
In military terminology, a missile is a guided airborne ranged weapon capable of self-propelled flight usually by a jet engine or rocket motor. Missiles are thus also called guided missiles or guided rockets. Missiles have five system components: targeting, guidance system, flight system, engine, and warhead. Missiles come in types adapted for different purposes: surface-to-surface and air-to-surface missiles, surface-to-air missiles, air-to-air missiles, and anti-satellite weapons.

An anti-tank guided missile (ATGM), anti-tank missile, anti-tank guided weapon (ATGW) or anti-armor guided weapon is a guided missile primarily designed to hit and destroy heavily armored military vehicles. ATGMs range in size from shoulder-launched weapons, which can be transported by a single soldier, to larger tripod-mounted weapons, which require a squad or team to transport and fire, to vehicle and aircraft mounted missile systems.

MISTRAM was a high-resolution tracking system used by the United States Air Force to provide highly detailed trajectory analysis of rocket launches.

Indirect fire is aiming and firing a projectile without relying on a direct line of sight between the gun and its target, as in the case of direct fire. Aiming is performed by calculating azimuth and inclination, and may include correcting aim by observing the fall of shot and calculating new angles.

A theodolite is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building and infrastructure construction, and some specialized applications such as meteorology and rocket launching.

The FGM-148 Javelin, or Advanced Anti-Tank Weapon System-Medium (AAWS-M), is an American-made man-portable anti-tank system in service since 1996, and continuously upgraded. It replaced the M47 Dragon anti-tank missile in US service. Its fire-and-forget design uses automatic infrared guidance that allows the user to seek cover immediately after launch, in contrast to wire-guided systems, like the system used by the Dragon, which require a user to guide the weapon throughout the engagement. The Javelin's high-explosive anti-tank (HEAT) warhead can defeat modern tanks by top attack, hitting them from above, where their armor is thinnest, and is also useful against fortifications in a direct attack flight.
Semi-active radar homing (SARH) is a common type of missile guidance system, perhaps the most common type for longer-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems. The name refers to the fact that the missile itself is only a passive detector of a radar signal—provided by an external ("offboard") source—as it reflects off the target. Semi-active missile systems use bistatic continuous-wave radar.

Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its Probability of Guidance (Pg).

A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched. Hence, it will not complete one orbital revolution, will not become an artificial satellite nor will it reach escape velocity.

A multiple rocket launcher (MRL) or multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) is a type of rocket artillery system that contains multiple launchers which are fixed to a single platform, and shoots its rocket ordnance in a fashion similar to a volley gun. Rockets are self-propelled in flight and have different capabilities than conventional artillery shells, such as longer effective range, lower recoil, typically considerably higher payload than a similarly sized gun artillery platform, or even carrying multiple warheads.

External or exterior ballistics is the part of ballistics that deals with the behavior of a projectile in flight. The projectile may be powered or un-powered, guided or unguided, spin or fin stabilized, flying through an atmosphere or in the vacuum of space, but most certainly flying under the influence of a gravitational field.

A counter-battery radar or weapon tracking radar is a radar system that detects artillery projectiles fired by one or more guns, howitzers, mortars or rocket launchers and, from their trajectories, locates the position on the ground of the weapon that fired it. Such radars are a subclass of the wider class of target acquisition radars.

Gun laying is the process of aiming an artillery piece or turret, such as a gun, howitzer, or mortar, on land, in air, or at sea, against surface or aerial targets. It may be laying for direct fire, where the gun is aimed similarly to a rifle, or indirect fire, where firing data is calculated and applied to the sights. The term includes automated aiming using, for example, radar-derived target data and computer-controlled guns.
The UDOP multistatic radar and multiradar system (MSRS) utilizes Doppler radar for missile tracking and trajectory measurement. A target is illuminated at 450 MHz. Five receiving stations, located along the baselines with the lengths from 40 to 120 km, receive signals from the target's transponder at 900 MHz. These five stations yield slant-range rate. To compute the range or position, an initial position is required from some other tracking system. The random error is 6 cm (2.4 in), but total error includes the systematic error of 2.7 m (8.9 ft) plus the initial error. UDOP had relatively low cost compared with other high-accuracy systems. In the US, MSRS has found important application in the precision measurement of missile trajectories at the Air Force Eastern Test Range, which extends from the Florida mainland to the Indian Ocean. These MSRSs include the AZUSA, the MISTRAM, and the UDOP. All systems employ a cooperative beacon transponder on the observed target and a ground-based transmitting station with several receiving stations at separate, precisely located sites.

The AN/FPS-16 is a highly accurate ground-based monopulse single object tracking radar (SOTR), used extensively by the NASA crewed space program, the U.S. Air Force and the U.S. Army. The accuracy of Radar Set AN/FPS-16 is such that the position data obtained from point-source targets has azimuth and elevation angular errors of less than 0.1 milliradian and range errors of less than 5 yards (5 m) with a signal-to-noise ratio of 20 decibels or greater.

The AN/FPS-17 was a ground-based fixed-beam radar system that was installed at three locations worldwide, including Pirinçlik Air Base in south-eastern Turkey, Laredo, Texas and Shemya Island, Alaska.
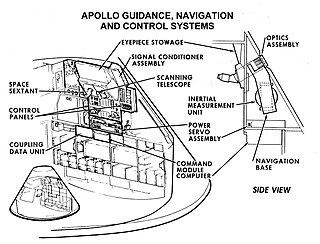
Guidance, navigation and control is a branch of engineering dealing with the design of systems to control the movement of vehicles, especially, automobiles, ships, aircraft, and spacecraft. In many cases these functions can be performed by trained humans. However, because of the speed of, for example, a rocket's dynamics, human reaction time is too slow to control this movement. Therefore, systems—now almost exclusively digital electronic—are used for such control. Even in cases where humans can perform these functions, it is often the case that GNC systems provide benefits such as alleviating operator work load, smoothing turbulence, fuel savings, etc. In addition, sophisticated applications of GNC enable automatic or remote control.

ALAS is a Serbian long-range multipurpose wire guided missile system developed by the private company EdePro and the state-owned Yugoimport SDPR. The ALAS missile system was developed primarily for missions against tanks, armored vehicles, fortifications, command posts, low-flying helicopters, coastal ships, industrial facilities and bridges. It can be deployed by any suitable platform including helicopters, armored vehicles, small ships and infantry. The guidance system is based on video/infrared technology, with the missile connected to the launcher by a fiber-optic cable. The ALAS flies at low altitude and has small radar and infrared (heat) signatures due to using a turbofan motor instead of a turbojet. In recent years, the ALAS platform has found a secondary use as a UAV.

An inertial navigation system is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors (gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors (magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous.

Non-ballistic atmospheric entry is a class of atmospheric entry trajectories that follow a non-ballistic trajectory by employing aerodynamic lift in the high upper atmosphere. It includes trajectories such as skip and glide.



















