
Griseofulvin is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of types of dermatophytoses (ringworm). This includes fungal infections of the nails and scalp, as well as the skin when antifungal creams have not worked. It is taken by mouth.
In organic chemistry, polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone and methylene groups: [−C(=O)−CH2−]n. First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.
Penicillium griseofulvum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin, penifulvin A, cyclopiazonic acid, roquefortine C, shikimic acid, griseofulvin, and 6-Methylsalicylic acid. Penicillium griseofulvum occurs on cereals and nuts.
In enzymology, a 6-methylsalicylic-acid synthase (EC 2.3.1.165) is a polyketide synthase that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.
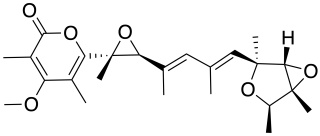
Verrucosidin is a toxic pyrone-type polyketide produced by Penicillium aurantiogriseum, Penicillium melanoconidium, and Penicillium polonicum.

Citromycin is a chemical compound produced by Penicillium. It was first discovered in 1969 and was found to have weak antibiotic activity.

Citreorosein is a polyketide made by Penicillium that has antimicrobial activity.
Penicillium aethiopicum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium. Penicillium aethiopicum produces viridicatumtoxin and griseofulvin, two structurally interesting polyketides.
Penicillium antarcticum is an ubiquitous, endophytic fungus species of the genus Penicillium. Penicillium antarcticum produces the polyketide compounds antarone A and antarone B.
Penicillium brefeldianum is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces brefeldin A a fungal metabolite.
Penicillium brocae is a fungal species of the genus Penicillium, which was isolated in Chiapas in Mexico. It is a symbiont of the mangrove tree Avicennia marina.
Penicillium freii is a psychrophilic species of the genus of Penicillium which produces xanthomegnin and patulin. Penicillium freii occurs in meat, meat products, barley and wheat
Penicillium herquei is an anamorph, filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citreorosein, emodin, hualyzin, herquline B, janthinone, citrinin and duclauxin,.
Penicillium multicolor is an anamorph species of the genus Penicillium which produces alpha-L-fucosidase, tilactase, sclerotiorin, 8-O-Methylsclerotiorinamine, multicolosic acid and isochromophilones.
Penicillium raistrickii is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces griseofulvin, patulin and verruculogen.
Penicillium striatisporum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of chilli peppers. Penicillium striatisporum has a selective antifungal activity against Candida albicans This species produces striatisporin A, striatisporolide A, versiol, calbistrin C, deformylcalbistrin A, citromycetin, citromycin, fulvic acid, (-)-2,3-dihydrocitromycetin and (+)-hexylitaconic acid
Penicillium turbatum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from Taxus baccata. Penicillium turbatum produces pipolythiopiperazinedione-antibiotics, hyalodendrin A and hadacitin.
Penicillium velutinum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil in the United States. It produces verruculogen, verrucosidin, verruculotoxin, decalpenic acid, dehydroaltenusin, cyciooctasulfur, atrovenetinone, altenusin and penitrem A

Penitanzacid F was found as one of the twelve new tanzawaic acid derivatives, which were the secondary metabolites of the fungi Pencillum sp. KWF32 isolated from the tissues of Bathymodiolus sp. collected in the cold spring area of the South China Sea in 2021.






