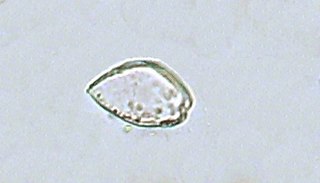
The Prorocentrales are a small order of dinoflagellates. They are distinguished by having their two flagella inserted apically, rather than ventrally as in other groups. One flagellum extends forward and the other circles its base, and there are no flagellar grooves. This arrangement is called desmokont, in contrast to the dinokont arrangement found in other groups. Accordingly, the Prorocentrales may be called desmoflagellates, and in some classifications were treated as a separate class Desmophyceae.

Palmaria palmata, also called dulse, dillisk or dilsk, red dulse, sea lettuce flakes, or creathnach, is a red alga (Rhodophyta) previously referred to as Rhodymenia palmata. It grows on the northern coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is a well-known snack food. In Iceland, where it is known as söl, it has been an important source of dietary fiber throughout the centuries.

The Fucales (fucoids) are an order in the brown algae. The list of families in the Fucales, as well as additional taxonomic information on algae, is publicly accessible at Algaebase.

Chlorococcales is an order of green algae in the class Chlorophyceae. Individual specimens are sometimes found in soil, but mostly in fresh and marine waters. The order contains approximately 780 species.

The cryptophyceae are a class of algae, most of which have plastids. About 220 species are known, and they are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella.
Chroomonas is a genus of cryptophytes first described by Anton Hansgirg. It includes the species Chroomonas elegans, Chroomonas placoidea, Chroomonas baltica, Chroomonas guttula and Chroomonas vectensis.
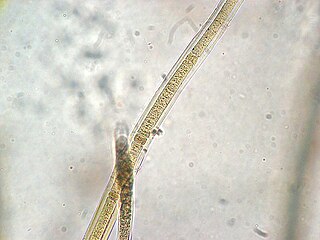
Scytonema is a genus of photosynthetic cyanobacteria that contains over 100 species. It grows in filaments that form dark mats. Many species are aquatic and are either free-floating or grow attached to a submerged substrate, while others species grow on terrestrial rocks, wood, soil, or plants. Scytonema is a nitrogen fixer, and can provide fixed nitrogen to the leaves of plants on which it is growing. Some species of Scytonema form a symbiotic relationship with fungi to produce a lichen.
Fritz Johann Hansgirg (1891–1949) was an Austrian electrochemist and metallurgist who in 1928 invented the carbothermic magnesium reduction process, similar to the Pidgeon process. In 1934, he left Austria for the Empire of Japan where he worked with industrialist Shitagau Noguchi to set up a magnesium plant and further helped the Japanese build a pilot plant to produce heavy water by the Combined Electrolysis Catalytic Exchange (CECE) he invented. Coming to the United States in 1940, he worked with American industrialist Henry J. Kaiser to design a magnesium plant in California, but at the outbreak of World War II, Hansgirg was arrested by the FBI on a Presidential warrant and interned for "the duration of the war." After the war, the Soviet Union captured Hansgirg's plants in northern Korea, using the plants' processes and equipment for their atomic bomb project against the United States, likewise, using them in the Manhattan Project, the exact details of which still remain classified in both the United States and Russia.

Stylonemataceae is a family of red algae in the class Stylonematophyceae. It is the only family in the monotypic order Stylonematales.
Anton Hansgirg was a Bohemian-born Austrian phycologist who described several new species of red algae, green algae, and cryptophytes, in Austria-Hungary between 1880 and 1905.
Scotinosphaera is a genus of algae belonging to the family Scotinosphaeraceae.
Chlorogloea is a genus of cyanobacteria belonging to the family Entophysalidaceae.
Gymnodiniaceae is a family of dinoflagellates belonging to the order Gymnodiniales.
Stephanodiscaceae is a family of diatoms belonging to the order Stephanodiscales.
Cosmioneis is a genus of diatoms belonging to the family Cosmioneidaceae.






