Coatepec Harinas is one of 125 municipalities in the State of Mexico, Mexico. The municipal seat is the town of Coatepec Harinas. The original name is "Coauhtepetl" which means 'serpent hill' in Náhuatl. Around 1825 because of a boom in flour production, the name "Harinas" was added.

Cuautitlán Izcalli is a city and one of the 125 municipalities that make up the State of Mexico. Its municipal seat is Cuautitlán Izcalli. It is located in the Valley of Mexico area, and is part of the Metropolitan area of Mexico City. It borders to the north and northwest with Tepotzotlán, to the northeast and to the east with Cuautitlán, to the south with Tlalnepantla de Baz, to the southeast with Tultitlán, to the southwest with Atizapán de Zaragoza and to the west with the municipality of Nicolás Romero.

Naucalpan, officially Naucalpan de Juárez, is one of 125 municipalities located just northwest of Mexico City in the adjoining State of Mexico. The municipal seat is the city of Naucalpan de Juárez, which extends into the neighboring municipality of Huixquilucan.
San Mateo Río Hondo is the name of a town and municipality in the state of Oaxaca, Mexico. It is part of the Miahuatlán District in the south of the Sierra Sur Region.It is 2,300 meters above sea level. Known in the colonial era as "Tetequipa" in Nahuatl and "Yegoyoxi" in Zapotec, both names meaning "river of sand." As municipal seat San Mateo Río Hondo has governing jurisdiction over the following communities: Barranca Grande, El Campanario, El Cuachepil, El Encino, El Esfuerzo, El Manzanal, El Naranjal, El Progreso, El Tavel, Falda de Portillo, Horno de Cal, Jalatengo, La Concepción, La Doncella, La Floreña, La Victoria, Las Nubes, Las Tinas, Loma San Marcial, Miramar, Piedra Gentil, Pinabete, Ranchería Yogoló, Rancho Cañas, Rancho Cerezales, Rancho Madroño, Rancho Nuevo, Río Cuapinol, Río Grande, Río Molino, Río Pacífico, San Antonio, San Felipe (Manzanillo), San Ildefonso Ozolotepec, San José del Pacífico, San Melchor, San Pablo, Tres Cruces, Yogoló, and Zapotitlán. San Mateo Rio Hondo is divided into three areas: Nochixtlán district, Mixtecan region and San Mateo Sindihui. The municipality has three hills: La Postura, Zaniltepec and Cerro León. The weather is mostly cold and wet. The population is 3,495. The surface area is 81.96 km².

Atizapán de Zaragoza is a municipality, in State of Mexico in Mexico. The municipality covers an area of 91.07 km². In 2010, the municipality had a total population of 489,937. At the west side of the city is the Zona Esmeralda district, considered one of the wealthiest in the State of Mexico and Greater Mexico City. The Valle Escondido and Chiluca country clubs are located here.

Tlalnepantla de Baz is one of 125 municipalities of the state of Mexico, north of Mexico City. The municipal seat and largest city in the municipality is the city of Tlalnepantla. Tlalnepantla comes from the Náhuatl words tlalli (land) and nepantla (middle) to mean the middle land. The city was known in prior times as Tlalnepantla de Galeana and Tlalnepantla de Comonfort, to honor Hermenegildo Galeana and Ignacio Comonfort, respectively. The current addition of Baz comes from the last name of Gustavo Baz Prada, an important politician and soldier of Emiliano Zapata's army during the Mexican Revolution. After the Revolution, Baz Prada became Governor of the State of Mexico and President of the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). It is located in the northeastern part of the state of Mexico, in the Valley of Mexico north of Mexico City proper. Together with Atizapán, it comprises the dense Region XII of Mexico State.

Ixtapaluca is a city and a municipality in the eastern part of the State of Mexico in Mexico. It lies between the Federal District and the western border of the state of Puebla. The name Ixtapaluca means "Where the salt gets wet".

Ciudad Nicolás Romero is the largest city and municipal seat of the municipality of Nicolás Romero in State of Mexico, Mexico. It is located 58 km from the city of Toluca, the state capital and lies in the north-central part of the state, just northwest of the Federal District. The seat/municipality's current name is to honor Nicolás Romero, who fought for Benito Juárez during the Reform War and the French intervention in Mexico. He was executed there by the French. The town adopted this name in 1898. The area was settled by the Otomi and named Azcapotzaltongo by the Aztecs after conquering it. During colonial times, it was known as San Pedro Azcapotzaltongo. It was then called Monte Bajo from 1821 to 1898, when the current name was adopted. Both the municipality and city are commonly referred to as Nicolás Romero.

Huixquilucan Municipality is one of the municipalities in State of Mexico, Mexico. It lies adjacent to the west side of the Federal District and is part of Greater Mexico City but independent of Mexico City itself. The name "Huixquilucan" comes from Nahuatl meaning, "place full of edible thistles".

The municipality of Tenango del Valle is located in the southern portion of the Valley of Toluca in Mexico State, about 72 km southwest of Mexico City and 25 km south of Toluca. The municipal seat is the city of Tenango de Arista. While the seat is officially named Tenango de Arista, it is more commonly referred to as Tenango del Valle, as this was the original name of the town. Tenango del Valle is best known as the site of the Teotenango archeological site, which was a walled city inhabited from about 900 C.E. to 1550 C.E.

Tlaxiaco is a city, and its surrounding municipality of the same name, in the Mexican state of Oaxaca. It is located in the Tlaxiaco District in the south of the Mixteca Region, with a population of about 17,450.
Ixtlahuaca de Rayón is the municipal seat and 5th largest city in the municipality of Ixtlahuaca north of Toluca in the northwest part of the State of Mexico, in Mexico. The distance between Mexico City and Ixtlahuaca is 32 km. The name Ixthahuaca comes from Náhuatl and means plains without trees. The city and municipality were officially established by decree on November 14, 1816 by the Congress of the State of Mexico.

Tequixquiac is a municipality located in the Zumpango Region of the State of Mexico in Mexico. The municipality is located 84 kilometres (52 mi) north of Mexico City within the valley that connects the Valley of Mexico with the Mezquital Valley. The name comes from Nahuatl and means "place of tequesquite waters". The municipal seat is the town of Santiago Tequixquiac, although both the town and municipality are commonly referred to as simply "Tequixquiac".

Almolya del Río is a town and municipality located in the State of Mexico 26 km from the state capital of Toluca. It is located 2,600 meters above sea level. The name Almoloya comes from the Nahuatl phrase almoloyán which means place where water flows out. "del Rio" means "of the river" in Spanish and refers to the Lerma River, which originates here.

Municipality of Culiacán is a municipality in the Mexican state of Sinaloa in northwestern Mexico.
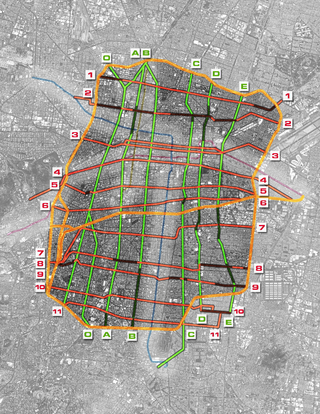
The system of ejes viales in Mexico City is a large network of wide arterial roads with coordinated traffic signals. They are mainly directed in one-way with a single lane going in the opposite direction used exclusively by public transportation. The network was a project of Mexico City mayor Carlos Hank González and the first part of the network, after extensive construction and demolition of buildings and removal of trees, opened in 1979. With the exception of the Eje Central, a south-to-north eje passing through the historic center of Mexico City, the ejes are numbered with cardinal directions, for example going north from the center: Eje 1 Norte, then Eje 2 Norte, and so forth. In addition to the Eje number and directional, the streets retain their individual names, with one eje thus consisting of multiple sequential individually named streets.
Escuela Sierra Nevada is a private school in the Mexico City metropolitan area. It was established in 1950 and serves preschool through high school.
Green Hills School is a private school in the Mexico City metropolitan area. Founded in 1962, the school serves levels preschool through preparatoria. The South Campus is in Col. San Jerónimo Lídice in Magdalena Contreras, Mexico City while the north campus is in Atizapán, State of Mexico.















