One of the most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters — about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way — and a jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends at least 1,500 parsecs, traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers.

A supermassive black hole is the largest type of black hole, with its mass being on the order of millions to billions of times the mass of the Sun (M☉). Black holes are a class of astronomical objects that have undergone gravitational collapse, leaving behind spheroidal regions of space from which nothing can escape, not even light. Observational evidence indicates that almost every large galaxy has a supermassive black hole at its center. For example, the Milky Way has a supermassive black hole in its Galactic Center, corresponding to the radio source Sagittarius A*. Accretion of interstellar gas onto supermassive black holes is the process responsible for powering active galactic nuclei and quasars.

The M2 machine gun or Browning .50 caliber machine gun is a heavy machine gun designed toward the end of World War I by John Browning. Its design is similar to Browning's earlier M1919 Browning machine gun, which was chambered for the .30-06 cartridge. The M2 uses the much larger and much more powerful .50 BMG cartridge, which was developed alongside and takes its name from the gun itself. It has been referred to as "Ma Deuce", in reference to its M2 nomenclature. The design has had many specific designations; the official US military designation for the current infantry type is Browning Machine Gun, Cal. .50, M2, HB, Flexible. It is effective against infantry, unarmored or lightly armored vehicles and boats, light fortifications, and low-flying aircraft.

The M113 is a fully tracked armored personnel carrier (APC) that was developed and produced by the FMC Corporation. The M113 was sent to United States Army Europe to replace the mechanized infantry's M59 APCs from 1961. The M113 was first used in combat in April 1962 after the United States provided the South Vietnamese Army (ARVN) with heavy weaponry such as the M113, under the Military Assistance Command, Vietnam (MACV) program. Eventually, the M113 was the most widely used armored vehicle of the U.S. Army in the Vietnam War and was used to break through heavy thickets in the midst of the jungle to attack and overrun enemy positions. It was largely known as an "APC" or an "ACAV" by the allied forces.

The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama and Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small portion of westernmost Brazil in South America, along with certain Caribbean and Atlantic islands.

The English Football League Championship is the highest division of the English Football League (EFL) and second-highest overall in the English football league system after the Premier League. The league is contested by 24 clubs.

The Burj Khalifa, known as the Burj Dubai prior to its inauguration in 2010, is a skyscraper in Dubai, United Arab Emirates. With a total height of 829.8 m (2,722 ft) and a roof height of 828 m (2,717 ft), the Burj Khalifa has been the tallest structure and building in the world since its topping out in 2009, supplanting Taipei 101, the previous holder of that status.

The 100 metres, or 100-metre dash, is a sprint race in track and field competitions. The shortest common outdoor running distance, the 100-metre dash is one of the most popular and prestigious events in the sport of athletics. It has been contested at the Summer Olympics since 1896 for men and since 1928 for women. The World Championships 100 metres has been contested since 1983.

The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami occurred at 07:58:53 local time (UTC+7) on 26 December, with an epicentre off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. It was an undersea megathrust earthquake that registered a magnitude of 9.1–9.3 , reaching a Mercalli intensity up to IX in certain areas. The earthquake was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma Plate and the Indian Plate.

The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term Milky Way is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλακτικός κύκλος, meaning "milky circle." From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies.

Contemporary climate change includes both global warming and its impacts on Earth's weather patterns. There have been previous periods of climate change, but the current changes are distinctly more rapid and not due to natural causes. Instead, they are caused by the emission of greenhouse gases, mostly carbon dioxide and methane. Burning fossil fuels for energy use creates most of these emissions. Certain agricultural practices, industrial processes, and forest loss are additional sources. Greenhouse gases are transparent to sunlight, allowing it through to heat the Earth's surface. When the Earth emits that heat as infrared radiation the gases absorb it, trapping the heat near the Earth's surface. As the planet heats up it causes changes like the loss of sunlight-reflecting snow cover, amplifying global warming.

Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes. By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae. The latter includes the Embryophyta which include the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses.

Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease spread worldwide, leading to the COVID-19 pandemic.